Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 14 2
Uploaded by
Miniyah WilliamsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 14 2
Uploaded by
Miniyah WilliamsCopyright:
Available Formats
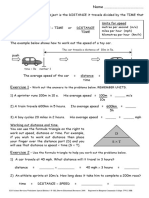
Name ___________________________ Class ___________________ Date _____________
Chapter 14 Work, Power, and Machines
Section 14.2 Work and Machines
(pages 417–420)
This section describes how machines change forces to make work easier to do.
Input forces exerted on and output forces exerted by machines are identified
and input work and output work are discussed.
Reading Strategy (page 417)
Summarizing As you read, complete the table for each machine.
After you read, write a sentence summarizing the idea that your
table illustrates. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see
the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook
at the end of your textbook.
Machine Increases or Decreases Increases or Decreases
Input Force Input Distance
Tire jack Decreases Increases
Lug wrench Decreases Increases
Rowing oar Increases Decreases
Summary: As input force decreases, the input distance increases.
Machines Do Work (pages 417–418)
1. Describe what a machine is able to do. A machine makes work easier to do by
changing a force.
2. Is the following sentence true or false? A machine can make work
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
easier to do by changing the size of the force needed, the direction
of a force, or the distance over which a force acts.
true
3. Consider the equation Work ⫽ Force ⫻ Distance. If a machine
increases the distance over which a force is exerted, the force
required to do a given amount of work decreases .
4. Give an example of a machine that changes the direction of
an applied force. Sample answers may include oars used in rowing.
5. When you make several trips to unload a few heavy items from a
car instead of moving them all at once, the total distance over which
you exert yourself increases .
Work Input and Work Output (pages 419–420)
6. The work done by a machine is always less than the work done on a
machine because of friction .
Physical Science Reading and Study Workbook ■ Chapter 14 163
Name ___________________________ Class ___________________ Date _____________
Chapter 14 Work, Power, and Machines
7. Circle the letter of the definition for input force.
a. the amount of force exerted by a machine
b. the amount of friction slowing the speed of a machine
c. the amount of work done by a machine
d. the amount of force exerted on a machine
8. Write a word equation that describes work input.
Work input equals the input force multiplied by the input distance.
9. Is the following sentence true or false? Every machine uses some
of its work input to overcome friction. true
10. The force exerted by a machine is called the output force.
11. Circle the letter of the expression that equals the work output
of a machine.
Input distance
a. b. Output distance ⫻ Input distance
Output distance
Output distance
c. d. Output distance ⫻ Output force
friction
12. Is the following sentence true or false? Output work always is less
than input work. true
For questions 13 through 15, refer to the figure below.
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Boat moves in
this direction.
Input distance
Input force
Output force
Output distance
13. Which arrow represents the input force? Label it on the figure.
14. Which arrow represents the input distance? Label it on the figure.
15. Which arrow represents the output force? Label it on the figure.
16. How can you increase a machine’s work output? The only way to increase work output
is to increase the amount of work put into a machine.
164 Physical Science Reading and Study Workbook ■ Chapter 14
You might also like
- Mechanical Advantage of SMDocument12 pagesMechanical Advantage of SMReffa PutraNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine Worksheet KeyDocument2 pagesSimple Machine Worksheet KeyuaragieNo ratings yet
- Section Key TermsDocument2 pagesSection Key TermsSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine Worksheet KeyDocument2 pagesSimple Machine Worksheet KeyKath GarletNo ratings yet
- Mechanical AdvantageDocument18 pagesMechanical AdvantageJosh Achaso LabragueNo ratings yet
- Handbook: STEM Handbook (Middle School) 1Document38 pagesHandbook: STEM Handbook (Middle School) 1giyon0No ratings yet
- Assigment 1 Work and MachinesDocument5 pagesAssigment 1 Work and Machines5NJR 99No ratings yet
- Physics-2012Ed-Ch05 - Work and EnergyDocument36 pagesPhysics-2012Ed-Ch05 - Work and EnergyBily roriguesNo ratings yet
- Question Answers Physics Class 9 IcseDocument4 pagesQuestion Answers Physics Class 9 IcseBepis BoiNo ratings yet
- CLSWK-HMWK 10.1 Work and EnergyDocument8 pagesCLSWK-HMWK 10.1 Work and EnergyJedi- AbiNo ratings yet
- Notebook L1Document4 pagesNotebook L1Somaya HussienNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5-physics CORRECTEDDocument47 pagesUNIT-5-physics CORRECTEDAyinalemNo ratings yet
- 7 Unit5Document22 pages7 Unit5samsonNo ratings yet
- Oxo Act02 P208 Su01 XxaannDocument1 pageOxo Act02 P208 Su01 XxaannFizzy PopNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines IntoDocument14 pagesSimple Machines IntoChristine Grace B. AquinoNo ratings yet
- (Owls) Reading Essentials c.3-3 Machines PDFDocument6 pages(Owls) Reading Essentials c.3-3 Machines PDFnearurheart1No ratings yet
- Awc708C Plus Panel Instruction Laser Cutting Motion ControlDocument35 pagesAwc708C Plus Panel Instruction Laser Cutting Motion ControlRobney Souza da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Physics LectureDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Physics LectureTirso FabillarNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective: To Be Able To Name Some Forces and Explain How They May AffectDocument4 pagesLearning Objective: To Be Able To Name Some Forces and Explain How They May Affect8558nk94z5No ratings yet
- M10 Group RESEARCH PAPERDocument5 pagesM10 Group RESEARCH PAPERDharmendra VermaNo ratings yet
- MACHINE ICSE (Part 1)Document5 pagesMACHINE ICSE (Part 1)Sujata SgNo ratings yet
- Pulleys, Wheels, and Gears Pulleys and Efficiency: Objectives AssessmentDocument8 pagesPulleys, Wheels, and Gears Pulleys and Efficiency: Objectives AssessmentAdemuyiwa NathanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesClass 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Notescharusheela charusheelaNo ratings yet
- Mouse-Trap Car Work: What Is A and How Does It ?Document32 pagesMouse-Trap Car Work: What Is A and How Does It ?Lauren PerryNo ratings yet
- Work, Power, and MachinesDocument29 pagesWork, Power, and Machinesmarkonyep namikazeNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument5 pagesSimple MachinesSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Arrays - Ronin Army The Green Ronin CommunityDocument1 pageDynamic Arrays - Ronin Army The Green Ronin CommunityTyler GouletNo ratings yet
- Adams Help of ForcesDocument43 pagesAdams Help of ForcesDENNIS songNo ratings yet
- 0 - 2 - Work and Power - Ms - 2024 - YiDocument31 pages0 - 2 - Work and Power - Ms - 2024 - YiGeun Jung YiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Simple Machines Study Guide KeyDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Simple Machines Study Guide KeyOlalekan OyekunleNo ratings yet
- Worded Content On The Powerpoint On Centripetal Force by Army SealsDocument2 pagesWorded Content On The Powerpoint On Centripetal Force by Army SealsJjay WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Class X-Physics (Simple Machines)Document11 pagesClass X-Physics (Simple Machines)Moosa Kaleem AzeemiNo ratings yet
- YT Slide Machines ICSE One Shot Class 10Document56 pagesYT Slide Machines ICSE One Shot Class 10ankityadav10291No ratings yet
- BackdrivabilityDocument6 pagesBackdrivabilityMarcoFernandoAullaNo ratings yet
- Building Models MotionDocument8 pagesBuilding Models MotionDENNIS songNo ratings yet
- Representing Functions in Real LifeDocument24 pagesRepresenting Functions in Real LifeAllyza Marie LiraNo ratings yet
- Simple Lifting Machines MyDocument14 pagesSimple Lifting Machines MyAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Easy Operation Guide For IR2022-2018Document17 pagesEasy Operation Guide For IR2022-2018Khin ZawNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Mechanical DesignDocument55 pagesTopic 10 Mechanical Designmschongkong100% (9)
- Faculty of Science and Mathematics Chemistry DepartmentDocument10 pagesFaculty of Science and Mathematics Chemistry DepartmentSalasiah Mohammad SaidNo ratings yet
- 344 Pump Intallation and Maintenance Course PreviewDocument17 pages344 Pump Intallation and Maintenance Course PreviewMostafa GimyNo ratings yet
- 5-2 Mechanical Advantage and EfficiencyDocument7 pages5-2 Mechanical Advantage and EfficiencyKelli McDaniel MarchbanksNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DrivetrainsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To DrivetrainsThiago PereiraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report No 7Document10 pagesLab Report No 7Mansoob Bukhari67% (3)
- Mechanical Advantage PDFDocument4 pagesMechanical Advantage PDFteng fsNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Using Dynamic Stiffness - A TutorialDocument11 pagesUnderstanding and Using Dynamic Stiffness - A TutorialNaba Raj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Machines - Selina Solutions Concise Physics Class 10 ICSE - KnowledgeBoatDocument81 pagesChapter 3 - Machines - Selina Solutions Concise Physics Class 10 ICSE - KnowledgeBoatskjNo ratings yet
- Activity4 1a Simple MachinesDocument19 pagesActivity4 1a Simple MachinesabdulmalikbkNo ratings yet
- KS3 Forces and Motion WSDocument5 pagesKS3 Forces and Motion WSStella Chiar Sin YeeNo ratings yet
- Gravity Force Lab Basics HTML Guide - enDocument2 pagesGravity Force Lab Basics HTML Guide - enbandinahrohanNo ratings yet
- MSD PreventionDocument6 pagesMSD PreventionParanikumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Experiemnt 4 Screw JackDocument13 pagesExperiemnt 4 Screw JackMansoob BukhariNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines II Study Guide 2020 by EcsaDocument5 pagesMechanics of Machines II Study Guide 2020 by Ecsasesethumkhungo16No ratings yet
- Easychair Preprint: Chatla Pavankalyan, Nayaki Sairam and Vemula Venkata KalyanDocument6 pagesEasychair Preprint: Chatla Pavankalyan, Nayaki Sairam and Vemula Venkata KalyanRAMACHANDRA DASNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery 2 Marks PDFDocument14 pagesDynamics of Machinery 2 Marks PDFThilli KaniNo ratings yet
- Inserting Functions in Microsoft Excel: 1. Left Click The "Formulas" Tab Which Is Located in The ToolbarDocument5 pagesInserting Functions in Microsoft Excel: 1. Left Click The "Formulas" Tab Which Is Located in The Toolbarapi-360968992No ratings yet
- Speed - Velocity - CalcwsKEYDocument1 pageSpeed - Velocity - CalcwsKEYMiniyah Williams0% (1)
- Response: ShortDocument12 pagesResponse: ShortMiniyah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Gizmos - EnergyConversionsSEDocument4 pagesKami Export - Gizmos - EnergyConversionsSEMiniyah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- The Necklace QuizDocument3 pagesThe Necklace QuizMiniyah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Miniyah Williams - 06 - RAFT Writing Assignment Online VersionDocument2 pagesKami Export - Miniyah Williams - 06 - RAFT Writing Assignment Online VersionMiniyah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- FRQ Vocabulary ReviewDocument1 pageFRQ Vocabulary ReviewDrew AbbottNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document16 pagesPractical Research 2Benedict Coloma BandongNo ratings yet
- Marisa Wolf Final New ResumeDocument2 pagesMarisa Wolf Final New Resumeapi-403499166No ratings yet
- Stability TestDocument28 pagesStability TestjobertNo ratings yet
- Cisco Nexus 7000 Introduction To NX-OS Lab GuideDocument38 pagesCisco Nexus 7000 Introduction To NX-OS Lab Guiderazzzzzzzzzzz100% (1)
- ISA Guidelines PPF 1Document19 pagesISA Guidelines PPF 1Vasu DevanNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Set 2 PDFDocument531 pagesPaper 1 Set 2 PDFabdul rehman aNo ratings yet
- South San Francisco Talks Plans For Sports Park ImprovementsDocument32 pagesSouth San Francisco Talks Plans For Sports Park ImprovementsSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/iesDocument1 pageDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/iesErma JalemNo ratings yet
- Arabian Choice General Trading Co. LLCDocument1 pageArabian Choice General Trading Co. LLCjaanNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modeling Analysis of Nano Composite Airfoil StructureDocument11 pagesFinite Element Modeling Analysis of Nano Composite Airfoil StructureSuraj GautamNo ratings yet
- MAPEH-Arts: Quarter 3 - Module 2Document24 pagesMAPEH-Arts: Quarter 3 - Module 2Girlie Oguan LovendinoNo ratings yet
- Jo - Mc.Donough. ESP in Perspective A Practical Guide. London. Collin ELT. 1984. p.3Document6 pagesJo - Mc.Donough. ESP in Perspective A Practical Guide. London. Collin ELT. 1984. p.3Falihatul Kholidiyah100% (1)
- Module 11 Activity Based CostingDocument13 pagesModule 11 Activity Based CostingMarjorie NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument10 pagesCover PageAvijit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Pemisah ZirconDocument10 pagesPemisah ZirconLorie Banka100% (1)
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET in Oral CommDocument4 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET in Oral CommTinTin100% (1)
- MINDSET 1 EXERCISES TEST 1 Pendientes 1º Bach VOCABULARY AND GRAMMARDocument7 pagesMINDSET 1 EXERCISES TEST 1 Pendientes 1º Bach VOCABULARY AND GRAMMARanaNo ratings yet
- Task 3: New - HTMLDocument12 pagesTask 3: New - HTMLGONELA SAI LOKESH (RA2011028010100)No ratings yet
- S P 01958 Version 2 EPD OVO ArmchairDocument16 pagesS P 01958 Version 2 EPD OVO ArmchairboiNo ratings yet
- Practical Search Techniques in Path Planning For Autonomous DrivingDocument6 pagesPractical Search Techniques in Path Planning For Autonomous DrivingGergely HornyakNo ratings yet
- 250 Conversation StartersDocument28 pages250 Conversation StartersmuleNo ratings yet
- Branch & Category Wise Opening & Closing Rank of JEE (Main) 2019Document46 pagesBranch & Category Wise Opening & Closing Rank of JEE (Main) 2019soni dwivediNo ratings yet
- Maharishi Language of Gravity - SoS 27Document3 pagesMaharishi Language of Gravity - SoS 27Prof. MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet On Arrangement of Springs in Various Casnub Trolleys Fitted On Air Brake Wagon PDFDocument9 pagesPamphlet On Arrangement of Springs in Various Casnub Trolleys Fitted On Air Brake Wagon PDFNiKhil GuPtaNo ratings yet
- Ashfaque Ahmed-The SAP Materials Management Handbook-Auerbach Publications, CRC Press (2014)Document36 pagesAshfaque Ahmed-The SAP Materials Management Handbook-Auerbach Publications, CRC Press (2014)surajnayak77No ratings yet
- Math Habits of MindDocument12 pagesMath Habits of MindAzmi SallehNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument4 pagesAnswer KeyLouina YnciertoNo ratings yet
- (Official) AVTC5 - Unit 1 - Before ClassDocument11 pages(Official) AVTC5 - Unit 1 - Before ClassNhân NguyễnNo ratings yet