Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buffer and Interrupts
Uploaded by
collenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Buffer and Interrupts
Uploaded by
collenCopyright:
Available Formats
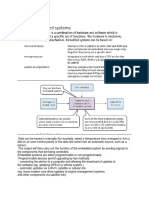
Buffer is a temporary store where data is held until it is ready to be processed.
For
example, data will be held in a printer buffer until the printer is ready to print out the
buffer contents; a keyboard buffer will store key presses until they can be processed,
etc.
Since input/output devices work more slowly than the CPU, buffers allow the data to be
stored until it can be processed (for example, printed) enabling the CPU to do other tasks in
the meantime.
Interrupts also allow for more efficient operation of a computer system. A device will send an
interrupt signal to the CPU indicating that it needs attention (for example, a printer is out of
paper or out of ink and a CD is almost full). The CPU will suspend what it is doing to service the
interrupt and then return to its task once the problem is cleared. Interrupts can also be
generated by software, for example, division by zero and out of data error – these interrupts
again will need to be serviced and the system cannot return to normal until the issue is resolved.
You might also like
- SRIBD - Simple Batch SystemsDocument2 pagesSRIBD - Simple Batch SystemsTro Jan OngNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Events: Polling Loops and Interrupts: Hard DiskDocument5 pagesAsynchronous Events: Polling Loops and Interrupts: Hard DiskDipak NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers (Concepts) : ObjectivesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Computers (Concepts) : Objectivesshraddha malhotraNo ratings yet
- Parts of Computers Topic PresentationDocument8 pagesParts of Computers Topic PresentationMuhammad Hadi shakirNo ratings yet
- A NotesDocument5 pagesA NotesNirav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Operating System ConceptsDocument45 pagesOperating System ConceptsYusufNo ratings yet
- The Basic Components of ComputersDocument77 pagesThe Basic Components of Computersnrssgy edpmanditNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganisationDocument25 pagesComputer OrganisationJessy RajasundarNo ratings yet
- Parts of ComputersDocument4 pagesParts of ComputersFe Marie JisonNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument16 pagesComputer Notesmunaxemimosa8No ratings yet
- Basic Operation of ComputerDocument5 pagesBasic Operation of ComputerRebecca Leyson100% (1)
- Buffering & SpoolingDocument5 pagesBuffering & SpoolingPrasad ShitoleNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer ScribDocument4 pagesComponents of Computer ScribZeeshan NasirNo ratings yet
- IT Application and ToolsDocument8 pagesIT Application and ToolsDia rielNo ratings yet
- Class - XI - IT - About Computer FundamentalsDocument15 pagesClass - XI - IT - About Computer Fundamentalsnakulshali1No ratings yet
- Introduction To IT NotesDocument33 pagesIntroduction To IT NotesJamesNo ratings yet
- Processing System: Processing System, Which Includes The Primary Memory, The Central Processing Unit (CPU), ExpansionDocument10 pagesProcessing System: Processing System, Which Includes The Primary Memory, The Central Processing Unit (CPU), ExpansionAregawi GebreyesusNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: 1.1 Introduction To ProgrammingDocument79 pagesUnit - 1: 1.1 Introduction To ProgrammingraviNo ratings yet
- Components of ComputerDocument1 pageComponents of ComputerCamille SampangNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 PPSDocument80 pagesUnit-1 PPSHarini KolliNo ratings yet
- Different Parts of Computer: Mobile PhonesDocument2 pagesDifferent Parts of Computer: Mobile PhonesdondonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document63 pagesChapter 1brajesh1989No ratings yet
- Reading - Material - On ITDocument37 pagesReading - Material - On ITKISHORETNo ratings yet
- Pps Notes (4 Files Merged)Document175 pagesPps Notes (4 Files Merged)atulya singhNo ratings yet
- C ProgrammingDocument255 pagesC ProgrammingAK GargNo ratings yet
- Peripheral DevicesDocument2 pagesPeripheral DevicesAngelus Mortis PrimeNo ratings yet
- Pps NotesDocument193 pagesPps Notesatulya singhNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Ict-Crush NotesDocument33 pagesForm 4 Ict-Crush NotesNkosana NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Cfa Prelims ReviewerDocument60 pagesCfa Prelims ReviewerTino SorianoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ICT NotesDocument25 pagesIGCSE ICT NotesPeibulu Koroye67% (3)
- Practical 1:-Introduction of Computer HardwareDocument13 pagesPractical 1:-Introduction of Computer HardwareKaveesh NykNo ratings yet
- CSE101-Lecture-2 NoteDocument8 pagesCSE101-Lecture-2 NoteAhsan HabibNo ratings yet
- Computer EssentialsDocument2 pagesComputer EssentialsRocio A RubecindoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Notes CompressDocument25 pagesIgcse Ict Notes CompressYara MohmoudNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamental Unit 1 Notes PDFDocument50 pagesComputer Fundamental Unit 1 Notes PDFDr.J.Nelson Raja Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- Info Tech Summary of Lesson 1 Grade 10Document2 pagesInfo Tech Summary of Lesson 1 Grade 10Kenya LevyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Document24 pagesUnit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Ujjwal KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Practical FileDocument23 pagesComputer Practical FilePreety VermaNo ratings yet
- Hardware Components of A Computer SystemDocument7 pagesHardware Components of A Computer SystemDENIS OKUMUNo ratings yet
- XI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Document20 pagesXI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6kemalNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastuctural Management NotesDocument26 pagesIT Infrastuctural Management NotesAayush JainNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 2 3Document40 pagesLecture1 2 3Prince AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Hardware and SoftwareDocument2 pagesChapter 2 - Hardware and SoftwareAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Nqobile Mpofu Introduction To Computers Bedm 207 p1139827cDocument7 pagesNqobile Mpofu Introduction To Computers Bedm 207 p1139827clordNo ratings yet
- Unit1-The Computer SystemDocument14 pagesUnit1-The Computer SystemLen CumminsNo ratings yet
- Module VII: Introduction To Operating Systems: 1. Need of Operating SystemDocument7 pagesModule VII: Introduction To Operating Systems: 1. Need of Operating SystemGaurav chauhanNo ratings yet
- Computer Education: Basic Concepts in Computer OperationDocument28 pagesComputer Education: Basic Concepts in Computer OperationEINSTEIN - Stephen Troy C. AlgenteraNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument6 pages1 - IntroductionmanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Five I. Types of Computers Analog ComputerDocument4 pagesLesson Five I. Types of Computers Analog ComputerCorneliu MagureanNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Computer Hardware (Faridi S.) (Z-Library)Document136 pagesBeginners Guide To Computer Hardware (Faridi S.) (Z-Library)Dikerson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Components of A Computer - Information Technology and CommunicationDocument7 pagesComponents of A Computer - Information Technology and CommunicationDarryl John PasambaNo ratings yet
- Essential Computer HardwareDocument4 pagesEssential Computer HardwareMd. RuHul A.No ratings yet
- Computer PracticalDocument20 pagesComputer PracticalRanuki BoroNo ratings yet
- The Main Components of Computer SystemDocument14 pagesThe Main Components of Computer SystemMofammere LendokohleNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document8 pagesLect 1Ahmed SalihNo ratings yet
- TO Computers: Neo BaDocument186 pagesTO Computers: Neo BaNaïGa UmutesiNo ratings yet
- The Different Parts of A CPU and Their FunctionsDocument33 pagesThe Different Parts of A CPU and Their Functionsigiz starkleNo ratings yet
- Homework Parts of A ComputerDocument3 pagesHomework Parts of A ComputerMike LadhaNo ratings yet
- Virtual MemoryDocument2 pagesVirtual MemorycollenNo ratings yet
- Foundations DisciplineDocument14 pagesFoundations DisciplinecollenNo ratings yet
- Comp Science BestDocument24 pagesComp Science BestcollenNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument15 pagesData TransmissioncollenNo ratings yet
- Types of StorageDocument9 pagesTypes of StoragecollenNo ratings yet
- High and Low Level Language What Is High Level Language?Document6 pagesHigh and Low Level Language What Is High Level Language?collenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.2 Computer ArchitectureDocument3 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.2 Computer ArchitecturecollenNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument7 pagesEmbedded SystemscollenNo ratings yet
- Data SecurityDocument13 pagesData SecuritycollenNo ratings yet
- Automated SystemsDocument5 pagesAutomated SystemscollenNo ratings yet
- CacheDocument1 pageCachecollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.1 Data TransmissionDocument7 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.1 Data TransmissioncollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.3 Input DevicesDocument15 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.3 Input DevicescollenNo ratings yet
- Write Equation 3Document2 pagesWrite Equation 3collenNo ratings yet
- 5 ComponentsDocument8 pages5 ComponentscollenNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Maths Scheme of Work Year 3 Unit 9: Shape, Space and MeasuresDocument4 pagesCheckpoint Maths Scheme of Work Year 3 Unit 9: Shape, Space and MeasurescollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.3 Internet PrinciplesDocument4 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.3 Internet PrinciplescollenNo ratings yet
- Igcse Computer Science (0478) Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.6 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageIgcse Computer Science (0478) Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.6 Operating SystemscollenNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Multiplication and Division of Decimals ZaDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Multiplication and Division of Decimals ZacollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES: by Awab AqibDocument4 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES: by Awab AqibcollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.4 Output DevicesDocument9 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.4 Output DevicescollenNo ratings yet
- Igcse Cs (0478) P1 Notes Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.1 Logic Gates & CircuitsDocument3 pagesIgcse Cs (0478) P1 Notes Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.1 Logic Gates & CircuitscollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.5 Memory, Storage and MediaDocument6 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.5 Memory, Storage and MediacollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.7 High Level & Low Level LanguagesDocument3 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.7 High Level & Low Level LanguagescollenNo ratings yet