Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cache
Uploaded by
collenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cache
Uploaded by
collenCopyright:
Available Formats
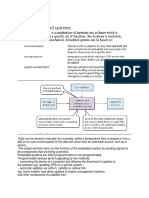
CLOCK
-The clock defines the clock cycle that synchronises all computer operations.
-The control bus transmits timing signals ensuring everything is fully synchronised.
-By increasing clock speed, the processing speed of the computer is also increased.
OVERCLOCKING
Overclocking is a factor to consider. The clock speed can be changed by
accessing the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and altering the settings.
However, using a clock speed higher than the computer was designed for can lead to problems,
-for example:
1) Execution of instructions outside design limits can lead to seriously unsynchronised operations.
2) Overclocking can lead to serious overheating of the CPU again leading to
Unreliable performance.
CACHE
-The use of cache memories can also improve CPU performance.
-Unlike RAM, cache memory is located within the CPU itself, which means it has much
faster data access times than RAM.
-Cache memory stores frequently used instructions and data that need to be accessed faster, which
improves CPU performance.
-when data is to be read the CPU first checks cache memory, if empty it then fetches it in main
memory.
Core
-cores can improve computer performance.
-One core is made up of an ALU, a control unit and the registers.
- Many computers are dual core or quad.
-The idea of using more cores alleviates the need to continually increase clock speeds.
Function of cores
• to process an instruction
• to carry out a fetch-execute cycle.
Why increasing cores?
process two instructions simultaneously (where suitable)
• … increasing the performance.
You might also like
- Chapter 3 New NewDocument5 pagesChapter 3 New NewziadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7: System Performance: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesLesson 7: System Performance: ObjectiveVikas GaurNo ratings yet
- How A CPU Works1Document56 pagesHow A CPU Works1Andrés GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part 2 - Central Processing UnitDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Part 2 - Central Processing UnitmeshNo ratings yet
- Com Data ProcessingDocument27 pagesCom Data ProcessingHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Coa Assignment-4: Akshit Aggarwal CS63 171294Document7 pagesCoa Assignment-4: Akshit Aggarwal CS63 171294Rajput RishavNo ratings yet
- Cpu and Its Working MechanismDocument9 pagesCpu and Its Working MechanismBais JumaniNo ratings yet
- How A CPU WorksDocument11 pagesHow A CPU Workshwa890No ratings yet
- CPU Fetch-Execute CycleDocument5 pagesCPU Fetch-Execute CycleDivaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 ArchitectureDocument8 pagesLecture 2 ArchitectureMuhammad ShehrzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2johnNo ratings yet
- System ClockDocument1 pageSystem ClockzaheerqurratulainNo ratings yet
- Processing: CPU and Memory. Without These A Computer Could Not FunctionDocument9 pagesProcessing: CPU and Memory. Without These A Computer Could Not FunctionThirdy CatalanNo ratings yet
- Computer Assgnment For Grade 6aDocument14 pagesComputer Assgnment For Grade 6aDebela TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument12 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureBhavya NaikNo ratings yet
- ComponentsDocument5 pagesComponentsderry6271No ratings yet
- Acfrogdiaftipgwq1irzch58whd3azotjvsxr7ohgz Caibujvtkvmulkk7n4uxxrv9skxl Rw0ggekv7cgpvz Bofos-Mssojc2edf7xjzw L0yclk9kgd4opw9b X3aa7ahcjdhoeojcq0vtpeDocument5 pagesAcfrogdiaftipgwq1irzch58whd3azotjvsxr7ohgz Caibujvtkvmulkk7n4uxxrv9skxl Rw0ggekv7cgpvz Bofos-Mssojc2edf7xjzw L0yclk9kgd4opw9b X3aa7ahcjdhoeojcq0vtpeapi-517796348No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 4 - 5Document16 pagesChapter 3 - 4 - 5forsidoterefeNo ratings yet
- Unit A451: Computer Systems and ProgrammingDocument15 pagesUnit A451: Computer Systems and ProgrammingJimmyconnors ChettipallyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 The Central Processing Unit (CPU)Document32 pagesLesson 7 The Central Processing Unit (CPU)Just MeNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument18 pagesCentral Processing Unitvinay ramanNo ratings yet
- @ Overcloc King Tutorial / Overclockin: Step 1: Getting Started Step 2: BIOS Step 3: Begin OverclockingDocument9 pages@ Overcloc King Tutorial / Overclockin: Step 1: Getting Started Step 2: BIOS Step 3: Begin OverclockingShamattNo ratings yet
- The CPU May Also Be Called The Microprocessor or The Computer ProcessorDocument6 pagesThe CPU May Also Be Called The Microprocessor or The Computer ProcessorWan Nur FathihahNo ratings yet
- Combination NotesDocument30 pagesCombination NotesmorrycjNo ratings yet
- How To Overclock CPUs and RAMDocument25 pagesHow To Overclock CPUs and RAMMihir PatelNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Balqees TalalDocument23 pagesOperating Systems: Balqees TalalamjdNo ratings yet
- Core PerformanceDocument13 pagesCore PerformanceNarendra SvNo ratings yet
- Gcse Computer Science Final VersionDocument72 pagesGcse Computer Science Final VersionZalifah AswanaNo ratings yet
- Wireless InformationDocument2 pagesWireless InformationNader AlFakeehNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Types of ProcessorsDocument6 pages1.1.2 Types of ProcessorsJakubNo ratings yet
- All About Intel Cpu OverclockDocument5 pagesAll About Intel Cpu OverclockDaria VisnicNo ratings yet
- Number of Cores (Processors)Document4 pagesNumber of Cores (Processors)Keith MutabvuriNo ratings yet
- HPCUnit 2Document14 pagesHPCUnit 260Abhishek KalpavrukshaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architectur1Document31 pagesComputer Architectur1Abigail ChitongoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Computer Science: Geraint D. Jones Mark D. ThomasDocument72 pagesGCSE Computer Science: Geraint D. Jones Mark D. ThomasMohit ChanganiNo ratings yet
- TSN2101/TOS2111 - Tutorial 1 (Introduction To Operating Systems)Document5 pagesTSN2101/TOS2111 - Tutorial 1 (Introduction To Operating Systems)MoonNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument21 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument15 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- Hardware Function - CpuDocument42 pagesHardware Function - CpumyzalNo ratings yet
- GCSE Computer ScienceDocument119 pagesGCSE Computer ScienceHai Anh LeNo ratings yet
- PankajDocument27 pagesPankajsanjeev2838No ratings yet
- M TalhaDocument5 pagesM TalhaTalha ZoniiNo ratings yet
- 1) Define MIPS. CPI and MFLOPS.: Q.1 Attempt Any FOURDocument10 pages1) Define MIPS. CPI and MFLOPS.: Q.1 Attempt Any FOURYashNo ratings yet
- It M Question BankDocument52 pagesIt M Question Bankravikiran1955No ratings yet
- 2 LectureDocument10 pages2 LecturealexpiusNo ratings yet
- A Level Computing ModuleDocument166 pagesA Level Computing ModuleFerguson UtseyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - CPUDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - CPUapi-3750451No ratings yet
- Basic Hardwares For ML - Aravind AriharasudhanDocument23 pagesBasic Hardwares For ML - Aravind AriharasudhanAravind AriharasudhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Processors and RAM'sDocument26 pagesTypes of Processors and RAM'sSneha NairNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OSDocument34 pagesIntroduction To OSTeo SiewNo ratings yet
- L-9 Processor and MemoryDocument27 pagesL-9 Processor and MemoryDiganta MondalNo ratings yet
- Hunting Down CPU Related Issues With Oracle: A Functional ApproachDocument9 pagesHunting Down CPU Related Issues With Oracle: A Functional ApproachphanithotaNo ratings yet
- What Is The CPU?Document18 pagesWhat Is The CPU?Christine Mary EspirituNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics & Computer OrganisationDocument17 pagesDigital Electronics & Computer Organisationabhishek125No ratings yet
- CPU Scheduling AlgorithmDocument17 pagesCPU Scheduling AlgorithmShekhar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesChapter 6-Computer ArchitectureVongai MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- The No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesFrom EverandThe No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesNo ratings yet
- Virtual MemoryDocument2 pagesVirtual MemorycollenNo ratings yet
- Foundations DisciplineDocument14 pagesFoundations DisciplinecollenNo ratings yet
- Comp Science BestDocument24 pagesComp Science BestcollenNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument15 pagesData TransmissioncollenNo ratings yet
- Types of StorageDocument9 pagesTypes of StoragecollenNo ratings yet
- High and Low Level Language What Is High Level Language?Document6 pagesHigh and Low Level Language What Is High Level Language?collenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.2 Computer ArchitectureDocument3 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.2 Computer ArchitecturecollenNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument7 pagesEmbedded SystemscollenNo ratings yet
- Data SecurityDocument13 pagesData SecuritycollenNo ratings yet
- Automated SystemsDocument5 pagesAutomated SystemscollenNo ratings yet
- Buffer and InterruptsDocument1 pageBuffer and InterruptscollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.1 Data TransmissionDocument7 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.1 Data TransmissioncollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.3 Input DevicesDocument15 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.3 Input DevicescollenNo ratings yet
- Write Equation 3Document2 pagesWrite Equation 3collenNo ratings yet
- 5 ComponentsDocument8 pages5 ComponentscollenNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Maths Scheme of Work Year 3 Unit 9: Shape, Space and MeasuresDocument4 pagesCheckpoint Maths Scheme of Work Year 3 Unit 9: Shape, Space and MeasurescollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.3 Internet PrinciplesDocument4 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES CHAPTER 1.2: Communication and Internet 1.2.3 Internet PrinciplescollenNo ratings yet
- Igcse Computer Science (0478) Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.6 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageIgcse Computer Science (0478) Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.6 Operating SystemscollenNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Multiplication and Division of Decimals ZaDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Multiplication and Division of Decimals ZacollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES: by Awab AqibDocument4 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES: by Awab AqibcollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.4 Output DevicesDocument9 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.4 Output DevicescollenNo ratings yet
- Igcse Cs (0478) P1 Notes Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.1 Logic Gates & CircuitsDocument3 pagesIgcse Cs (0478) P1 Notes Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.1 Logic Gates & CircuitscollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.5 Memory, Storage and MediaDocument6 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.5 Memory, Storage and MediacollenNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.7 High Level & Low Level LanguagesDocument3 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.7 High Level & Low Level LanguagescollenNo ratings yet