Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABB Hospital 14
ABB Hospital 14
Uploaded by
pitigoi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageABB hospital
Original Title
ABB hospital 14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentABB hospital
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageABB Hospital 14
ABB Hospital 14
Uploaded by
pitigoiABB hospital
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
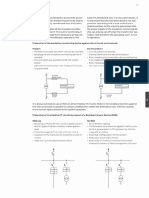
Examples of classification of medical locations
Type ofa ‘Groupo Group Group?
Massageroom 7.
Delivery room a
Endoscopy room oe
‘Outpatient departments 7
Urology room *
Radiology and radiotherapy
Hycrotherapy room .
Physiotherapy room .
[Anaesthesia room
‘Operation preparation room
Surgical plaster room
ee] se] le
Post-operative waking room
Room for apalieations of
eardlaceatheters
haemodynamic analysis room
Haemodtalysi room .
Magnetic resonance room
oa
Nuclear medicine room =
Premature infant room ~
(If not a surgical operating theatre.
(@ it general anaesthesia ts practiced,
@) if itholds patients while they are waking up
from general anaesthesia.
Kotetatsagood conductor wich
‘Sacedentaly We). thiscase a
‘tn gresterintnsty atte pot ot
“Spplstion tthe prabe causing sah
onaby trogen ation
2.2.7 Patient environment
‘Any volume in which intentional or unintentional
‘contact can occur between patient and parts of
the system or between patient and other persons
touching parts of the system,
‘The centre of reference in order to determine the
patient environment may be, for example, the op-
‘erating table, the bed in the hospital accommoda-
tion room or the dentist's chair. The patient en
ronment does not extend more than 2.5m above
the walking surface and outside the premises.
Note that the patient environment can be the
‘container of the patient environments relating to
the positions in which the patient may reasonably
be located while in contact with applied parts,
Similarly, ff thare ara multiple and/or movable
‘electromedical devices, the patient environment
is extended to include at most the entire prem-
‘ses, Therefore account is taken of possible move-
ments to which the electromedical devices or the
patient may be subjected over time,
Determining the patient environment during the
design phase makes it possible to avoid connec-
tion of the extraneous conductive parts located
‘outside the patient environment to the equipo-
tential node, reducing the size of the node and
simplifying installation, with a consequent reduc-
tion of costs, This means therefore that all the
possible positions in which the patient may be lo-
‘cated while in contact with an elactromadical de-
vice with applied parts must be established in ad-
vance; otherwise, there is a risk that the electrical
system will be inadequate when, for medical
needs, it becomes necessary to move a medical
electrical equipment with parts applied into a po-
sition other than those positions originally envis-~
aged.
Sometimes, therefore, it may be opportune to
consider the entire room as the patient environ-
ment, allowing greater flexibility in the use of the
spaces.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ABB Hospital 61Document1 pageABB Hospital 61pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 66Document1 pageABB Hospital 66pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 53Document1 pageABB Hospital 53pitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 64Document1 pageABB Hospital 64pitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 52Document1 pageABB Hospital 52pitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 56Document1 pageABB Hospital 56pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 67Document1 pageABB Hospital 67pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 49Document1 pageABB Hospital 49pitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 58Document1 pageABB Hospital 58pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 39Document1 pageABB Hospital 39pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 54Document1 pageABB Hospital 54pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 60Document1 pageABB Hospital 60pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 46Document1 pageABB Hospital 46pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 44Document1 pageABB Hospital 44pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 35Document1 pageABB Hospital 35pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 42Document1 pageABB Hospital 42pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 45Document1 pageABB Hospital 45pitigoiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledpitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 48Document1 pageABB Hospital 48pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 55Document1 pageABB Hospital 55pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 43Document1 pageABB Hospital 43pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 41Document1 pageABB Hospital 41pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 26Document1 pageABB Hospital 26pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 25Document1 pageABB Hospital 25pitigoiNo ratings yet