Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Paper 30
Research Paper 30
Uploaded by
Farar MandOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Paper 30
Research Paper 30
Uploaded by
Farar MandCopyright:
Available Formats
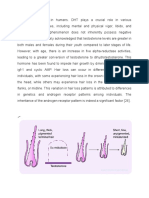
Figure 7.
Androgen-mediated hair follicle [27]
References
24. Trüeb, R.M.J.S.a.d., Further clinical evidence for the effect of IGF-1 on
hair growth and alopecia. 2018. 4(2): p. 90-95.
25. Tazdanian, N., S. Mozafarpoor, and A.J.D.T. Goodarzi, Phosphodiesterase
inhibitors and prostaglandin analogues in dermatology: A comprehensive
review. 2021. 34(1): p. e14669.
26. Miranda, B.H., et al., Androgens trigger different growth responses in
genetically identical human hair follicles in organ culture that reflect their
epigenetic diversity in life. Faseb j, 2018. 32(2): p. 795-806.
27. Yip, L. and R. Sinclair, Antiandrogen therapy for androgenetic alopecia.
Expert Review of Dermatology, 2006. 1: p. 261-269.
(10): 01:15:46 Topical Caffeine & Slowing Hair Loss
Another significant chemical that has the potential to promote hair growth is
caffeine, a stimulant that is commonly consumed. In addition to its effects on
the nervous system, caffeine has been found to have various other properties.
This substance exhibits considerable potency as a phosphodiesterase (PDE)
inhibitor. Its PDE inhibitory properties indirectly promote the stimulation of
insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), as PDE has been shown to suppress
IGF-1. The consumption of caffeine or the application of topical caffeine
ointment has been observed to effectively inhibit PDE, thereby leading to an
You might also like
- Gupta Non Surgical Hair LossDocument14 pagesGupta Non Surgical Hair Loss049 VIMAL CHANDERNo ratings yet
- Study Effect of Minoxidil On BeardDocument2 pagesStudy Effect of Minoxidil On BeardAli RahmanNo ratings yet
- M CAD Ermatol: JA A DDocument4 pagesM CAD Ermatol: JA A DFa iNo ratings yet
- 154 PDFDocument8 pages154 PDFestudos.eaoapNo ratings yet
- 2015 Link Between Foot and Cerebellum in Resolving Chronic PainDocument74 pages2015 Link Between Foot and Cerebellum in Resolving Chronic PainprofessorrothbartNo ratings yet
- Tsunemi 2016Document8 pagesTsunemi 2016Nicolas BaronNo ratings yet
- Hair-Growth Potential of Ginseng and Its Major Metabolites: A Review On Its Molecular MechanismsDocument13 pagesHair-Growth Potential of Ginseng and Its Major Metabolites: A Review On Its Molecular MechanismsFelicia JesslynNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Monotherapy For Men With Hypogonadal Symptoms and Normal TestosteroneDocument3 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Monotherapy For Men With Hypogonadal Symptoms and Normal TestosteronefrankiesdumpsterNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Cell: Sara Abdel Gawad Elsebay, Hoda Fouad Nada, Nancy Sultan Saad Sultan, Dalia Alaa El-Din Aly El-WaseefDocument13 pagesTissue and Cell: Sara Abdel Gawad Elsebay, Hoda Fouad Nada, Nancy Sultan Saad Sultan, Dalia Alaa El-Din Aly El-WaseefiuventasNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument5 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Universitas Sumatera UtaraSiti Azliyana Azura AdzharNo ratings yet
- tmp991D TMPDocument10 pagestmp991D TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- tmp5811 TMPDocument10 pagestmp5811 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Is Tranexamic Acid Use Effective in Preventing PosDocument10 pagesIs Tranexamic Acid Use Effective in Preventing PosLong HoàngNo ratings yet
- Dermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaDocument8 pagesDermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaEka LimNo ratings yet
- Dermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaDocument8 pagesDermatology in General Medicine 7: Daftar PustakaEka LimNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA IntipDocument12 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Intipputri rizkiNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument6 pagesDaftar PustakaMitrahusada OfficialNo ratings yet
- Références Bibliographiques TotaleDocument5 pagesRéférences Bibliographiques TotaleSignorina BenNo ratings yet
- 1310 Anti-Aging Effects of Retinoid HydroxypinacolDocument2 pages1310 Anti-Aging Effects of Retinoid HydroxypinacolTrâm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka DR - Refla Syarif, SPDVDocument15 pagesDaftar Pustaka DR - Refla Syarif, SPDVDiary JafNo ratings yet
- Inh Alfa Reductasa Alopecia 2014Document6 pagesInh Alfa Reductasa Alopecia 2014Edna R. Alvarez PaezNo ratings yet
- Study of The Consciousness Energy Healing Treated Ashwagandha Root Extract by LC-MS, GC-MS, and NMR SpectrosDocument10 pagesStudy of The Consciousness Energy Healing Treated Ashwagandha Root Extract by LC-MS, GC-MS, and NMR SpectrosTrivedi EffectNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Minoxidil 3% Lotion For BeardDocument2 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Minoxidil 3% Lotion For BeardPedro SauloNo ratings yet
- Bener Dapus NewestDocument9 pagesBener Dapus NewestnunungNo ratings yet
- Norma para Citas BibliográficasDocument7 pagesNorma para Citas BibliográficasmaciruloNo ratings yet
- Low-Level Laser (Light) Therapy (LLLT) For Treatment of Hair LossDocument8 pagesLow-Level Laser (Light) Therapy (LLLT) For Treatment of Hair Lossmarco gutierrezNo ratings yet
- 6 Be 46595156Document5 pages6 Be 46595156Ikhwan AmirudinNo ratings yet
- References PDFDocument27 pagesReferences PDFgalal mostafaNo ratings yet
- Cannabis SativaDocument15 pagesCannabis SativamaryNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument5 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFdianjabalNo ratings yet
- Superiority of Dutasteride Over Fi Nasteride in Hair: Original ArticleDocument8 pagesSuperiority of Dutasteride Over Fi Nasteride in Hair: Original ArticleJasonNo ratings yet
- Paper 8841Document7 pagesPaper 8841IJARSCT JournalNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: The Concept of The"big 4" Still Relevant and Useful?. Wilderness EnvironDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: The Concept of The"big 4" Still Relevant and Useful?. Wilderness EnvironSyarofis Si'ayahNo ratings yet
- Micro NeedlingDocument2 pagesMicro NeedlingDNo ratings yet
- Refference: Palaestinum On Uterine Smooth Muscle of Rats and Guinea Pigs. J Ethnopharmacol. 65: 173Document3 pagesRefference: Palaestinum On Uterine Smooth Muscle of Rats and Guinea Pigs. J Ethnopharmacol. 65: 173Radowan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hair Therapy & TransplantationDocument2 pagesHair Therapy & TransplantationÝãsh MåhälêNo ratings yet
- Psychedelic Medicine Course Syllabus - 2020.11.11 - 401182 - 284 - 30152 - v1Document6 pagesPsychedelic Medicine Course Syllabus - 2020.11.11 - 401182 - 284 - 30152 - v1Rodrigo NikobinNo ratings yet
- Biological Sciences. University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, PakistanDocument10 pagesBiological Sciences. University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistanafaisal76No ratings yet
- The Importance of Dual 5 Alpha-Reductase InhibitioDocument11 pagesThe Importance of Dual 5 Alpha-Reductase InhibitioIslam YANo ratings yet
- Yu 2018Document7 pagesYu 2018Devanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Bab 8Document6 pagesBab 8AGATA M.H KINANTINo ratings yet
- Tabular Data of Studies Enrolled in Meta-Analysis and Synthesis Study (Ttileauthors and Year of Publication)Document3 pagesTabular Data of Studies Enrolled in Meta-Analysis and Synthesis Study (Ttileauthors and Year of Publication)Luwila Batoctoy-EstoseNo ratings yet
- RefferenceDocument6 pagesRefferenceJeeban SarangiNo ratings yet
- Samples of Formatted References For Authors of Medical Journal ArticlesDocument12 pagesSamples of Formatted References For Authors of Medical Journal ArticlesnoxleekNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of A Nutritional Supplement StandardizedDocument8 pagesEfficacy of A Nutritional Supplement StandardizedAkos SzaboNo ratings yet
- Trivedi Effect - Characterization of Physical, Structural, Thermal, and Behavioral Properties of The Consciousness Healing Treated Zinc ChlorideDocument10 pagesTrivedi Effect - Characterization of Physical, Structural, Thermal, and Behavioral Properties of The Consciousness Healing Treated Zinc ChlorideTrivedi EffectNo ratings yet
- Trivedi Effect - Effect of Biofield Energy Healing Treatment (The Trivedi Effect®) Based Herbomineral Formulation On Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Expression in Murine Dendritic and Splenocyte CellsDocument10 pagesTrivedi Effect - Effect of Biofield Energy Healing Treatment (The Trivedi Effect®) Based Herbomineral Formulation On Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Expression in Murine Dendritic and Splenocyte CellsTrivedi EffectNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Laser Effects On Skin RejuvenationDocument8 pagesAssessment of Laser Effects On Skin RejuvenationOrel LachianiNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid and Its Congeners in The Treatment of SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesFolic Acid and Its Congeners in The Treatment of SchizophreniaEka FaridaNo ratings yet
- (Medline) : Dermatol. 2016 Sep 19Document2 pages(Medline) : Dermatol. 2016 Sep 19Rahmatullah AhmadNo ratings yet
- tmp938B TMPDocument6 pagestmp938B TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Tmpa693 TMPDocument6 pagesTmpa693 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: (Moringa Oliefera) Dalam Sediaan Gel-Mikroemulsi. Malang: SkripsiDocument7 pagesDaftar Pustaka: (Moringa Oliefera) Dalam Sediaan Gel-Mikroemulsi. Malang: SkripsiAlena Putri JathyNo ratings yet
- Pac J Trop Dis. 2014 4, Supplement 1:S250-4. Doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808 (14) 60449-7Document11 pagesPac J Trop Dis. 2014 4, Supplement 1:S250-4. Doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808 (14) 60449-7Alif Iffah Nur DianaNo ratings yet
- Samples of Formatted References For Authors of Journal ArticlesDocument9 pagesSamples of Formatted References For Authors of Journal ArticlesFemin PambharNo ratings yet
- Uniform Requirements For Manuscripts Submitted To Bio Medical Journals (ICMJE)Document9 pagesUniform Requirements For Manuscripts Submitted To Bio Medical Journals (ICMJE)Omair RiazNo ratings yet
- Current Molecular Targets of Heterocyclic Compounds for Cancer TherapyFrom EverandCurrent Molecular Targets of Heterocyclic Compounds for Cancer TherapyVivek AsatiNo ratings yet
- Biologic and Systemic Agents in DermatologyFrom EverandBiologic and Systemic Agents in DermatologyPaul S. YamauchiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 33Document1 pageResearch Paper 33Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 21Document1 pageResearch Paper 21Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 46Document1 pageResearch Paper 46Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 42Document1 pageResearch Paper 42Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 47Document1 pageResearch Paper 47Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 32Document1 pageResearch Paper 32Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 43Document1 pageResearch Paper 43Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 37Document1 pageResearch Paper 37Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 48Document1 pageResearch Paper 48Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 44Document1 pageResearch Paper 44Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 36Document1 pageResearch Paper 36Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 38Document1 pageResearch Paper 38Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 31Document1 pageResearch Paper 31Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 35Document1 pageResearch Paper 35Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 24Document1 pageResearch Paper 24Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 18Document1 pageResearch Paper 18Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 29Document1 pageResearch Paper 29Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 39Document1 pageResearch Paper 39Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 40Document1 pageResearch Paper 40Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 27Document1 pageResearch Paper 27Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 28Document1 pageResearch Paper 28Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 45Document1 pageResearch Paper 45Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 41Document1 pageResearch Paper 41Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 19Document1 pageResearch Paper 19Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 26Document1 pageResearch Paper 26Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 16Document1 pageResearch Paper 16Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 20Document1 pageResearch Paper 20Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 34Document1 pageResearch Paper 34Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 15Document1 pageResearch Paper 15Farar MandNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 22Document1 pageResearch Paper 22Farar MandNo ratings yet