Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHPT 3 Study Guide
CHPT 3 Study Guide
Uploaded by
bri mOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHPT 3 Study Guide
CHPT 3 Study Guide
Uploaded by
bri mCopyright:
Available Formats
Standards: SC.912.L.17.10, SC.912.L.17.14, SC.912.N.3.
5,
Name _______________________________ Date: ___________ Period: _______
Chapter 3.1 – Earth’s Environmental Systems Study Guide
Vocabulary: Know the defentions of each term.
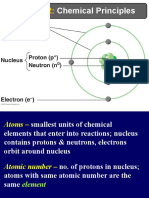
Atoms- basic unit of matter
Nucleus- contains protons and neutrons
matter- any material that has mass and occupies space
element- a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances
molecule- Two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds
compound- substance composed of atoms of two or more different elements
lipid- chemically diverse compound that does not dissolve in water
hydrocarbon- an organic compound combining hydrogen and carbon
solution- a mixture in which all the ingredients are evenly distributed
macromolecule- a large organic molecule that includes, proteins, nucleic acid,
carbohydrates, and lipids
protein-an organic compound made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen,
and sometimes sulfur
nucleic acid-the macromolecule that carries hereditary information including
DNA and RNA
carbohydrate-a organic compound that consists of atoms, hydrogen, hydrogen
and oxygen
pH- a measure of the acidity or alkalinity
Atoms and Elements
Atoms are the basic unit of matter.
Nucleus: Contains protons and neutrons
Electrons: Move around the nucleus and have a negative charge.
An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances.
Ion: An atom loses or gains an electron and becomes charged (+ or -)
Bonding
Covalent bonds: Electrons are shared.
Ionic bonds: A positive ion attracts a negative ion.
Molecule: Two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds
Compound: Substance composed of atoms of two or more different elements
Organic and Inorganic Compounds
Organic compounds: Consist of covalently bonded carbon atoms and
often include other elements, especially hydrogen
Hydrocarbons: Organic compounds, such as petroleum, that contain
only hydrogen and carbon
Inorganic compounds: Lack carbon-to-carbon bonds
Organic compounds include natural gas, petroleum, coal and gasoline
Water
A mixture is a combination of elements, molecules, or compounds that are not
bonded chemically.
Solutions are mixtures in which all ingredients are equally distributed.
Mixtures can be solids, liquids, or gases.
Hydrogen bonding gives water many unique properties:
High specific heat: Resists temp changes
Much energy needed to break water bonds
Helps to maintain a constant body temp
Adhesion: polar water sticks to other molecules
Cohesion – water sticks to itself
Resistance to temperature change
Less dense when frozen
Ability to dissolve many other molecules
Acids, Bases, and pH
The separation of water molecules into ions causes solutions to be acidic, basic,
or neutral.
+ -
pH of 7—Neutral: Equal concentrations of H and OH
+
pH below 7—Acidic: Relatively high concentration of H
-
pH above 7—Basic: Relatively high concentration of OH
You might also like
- Chemistry The Central Science NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry The Central Science Noteslucykipper100% (1)
- Statistical Reasoning For Everyday Life 5th Edition Bennett Briggs Triola Test BankDocument10 pagesStatistical Reasoning For Everyday Life 5th Edition Bennett Briggs Triola Test Bankevelyn100% (15)
- Chemistry of Life Study Guide Answer KeyDocument3 pagesChemistry of Life Study Guide Answer Keyapi-293006069100% (1)
- Sing Learn ArabicDocument15 pagesSing Learn ArabicUmmu Umar BaagilNo ratings yet
- Customer Onboarding Process GuidelinesDocument1 pageCustomer Onboarding Process Guidelinesinekeh100% (1)
- BiologyStudyGuide-1 2Document29 pagesBiologyStudyGuide-1 2melissagfreyNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review of Chemistry: Positively ChargedDocument50 pagesA Brief Review of Chemistry: Positively ChargedElijah PunzalanNo ratings yet
- BIO 22 MODULE 1 - Chemical Basis of LifeDocument14 pagesBIO 22 MODULE 1 - Chemical Basis of LifeBryan DGNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Week 1Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Week 1Wayne AngeloNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsMarlo Cardinez100% (1)
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument6 pagesChapter 2: The Chemical Basis of LifeThalia LauNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document23 pagesActivity 1KassyKasNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesDocument13 pagesYr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesadfknaljhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Winter 2020Document53 pagesChapter 02 Winter 2020LESLI RODRIGUEZ BENDEZUNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The BodyDocument39 pagesChemical Composition of The BodyAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life 1Document70 pagesChemical Basis of Life 1mllgb132No ratings yet
- Biology Quiz 12 - Water Carbon Chemistry Carbohydrates LipidsDocument11 pagesBiology Quiz 12 - Water Carbon Chemistry Carbohydrates LipidsMafalda SeabraNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument3 pagesREVIEWEREmelly PadillaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument4 pagesDefinitionsSimone GhiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Molecular Biology: Synthesis of UreaDocument23 pagesChapter 2: Molecular Biology: Synthesis of UreaHiya GoyalNo ratings yet
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 2Document4 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 2Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - BSN 1Document6 pagesChemistry - BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, and MixturesDocument35 pagesElements, Compounds, and Mixturesapi-419037032No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 WorkbookDocument12 pagesChapter 2 WorkbookChantelle LemieuxNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam 4 Study GuideDocument12 pagesBiology Exam 4 Study GuideKhusbu PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemical Bsis of LifeDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Chemical Bsis of LifeMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Chemistry: Ionization, DissociationDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - Chemistry: Ionization, Dissociationtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Unit 1Document12 pagesChapter 2 Unit 1harshit khareNo ratings yet
- Ejara Zge4301 M2act1Document4 pagesEjara Zge4301 M2act1JAMAICA EJARANo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument38 pagesChemical Basis of LifeFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Unit 9.1. Main Biological MoleculesDocument14 pagesUnit 9.1. Main Biological Moleculesminh TomNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of LifeDocument4 pagesChemicals of LifeZoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes and WorksheetsDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Notes and WorksheetsConner ChingNo ratings yet
- Water: The Solvent of Life Where There Is Water, There Is LifeDocument18 pagesWater: The Solvent of Life Where There Is Water, There Is LifeIsaiah Fidelis Maji100% (1)
- Substance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific PropertiesDocument8 pagesSubstance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific Propertiesaishajutt041No ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Review: Earth and Space ScienceDocument48 pagesBasic Chemistry Review: Earth and Space SciencefluronineNo ratings yet
- Life, The Universe, and EverythingDocument12 pagesLife, The Universe, and EverythingBatisane Kantsu MathumoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Vocabulary - H. Bio. Web VersionDocument42 pagesChemistry Vocabulary - H. Bio. Web VersionAshrafNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 1Document30 pagesBio Chapter 1Alicia LamNo ratings yet
- Molecules of LifeDocument16 pagesMolecules of LifeSumeet MhamunkarNo ratings yet
- Walang MakakaseethisDocument3 pagesWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Definition ListDocument3 pagesSPM Chemistry Definition ListLooiNo ratings yet
- Midterm ChemDocument6 pagesMidterm Chem分開倉庫喔噢罰款No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic ChemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Basic ChemistryHannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Basic ChemistryMayross GoldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument65 pagesChapter 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeMc LevoNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-4 Chapter 1 - Cell Theory: The Kool-Aid Is Cloudy. Why Is The Kool-Aid Cloudy?Document5 pagesChapters 1-4 Chapter 1 - Cell Theory: The Kool-Aid Is Cloudy. Why Is The Kool-Aid Cloudy?jackardiNo ratings yet
- Cap 2Document19 pagesCap 2Francesca PrevitaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Matter: Atoms and MoleculesDocument6 pagesThe Nature of Matter: Atoms and Moleculesmelan pNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life - AP BiologyDocument8 pagesChemistry of Life - AP Biologyejung26No ratings yet
- Chemistry-Element: MetalDocument2 pagesChemistry-Element: MetalIan BelenNo ratings yet
- (w3) Basic Chemistry and Chemical CompositionDocument4 pages(w3) Basic Chemistry and Chemical Compositioncsiman2431No ratings yet
- Biochem Lab NotesDocument5 pagesBiochem Lab NotesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- 1610assignment 1 ListDocument7 pages1610assignment 1 Listapi-341205347No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document9 pagesLecture 2hfzyahmd613No ratings yet
- Bio Study SheetDocument9 pagesBio Study SheetJennyNo ratings yet
- 940 Elements Compounds MixturesDocument33 pages940 Elements Compounds MixturesEllen Grace Aguirre TobezaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chemistry of LifeDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Chemistry of Liferaghad mohammedNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocument33 pagesElements Compounds MixturesKunwar DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Spe 3510 Chapt 2Document48 pagesSpe 3510 Chapt 2hitfliinnurNo ratings yet
- Expressing The Significance of Water in Living MatterDocument6 pagesExpressing The Significance of Water in Living MatterJacinth ManuelNo ratings yet
- STUDYGUIDEUNIT2Document7 pagesSTUDYGUIDEUNIT2bri mNo ratings yet
- CH 1-2 NotesDocument43 pagesCH 1-2 Notesbri mNo ratings yet
- WordDocument2 pagesWordbri mNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide Chapter 1-4: Chapter 1 - Intro To Environmental Science Vocabulary: Know The Defentions of Each TermDocument14 pagesMidterm Study Guide Chapter 1-4: Chapter 1 - Intro To Environmental Science Vocabulary: Know The Defentions of Each Termbri mNo ratings yet
- Humanities Essay 1Document2 pagesHumanities Essay 1bri mNo ratings yet
- College Success 1Document1 pageCollege Success 1bri mNo ratings yet
- Tucss 35B 00010011Document12 pagesTucss 35B 00010011Đào Nhật HiểnNo ratings yet
- Chinese Tea CultureDocument56 pagesChinese Tea CultureWei Yu LowNo ratings yet
- Classic Hallucinogens: LSD (D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide) - Also Known As Acid, Blotter, Doses, HitsDocument3 pagesClassic Hallucinogens: LSD (D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide) - Also Known As Acid, Blotter, Doses, HitsName ToomNo ratings yet
- Logic Universals (Al-Kulli Al-Khams)Document21 pagesLogic Universals (Al-Kulli Al-Khams)Afra' Azam100% (1)
- Prayer ListDocument3 pagesPrayer ListGinalyn Melig BandaoNo ratings yet
- 2019 - 3 1357NI Blue Cross of Idaho Prior Authorization List Fully InsuredDocument1 page2019 - 3 1357NI Blue Cross of Idaho Prior Authorization List Fully InsuredRaja Churchill DassNo ratings yet
- Date A Live - Tohka SSDocument8 pagesDate A Live - Tohka SStorrisiangelo8No ratings yet
- Botanical Classification of CottonDocument6 pagesBotanical Classification of Cottontex_hasan_014No ratings yet
- Falcon Nir Online AnalyzerDocument4 pagesFalcon Nir Online AnalyzerCesc MezaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Employment Forms 2023Document20 pagesPre-Employment Forms 2023HR JeanNo ratings yet
- TE. Toefl Reading 2Document5 pagesTE. Toefl Reading 2beatriceNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2d Module 23 PDFDocument0 pagesAutocad 2d Module 23 PDFRam LamaNo ratings yet
- y Og YIA8 Ew Gcu JMXDocument14 pagesy Og YIA8 Ew Gcu JMXDevendra KunjamNo ratings yet
- EC3000E-UPS - (EPM) Elevator Inatelligent Integrated Machine: Scan QR Code To Download EC3000E Manual DocumentDocument22 pagesEC3000E-UPS - (EPM) Elevator Inatelligent Integrated Machine: Scan QR Code To Download EC3000E Manual DocumentViệt Thảo TrầnNo ratings yet
- Duke SOM 2016-2017Document266 pagesDuke SOM 2016-2017chocolatec00kieNo ratings yet
- Publication - Catalogue Price List PDFDocument28 pagesPublication - Catalogue Price List PDFpranavpremNo ratings yet
- Enzo Catalogue (Revised NTH Time)Document21 pagesEnzo Catalogue (Revised NTH Time)JessannDucTranNo ratings yet
- TFTP 1Document3 pagesTFTP 1Tbs PrasadNo ratings yet
- IADC/SPE 59209 A New Selective Lateral Re-Entry SystemDocument6 pagesIADC/SPE 59209 A New Selective Lateral Re-Entry SystemJorge FernandoNo ratings yet
- Rhapsody For Clarinet and Piano: Download NowDocument21 pagesRhapsody For Clarinet and Piano: Download NowTinamou0001No ratings yet
- A Study On Effect of TDS On Paddy Yield: by The Students of Dept - of Chemistry, Government Degree College, ArmoorDocument28 pagesA Study On Effect of TDS On Paddy Yield: by The Students of Dept - of Chemistry, Government Degree College, ArmoorRamya RajeshNo ratings yet
- Iep ProjectDocument16 pagesIep Projectapi-494142720No ratings yet
- Strategic Thinking: Catalyst To Competitive AdvantageDocument26 pagesStrategic Thinking: Catalyst To Competitive AdvantagenoorgikiNo ratings yet
- Mark Tribe InterviewDocument3 pagesMark Tribe InterviewGerardo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Astm 3441 98 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm 3441 98 PDFRemulo SousaNo ratings yet
- Statement From Peter Seidler and Dan SheaDocument2 pagesStatement From Peter Seidler and Dan SheaLisa HalverstadtNo ratings yet
- Intertestamental Period PaperDocument6 pagesIntertestamental Period PaperMrNo ratings yet