Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Speech
Project Speech
Uploaded by
Pranjal Mali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageSonar is a technique that uses sound waves to detect underwater objects. It works by emitting sound waves and receiving the echoes to determine distance, direction, and other properties. There are three main types of sonar systems - active systems which emit a sound wave and analyze its reflection, passive systems which listen for sounds made by targets, and acoustic communication systems which require projectors and receivers at both ends. Sonar has military and non-military uses such as detecting submarines, fish finding, navigation, and more.
Original Description:
Original Title
project speech
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSonar is a technique that uses sound waves to detect underwater objects. It works by emitting sound waves and receiving the echoes to determine distance, direction, and other properties. There are three main types of sonar systems - active systems which emit a sound wave and analyze its reflection, passive systems which listen for sounds made by targets, and acoustic communication systems which require projectors and receivers at both ends. Sonar has military and non-military uses such as detecting submarines, fish finding, navigation, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageProject Speech
Project Speech
Uploaded by
Pranjal MaliSonar is a technique that uses sound waves to detect underwater objects. It works by emitting sound waves and receiving the echoes to determine distance, direction, and other properties. There are three main types of sonar systems - active systems which emit a sound wave and analyze its reflection, passive systems which listen for sounds made by targets, and acoustic communication systems which require projectors and receivers at both ends. Sonar has military and non-military uses such as detecting submarines, fish finding, navigation, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
GOOD MORNING SIR /MAAM,
I am Pranjal Mali (pranjal) and I am Shravani Yewale (shravani).
Today, we are presenting the project of SONAR. (both)
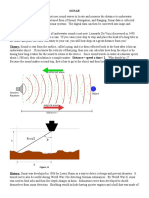
PRANJAL: SONAR, Sound Navigation and Ranging is technique for
detecting and determining the distance and direction of underwater objects
by audible means. Sound waves emitted by or reflected from the object are
detected by sonar apparatus and analyzed for the information they contain.
As you can see, the transmitter emits the sound waves and receiver receives
the emitted sound waves.
SHRAVANI: Sonar systems may be divided into three categories. In active
sonar systems an acoustic projector generates a sound wave that spreads
outward and is reflected back by a target object. A receiver picks up and
analyzes the reflected signal and may determine the range, bearing, and
relative motion of the target.
PRANJAL: The second type is Passive systems. It consist simply of
receiving sensors that pick up the noise produced by the target (such as
a ship, submarine, or torpedo). Waveforms thus detected may be analyzed
for identifying characteristics as well as direction and distance.
SHRAVANI: The third category of sonar devices is acoustic communication
systems, which require a projector and receiver at both ends of the acoustic
path. The model shown here is of this type.
PRANJAL: Firstly it was used to detect submarines by 1916, and by 1918 an
operational active system had been built by British and U.S. scientists.
SHRAVANI: today, they are used In the military field are a large number of
systems that detect, identify, and locate submarines. Sonar is also used in
acoustic homing torpedoes, in acoustic mines, and in mine detection.
PRANJAL: Non-military uses of sonar include fish finding, depth sounding,
mapping of the sea bottom, Doppler navigation, and acoustic locating for
divers.
NOTE: Show all the parts of the model if they ask to do so.
You might also like
- Accuracy of Phyphox SonarDocument4 pagesAccuracy of Phyphox SonarWilbert Dimaculangan100% (1)
- Blue Book of Submarine OperationsDocument39 pagesBlue Book of Submarine OperationstcstNo ratings yet
- Sonar As A DSP ApplicationDocument14 pagesSonar As A DSP Applicationmagalhaespaulo565No ratings yet
- PPTDocument38 pagesPPTSantiago KeLvinNo ratings yet
- Physics Sonar Technology Group 3 PresentationDocument14 pagesPhysics Sonar Technology Group 3 Presentationleonardo.harrison.01.09.07No ratings yet
- Sonar Technology: DefinitionDocument7 pagesSonar Technology: DefinitionMuhammad Haseeb JavedNo ratings yet
- Sonar: - Swapnil Hole (17) - Akshay Bramhane (18) - Amey Dandge (19) - Kshitij S. Dasture (20) Prof.P.A.PATHADEDocument30 pagesSonar: - Swapnil Hole (17) - Akshay Bramhane (18) - Amey Dandge (19) - Kshitij S. Dasture (20) Prof.P.A.PATHADEChinmay ApasangiNo ratings yet
- Sonar Technology: Measurement and InstrumentationDocument8 pagesSonar Technology: Measurement and InstrumentationMuhammad Haseeb JavedNo ratings yet
- SonarDocument3 pagesSonarJAIVISHNU MNo ratings yet
- SonarDocument2 pagesSonarLet's musicoNo ratings yet
- 634320547467133544Document18 pages634320547467133544Uday Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Echolocation (Written Report)Document2 pagesEcholocation (Written Report)Roscarl GorospeNo ratings yet
- SONARDocument13 pagesSONARSubir Maity100% (4)
- SonarDocument33 pagesSonarFelipe CardosoNo ratings yet
- Report On Working of SonarDocument15 pagesReport On Working of SonarvibhaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Modern Physics and Electronics PHY112: Topic: SONARDocument24 pagesTerm Paper Modern Physics and Electronics PHY112: Topic: SONARprateek154No ratings yet
- Sonar: Presented By: Mike Puato & Neil CorpuzDocument33 pagesSonar: Presented By: Mike Puato & Neil CorpuzMax100% (1)
- Gitika's Science ProjectDocument4 pagesGitika's Science ProjectSamara ShindeNo ratings yet
- Insights Current Events: 03 November 2014: Indian-Built Scorpene To Carry Critical DRDO SystemDocument3 pagesInsights Current Events: 03 November 2014: Indian-Built Scorpene To Carry Critical DRDO Systemsatoni12No ratings yet
- SonarDocument2 pagesSonarRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- SonarDocument11 pagesSonarIzhar Shaikh67% (3)
- SONARDocument4 pagesSONARakNo ratings yet
- DSP Project Sonar PresentationDocument27 pagesDSP Project Sonar PresentationThajid Ibna Rouf Uday100% (1)
- Side Scan Sonar and Sub-Bottom Profiler SurveyingDocument29 pagesSide Scan Sonar and Sub-Bottom Profiler SurveyingAlfian RomadhoniNo ratings yet
- Technology Lesson RevDocument5 pagesTechnology Lesson RevdidikhartadiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Underwater SensorsDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Underwater SensorsSheena Mae LantacaNo ratings yet
- SONARDocument6 pagesSONARĐoàn ThịnhNo ratings yet
- SonarDocument14 pagesSonarhusnrhnNo ratings yet
- Sonar - PajoDocument9 pagesSonar - PajoSOPHIA PAJONo ratings yet
- Sonar Application: DSP ProjectDocument27 pagesSonar Application: DSP ProjectMuhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- Passive Sonar Fusion For Submarine C Systems: Pailon Shar and X. Rong LiDocument7 pagesPassive Sonar Fusion For Submarine C Systems: Pailon Shar and X. Rong LiFlorentin PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Sonar Communication PDFDocument7 pagesSonar Communication PDFBùi Trường GiangNo ratings yet
- SonarDocument17 pagesSonarjoshigauta50% (2)
- Assignment SONAR Experiment FullDocument12 pagesAssignment SONAR Experiment FullPykah Watif100% (1)
- Sound Enery Q3 W3Document19 pagesSound Enery Q3 W3RASSEL DULOSNo ratings yet
- InTech-Sonar Systems and Underwater Signal Processing Classic and Modern ApproachesDocument35 pagesInTech-Sonar Systems and Underwater Signal Processing Classic and Modern ApproachesDiego CardosoNo ratings yet
- Side Scan SonarDocument3 pagesSide Scan SonarNur Fatmala100% (1)
- RadarDocument27 pagesRadarluluNo ratings yet
- SONAR - NavigationDocument25 pagesSONAR - NavigationKarlaColinaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Telephony PresentationDocument39 pagesGroup 4 Telephony Presentationholy fartNo ratings yet
- Principles: Radar Is An Object Detection System That UsesDocument36 pagesPrinciples: Radar Is An Object Detection System That UsesdeedepatilNo ratings yet
- Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging)Document27 pagesSonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging)Ralph Lorenz Hortillosa100% (1)
- How Does The Doppler Radar WorkDocument2 pagesHow Does The Doppler Radar Workcats1298100% (1)
- Microwave RSDocument7 pagesMicrowave RSapi-3733802No ratings yet
- Sonar Technology: Name: Mandira NagarDocument11 pagesSonar Technology: Name: Mandira NagarMandira NagarNo ratings yet
- MODULE-4 21BE45 - PPT FinalDocument55 pagesMODULE-4 21BE45 - PPT Finalezekiel david100% (1)
- Equipment and Tools Used in Marine ScienceDocument4 pagesEquipment and Tools Used in Marine Sciencejaelajeanine326No ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument26 pagesRemote SensingPIBRACNo ratings yet
- Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging) : Principle of An Active Sonar - Send and Return PingsDocument15 pagesSonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging) : Principle of An Active Sonar - Send and Return Pingsmonikajoon29No ratings yet
- SONAR Systems and Underwater Signal Processing: Classic and Modern ApproachesDocument35 pagesSONAR Systems and Underwater Signal Processing: Classic and Modern Approachesdusan cincarNo ratings yet
- Radar BulletDocument8 pagesRadar BulletDevenderGoudNo ratings yet
- Radar Written ReportDocument4 pagesRadar Written Reportcamingao.kristineNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Detection and Ranging: ECE Department, NNRGDocument36 pagesUltrasonic Detection and Ranging: ECE Department, NNRGlakshmi prasannaNo ratings yet
- Gec108 BarroaDocument2 pagesGec108 Barroaalberto BarroaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument26 pagesSeminar ReportPratik Priyasmit SahooNo ratings yet
- Microwave Remote Sensing: AN TODocument4 pagesMicrowave Remote Sensing: AN TOTejaswi RatnakaranNo ratings yet
- Underwater Object Detection Based On Distance Measurement Using UltrasonicDocument8 pagesUnderwater Object Detection Based On Distance Measurement Using UltrasonicFaiz gamers.No ratings yet
- Remote Sensing: Advancements and Applications in Computer Vision for Remote SensingFrom EverandRemote Sensing: Advancements and Applications in Computer Vision for Remote SensingNo ratings yet
- Multispectral Imaging: Unlocking the Spectrum: Advancements in Computer VisionFrom EverandMultispectral Imaging: Unlocking the Spectrum: Advancements in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Getting Started in Radio Astronomy: Beginner Projects for the AmateurFrom EverandGetting Started in Radio Astronomy: Beginner Projects for the AmateurNo ratings yet