Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry of Lipids: Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, Mls (Ascpi) - April, 2023
Uploaded by
May Ann EnoserioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochemistry of Lipids: Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, Mls (Ascpi) - April, 2023
Uploaded by
May Ann EnoserioCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPIDS
MLS 414
Second Semester
Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, MLS(ASCPi) | April, 2023
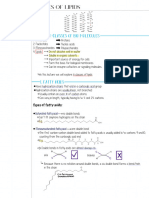
OUTLINE Saturated Fatty Acid
o No double bonds
I. LIPIDS
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
II. FATTY ACID
o Contains a double bond
III. GLYCERIDES
o Monounsaturated – has only 1 double
IV. NONGLYCERIDE LIPIDS
bond
V. COMPLEX LIPIDS
o Polyunsaturated – has multiple double
bonds
LIPIDS Omega number
Comes from the Greek word Lipos which o Locate the methyl end (CH3)
means Lard or Fat o After locating the methyl end, Count
Nonpolar or Hydrophobic the Carbon atoms until the first
double bond
Triglycerides (TAG) is the storage form of lipids
found in the adipocytes
Example:
BIOLOGICAL FUNCTION
● Energy Source
○ Each gram of fat releases 9 kcal of
energy
● Cell Membrane Structural Components
○ Phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and
steroids
● Hormone
○ Steroid hormone Answer: Omega-3 Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
● Lipid Soluble Vitamins
○ A, D, E, K Try this:
● Vitamin Absorption
● Protection
○ Shock absorber Answer:
● Insulation
○ Subcutaneous fat Cis-Fatty Acid
o Hydrogen atoms at the double bond is
FATTY ACID at the same side
o U-shaped
Trans-Fatty Acid
o Hydrogen atoms at the double bond are
at different sides
o Linear
Essential Fatty Acid
o Double bond can be found before the
9th Carbon atom
Nonessential Fatty Acid
o NO double bond found before the 9th
Carbon atom
Has Carboxyl group (COOH)
Has even number of Carbon atoms
TRANSCRIBED BY: LLOYD T. CABALLERO | MLS 414-LEC | Second Semester 1
MLS 414-LEC | BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPIDS | Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, MLS(ASCPi)
Example: Determine if the fatty acid is essential or NONGLYCERIDE LIPIDS
nonessential
Sphingolipids
o Not derived from glycerol
o Sphingosine is its backbone
o Amphipathic
o Sphingomyelins
Smallest sphingolipid
Answer: Nonessential because the double bond lies at Considered as a phospholipid
the 9th Carbon atom
Found in the myelin sheath
o Glycosphingolipids (Glycolipids)
Try this: Identify if the fatty acid is essential or
nonessential Its backbone is ceramide
which is a derivative of
sphingosine
Cerebroside
Singe monosaccharide
heads
Glucocerebroside –
macrophage
Answer:
Galactocerebroside –
neurons
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF FATTY ACID Steroids
o Steroid nucleus (OH- Sterol)
Esterification Cholesterol
o Amphipathic
o Fatty acid + Alcohol → Ester + Water
o Esters are the end product o Contains a hydroxyl group (OH) which
Acid Hydrolysis is polar
o Opposite to esterification o Chemical name is
o Ester → Fatty acid perhydrocyclopentanophenanthrene
Saponification ring
o Strong base to hydrolyze esters o OH replaced → esterification =
o End product is soap Cholesteryl ester
o Common bases used: NaOH, KOH, Lard Hydrophobic
Hydrogenation o Synthesized by animals
o Polyunsaturated oil → Saturated solid o Not a source of energy
fats o Converted in liver into bile acid
Partial Hydrogenation Bile salts
o Polyunsaturated oil → Saturated solid o Derivative of cholesterol
fats but not all Hydrogen atoms involved
o Amphipathic
in the reaction
o Emulsifying agent
Polar hydroxyl – interact with
GLYCERIDES
water
Glycerol + Fatty Acid Hydrophobic regions – binds
Neutral glyceride to lipid
o Nonionic and nonpolar Steroid hormone
o Monoglyceride, diglyceride, triglyceride o Testosterone, estrogen, progesterone,
Phosphoglycerides cortisol, cortisone, aldosterone
o Has a polar region, phosphoryl group o Does not mix with blood requires
(hydrophilic), and nonpolar fatty acid tail
carrier to travel in bloodstream
o Phosphatide is the simplest
Waxes
phosphoglyceride
o Hydrocarbon tails are hydrophobic
o Lanolin
Protective coating of skin and
hair
TRANSCRIBED BY: LLOYD T. CABALLERO | MLS 414-LEC | Second Semester 2
MLS 414-LEC | BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPIDS | Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, MLS(ASCPi)
COMPLEX LIPIDS
Bonded to other type of molecules Apo B-100
Lipoprotein o LDL and VLDL
o Hydrophobic lipids surrounded by o Ligand for LDL receptor
amphipathic proteins, phospholipids, Apo B-48
and cholesterol o Chylomicrons
o Apolipoproteins – Lipid + protein Apo E
Protein portion of lipoprotein o LDL, VLDL, HDL
o The larger the more lipids o Ligand for LDL and chylomicron
More lipid LDL remnant receptor
More protein HDL Chylomicron
o Apo B-48
o Account for the turbidity of
postprandial plasma
o Produced by the intestine
Low Density Lipoprotein
o Contains apo B-100 and apo E
o Significantly smaller than VLDL and
chylomicrons
o formed as a consequence of the
lipolysis of VLDL
High Density Lipoprotein
o Smallest and most dense
o Synthesized by liver and intestine
o Discoidal HDL
Most active form in removing
excess cholesterol
o Spherical HDL
HDL2
Larger in sizer and
richer in lipid
Efficient in delivering
lipid to liver
VLDL = Beta-Lipoprotein
LDL = Pre Beta-Lipoprotein
HDL = Alpha-Lipoprotein
Apo A-I
o HDL
o Anti-atherogenic HDL present in
plasma
Apo B
o LDL, VLDL, Chylomicrons
TRANSCRIBED BY: LLOYD T. CABALLERO | MLS 414-LEC | Second Semester 3
MLS 414-LEC | BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPIDS | Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, MLS(ASCPi)
Minor Lipoprotein
o Intermediate Density Lipoprotein
Formed through the
metabolism of VLDL in
circulation
o Lipoprotein (a)
is similar to LDL in terms of
density and overall
composition, and can be
thought of as an LDL particle to
which apo(a) has been added,
linked to apoB-100 via a
disulfide bond
Abnormal Lipoprotein
o LpX Lipoprotein
Found in patients with
obstructive biliary disease and
familial lecithin/cholesterol
acyltransferase (LCAT)
deficiency
o ẞ-VLDL Lipoprotein / Floating ẞ
Lipoprotein
accumulates in type 3
hyperlipoproteinemia
-END-
[Review] Answer the following:
It is the protein portion of lipoprotein
Its backbone is sphingosine
What is the opposite of esterification?
What is the chemical name of cholesterol?
Fatty acid that is U-shaped
It is the protective coating of hair and skin
It is the smallest and densest lipoprotein
It is the simplest phosphoglyceride
It is Derived from cholesterol
Its end product is saturated solid fats but not
all Hydrogen atoms involved in the reaction
TRANSCRIBED BY: LLOYD T. CABALLERO | MLS 414-LEC | Second Semester 4
You might also like
- CC Lec-Lipids-And-LipoproteinsDocument7 pagesCC Lec-Lipids-And-LipoproteinsFallen GwiyeobdaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument4 pagesLipidsKriszel Joy MaderiaNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 2 LipidsDocument21 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 2 LipidsJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- 2.04 - LipidsDocument5 pages2.04 - LipidsJuan Miguel SalvadorNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsladyNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Key Notes 2020Document14 pagesBiomolecules Key Notes 2020Jai Mata DiNo ratings yet
- Ruphele Anne I. QuitagDocument4 pagesRuphele Anne I. QuitagCiara marie BernardoNo ratings yet
- Lipids I-Iv: Prepared By: Group 6Document11 pagesLipids I-Iv: Prepared By: Group 6Jan Edward Abarientos MandaniNo ratings yet
- Lipids I-Iv: Prepared By: Group 6Document11 pagesLipids I-Iv: Prepared By: Group 6Jan Edward Abarientos MandaniNo ratings yet
- L16 - LipidsDocument15 pagesL16 - LipidsBobbyNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Key Notes 2020Document14 pagesBiomolecules Key Notes 2020Pon Adityan JeyamuruganNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer Weeks 1-3Document10 pagesBiochem Reviewer Weeks 1-3Fiona Marie ObañaNo ratings yet
- Midterm - LipidsDocument7 pagesMidterm - LipidsTherese Vince J. LazosNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument7 pagesLipidsHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument24 pagesLipidsRandy AminolaNo ratings yet
- Chem123lec MidtermDocument18 pagesChem123lec Midtermlily of the valleyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 8 - LipidsDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Week 8 - LipidsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Chapter 17Document3 pagesBiochemistry - Chapter 17Denise Mae DivinoNo ratings yet
- Chem 123 - LipidsDocument11 pagesChem 123 - LipidsGylene GardonNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Lipids O (HydrophobicDocument11 pagesCharacterization of Lipids O (HydrophobicSVMNo ratings yet
- 3 ProteinsDocument85 pages3 ProteinsEstella AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I BSC 211: LipidsDocument16 pagesBiochemistry I BSC 211: LipidsKelvin ChipezeniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. LipidsDocument33 pagesUnit 3. LipidsHBJBHNo ratings yet
- Lipids Chapter 8-2Document80 pagesLipids Chapter 8-2nik maisarahNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Key Notes 2020Document14 pagesBiomolecules Key Notes 2020Dipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Q: Why Do Lipids Release More Energy Than Carbohydrates or Protein?Document10 pagesLipids: Q: Why Do Lipids Release More Energy Than Carbohydrates or Protein?AlyssaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument70 pagesLipidsFazal Akbar KhaliliNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Document6 pages2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Alexandra DalisayNo ratings yet
- Semana 04 Biomoleculas IIDocument15 pagesSemana 04 Biomoleculas IIJean Pierre MoralesNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS MidtermDocument8 pagesLIPIDS MidtermMariaGay Albite Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lipids 2Document132 pagesLipids 2jasonenmanuel10No ratings yet
- Lipids PDFDocument17 pagesLipids PDFEnrico DarylNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9025796000039556153Document41 pagesInbound 9025796000039556153ellaverino6No ratings yet
- Biochemistry LipidsDocument14 pagesBiochemistry LipidsCeline Ricci AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 LipidsDocument109 pagesChapter 2 LipidsTiffany Shane VallenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 2SPP PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 08 2SPP PDFAdamFerdianNo ratings yet
- Lipids PT 1 Lipids?: StorageDocument14 pagesLipids PT 1 Lipids?: StorageRegil Mae GaleroNo ratings yet
- LokmlDocument6 pagesLokmlJelyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Organic Chemistry Material For 12th GradeDocument83 pagesLipid Organic Chemistry Material For 12th GradeAzizah Alya RaihanNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherDocument26 pagesLipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherputryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Lipids PbeDocument51 pagesLecture 6 Lipids PbeCeylin BaykoçNo ratings yet
- Lipids NotesDocument17 pagesLipids Notescsdeguzman7241pamNo ratings yet
- Biochem: Classes of LipidsDocument4 pagesBiochem: Classes of LipidsoliviaNo ratings yet
- (BIOCHEM LAB) LipidsDocument8 pages(BIOCHEM LAB) Lipidsprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Biochemistry LipidsDocument17 pagesBiochemistry LipidsMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Snaprevise Biology A2 Revision CheatsheetDocument15 pagesSnaprevise Biology A2 Revision CheatsheetSomaya AliNo ratings yet
- Lipids - L.L-N.V.Document34 pagesLipids - L.L-N.V.ViragNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lipids Study GuideDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lipids Study GuideJanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SHS 8.3 LipidsDocument17 pagesPhysical Science SHS 8.3 LipidsjouselleduayNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument2 pagesLipidsGianneCarloGomedNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes APDocument15 pagesBiochemistry Notes APNicholas CuevasNo ratings yet
- Eanbfdew 34567 OplkjhgfdewerijsaDocument16 pagesEanbfdew 34567 OplkjhgfdewerijsaShifa RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lipid Chemistry & Biological Membranes: Functions of LipidsDocument14 pagesLipid Chemistry & Biological Membranes: Functions of LipidsALYSSA SEVEN VELASCONo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Ihrevale LIPID META Bolism 1Document92 pagesBiochemistry: Ihrevale LIPID META Bolism 1Roy BelenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherNeenu RajputNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherChatie PipitNo ratings yet
- Notes in Lipids - PDFDocument26 pagesNotes in Lipids - PDFJanelle Lois EscolanoNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument14 pagesLipidsBeverlyNo ratings yet
- Total ProteinDocument2 pagesTotal ProteinMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- AlbuminDocument1 pageAlbuminMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Lit 101 Midterms CompiledDocument12 pagesLit 101 Midterms CompiledMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Biochemistry and Clinical Significance: Prof. Fritz Von T. Gella, RMT, MD October 5, 2021Document10 pagesCarbohydrates: Biochemistry and Clinical Significance: Prof. Fritz Von T. Gella, RMT, MD October 5, 2021May Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Laboratory ApplicationsDocument47 pagesCarbohydrates: Laboratory ApplicationsMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Lecture Topic 8: Lipids and Lipoproteins: SAN PEDRO COLLEGE - Created By: JC Louise P. BandalaDocument6 pagesLecture Topic 8: Lipids and Lipoproteins: SAN PEDRO COLLEGE - Created By: JC Louise P. BandalaMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- The 6 Styles of FastingDocument7 pagesThe 6 Styles of FastingGeorgina Lúa100% (4)
- New Way To Reverse Type 2 DiabetesDocument104 pagesNew Way To Reverse Type 2 DiabetesPip LockoutNo ratings yet
- SupeHeightheight Super - ChargeDocument39 pagesSupeHeightheight Super - ChargechicoskincareNo ratings yet
- Ajfn 3 4 31Document7 pagesAjfn 3 4 31gilarNo ratings yet
- GCSE-Biology-7-Summer2019-Foundation Tier, Unit 1-PaperDocument24 pagesGCSE-Biology-7-Summer2019-Foundation Tier, Unit 1-PaperjramatlhakolaneNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesMacromolecules Review WorksheetTaylor Delancey100% (1)
- 4 Day DietDocument38 pages4 Day Dietoswaldocampos100% (1)
- Food and NutritionDocument5 pagesFood and NutritionCes Blanco LicerioNo ratings yet
- SHARAN - Nandita Shah - Healthy-Living-BookDocument82 pagesSHARAN - Nandita Shah - Healthy-Living-Bookbal_thakreNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document37 pagesWeek 6Wong ChocolateNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Module PDFDocument245 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Module PDFKim Gyeoljong100% (1)
- CODEX AC ALINORM 97 - 22e PDFDocument41 pagesCODEX AC ALINORM 97 - 22e PDFWiwiek Hendrawati0% (1)
- Food and Nutrition PDFDocument82 pagesFood and Nutrition PDFMasheer Khan0% (1)
- Argument TopicsDocument56 pagesArgument Topicsrobionic100% (1)
- Production and Evaluation of Smoothies Made From Various Fruits Sold in Lagos MarketDocument5 pagesProduction and Evaluation of Smoothies Made From Various Fruits Sold in Lagos MarketInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Personal Nutrition 9th Edition Boyle Test BankDocument29 pagesPersonal Nutrition 9th Edition Boyle Test Bankannabellaauroravb5cf100% (32)
- 10 Good Reasons To Avoid Sugar ConsumptionDocument10 pages10 Good Reasons To Avoid Sugar ConsumptionIssahak CromwellNo ratings yet
- The Life Guide (22 Actions To A Better Life 01)Document96 pagesThe Life Guide (22 Actions To A Better Life 01)McDaryl Mateo100% (1)
- Prohance D NUTRITIONAL INFORMATION - 1Document1 pageProhance D NUTRITIONAL INFORMATION - 1Sistla567No ratings yet
- NCM 105 Week 1 Part 2Document6 pagesNCM 105 Week 1 Part 2Clint Mikael EulatrizNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit II - Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Saponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Document5 pagesSaponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Anonymous UoRu4sNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0963996923003812 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0963996923003812 Mainjair barruetaNo ratings yet
- 91xtad8xw - Module 4 - Pe1 - Health and NutritionDocument6 pages91xtad8xw - Module 4 - Pe1 - Health and NutritionSteve Laurence PontilloNo ratings yet
- Tugas PK Lemak Dan LaktosaDocument41 pagesTugas PK Lemak Dan LaktosaAdita KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins McqsDocument4 pagesVitamins Mcqsmarchkot100% (1)
- The Great Cholesterol MythDocument11 pagesThe Great Cholesterol Mythpantera neagră100% (1)
- Keto Food ListDocument4 pagesKeto Food ListIonela VelicuNo ratings yet
- Potential of Various Fatty Feeds To Reduce Methane Release From Rumen Fermentation in Vitro RusitecDocument14 pagesPotential of Various Fatty Feeds To Reduce Methane Release From Rumen Fermentation in Vitro RusitecGabriela Casarotto DanielNo ratings yet
- Embutido A Base de Proteínas VegetalesDocument9 pagesEmbutido A Base de Proteínas VegetalesMELISSA VERONICA TUDELANO OSPINANo ratings yet