Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Internet and Communication Protocols
Uploaded by
ezzeddinezahra_55049Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Internet and Communication Protocols
Uploaded by
ezzeddinezahra_55049Copyright:
Available Formats
The Internet
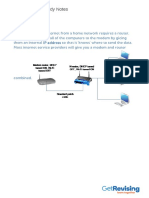
In order to connect to the Internet, you require a device called a
router. A router forwards data packets to the device requesting it.
Without a router, you have no way of connecting to the Internet
from your home.
Bandwidth – a measurement of capacity. Bandwidth is the number
of bits that can go through the network connection in a second.
Bandwidth is always measured in bits, however:
If you have a slow internet connection, your reading will
probably be in bits per second (bps). This will likely result in you
being unavailable to stream video of any kind without high
amount of buffering, as well as slow webpage loading times.
If you have an average connection speed, the one for most
households now in the UK, your bandwidth will be measured in
megabits per second (mbps). 5mbps and above will allow you
to stream HD videos with little to no buffer, however if multiple
users are on the same network, it will likely result in poor
connections. A fibre optic network typically sees speeds of
30mbps or more, which will be plentiful in streaming multiple
contents and viewing webpages/downloading files.
A very high bandwidth, not common at all in the UK but in
some places in the world, receives bandwidths of over 1
gigabyte per second (gbps). In honesty, it’s wasted, because not
a lot of technology can take that speed appropriately.
Latency – a measurement of delay. Latency is measured in
milliseconds. It’s the delay between a bit leaving one device, and
arriving at the other.
When playing video games or on Google you want a low
latency as you want it to be quick.
If you’re browsing on the internet, it doesn’t really matter what
the latency is, you won’t be affected greatly.
REMEMBER! You want a HIGH BANDWIDTH but LOW LATENCY!
Communication Protocols
VoIP – Voice over Internet Protocol - enables you to make free voice
calls over the Internet through services like Skype, Xbox LIVE, PSN
etc. It is also the same protocol used for sending videos over the
internet.
SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol – used when the user sends an
email to the senders email server and delivered to the recipients
email server
POP3 – Post Office Protocol – the protocol potentially used by the
recipient. It downloads the email to the recipients device and is then
deleted off the server. The email can be read offline.
IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol – email is read on the
recipients server but is not delivered. Can be accessed anywhere in
the world with an internet connection.
REMEMBER!
Post Office Protocol – a Postman delivers a letter. He or she doesn’t
store it as well at the post office.
IMAP is just the opposite.
WAN – Wide Area Network
LAN – Local Area Network
You might also like
- How Much Bandwidth Do You Have? (& How Much Do You Need?)Document7 pagesHow Much Bandwidth Do You Have? (& How Much Do You Need?)J A Y T R O NNo ratings yet
- What Is Streaming?: Client DeviceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Streaming?: Client DevicePriti rathoreNo ratings yet
- Candidates Should Be Able To: OCR 2.1.6 (I) Describe The Nature of The Internet As A Worldwide Collection of Computer NetworksDocument7 pagesCandidates Should Be Able To: OCR 2.1.6 (I) Describe The Nature of The Internet As A Worldwide Collection of Computer NetworksSumathi SelvarajNo ratings yet
- IPv4 CIDR Notation TutorialDocument1 pageIPv4 CIDR Notation TutorialAmidu MansarayNo ratings yet
- Zixi ProtocolDocument9 pagesZixi ProtocolJvst JashNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Vs ZigbeeDocument20 pagesBluetooth Vs ZigbeeZarnigar AltafNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Lec10Document5 pagesComputer Network Lec10Numan arshadNo ratings yet
- What Is Quality of ServiceDocument5 pagesWhat Is Quality of ServicelordvaughnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document5 pagesLecture 2owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Adsl and VDSL: 1. What Is The Difference Between ADSL, ISDN and Diginet or Leased Line Services?Document3 pagesAdsl and VDSL: 1. What Is The Difference Between ADSL, ISDN and Diginet or Leased Line Services?joyNo ratings yet
- F3-ICT Unit Activity Exam: 1. What's The Difference Between Buffer and Bandwidth?Document4 pagesF3-ICT Unit Activity Exam: 1. What's The Difference Between Buffer and Bandwidth?Phantom GamezNo ratings yet
- G6 PPT LESSON 6 hOW THE nET cONNECTSDocument9 pagesG6 PPT LESSON 6 hOW THE nET cONNECTSEmmanuel Bartolome100% (1)
- Intro To Live Streaming: Andy Beach Techgeist, Inc @andybeachDocument22 pagesIntro To Live Streaming: Andy Beach Techgeist, Inc @andybeachAntonio Edmundo Martinez AndradeNo ratings yet
- Internet Access SpeedDocument7 pagesInternet Access Speedakhmad faiz al khairiNo ratings yet
- S3 Computer Literacy: Internet TechnologyDocument28 pagesS3 Computer Literacy: Internet TechnologyAkshay KaushalNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesSeminar ReportVaibhav BhurkeNo ratings yet
- This Updated Version Was Graciously Sponsored by Kate StoryDocument16 pagesThis Updated Version Was Graciously Sponsored by Kate StoryHope Avalon LittleNo ratings yet
- Reg No: 1947234: Performance Problems in Computer NetworksDocument5 pagesReg No: 1947234: Performance Problems in Computer NetworksAbhiNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2 Wired and Wireless Networks, Protocols and Layers - Workbook OCR GCSEDocument10 pages1.3.2 Wired and Wireless Networks, Protocols and Layers - Workbook OCR GCSEemona.mockuNo ratings yet
- Application NoteDocument11 pagesApplication NoteanirudhaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth For StreamingDocument6 pagesBandwidth For StreamingfarrukhmohammedNo ratings yet
- Qo SDocument23 pagesQo SBijay LamaNo ratings yet
- The Design and Implementation of A Media On Demand System For WWWDocument10 pagesThe Design and Implementation of A Media On Demand System For WWWfarrukhsharifzadaNo ratings yet
- NTDocument2 pagesNTPayal KhannaNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: How Do I Connect To The Internet?Document8 pagesComputer Basics: How Do I Connect To The Internet?Ser Crz JyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Data Transmission RatesDocument4 pagesTopic 4 Data Transmission Rateskvidiniotis99No ratings yet
- Complete Reference To DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)Document66 pagesComplete Reference To DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)Chandni MehtaNo ratings yet
- What Is Broadband??: Services Provided by BroadbandDocument14 pagesWhat Is Broadband??: Services Provided by BroadbandParveen KumarNo ratings yet
- MI&K Eyuti 3Document7 pagesMI&K Eyuti 3አረጋዊ ሐይለማርያምNo ratings yet
- How To Network DevicesDocument17 pagesHow To Network DevicesPiyush PanchalNo ratings yet
- Module - 5 Multimedia NetworkingDocument27 pagesModule - 5 Multimedia NetworkingINDIAN ARMYNo ratings yet
- Module - 5 Multimedia NetworkingDocument27 pagesModule - 5 Multimedia NetworkingVarun GowdaNo ratings yet
- VoIP Network Design ChecklistDocument3 pagesVoIP Network Design ChecklistJonathan AkisanmiNo ratings yet
- MPEG-4 Video Transfer Over IEEE 802.11 WLAN: Ivan Gagro, B.Sc.E.E. Riko Luša, B.Sc.E.E. Vanesa Čačković B.Sc.E.EDocument5 pagesMPEG-4 Video Transfer Over IEEE 802.11 WLAN: Ivan Gagro, B.Sc.E.E. Riko Luša, B.Sc.E.E. Vanesa Čačković B.Sc.E.EBakhtiar TiarNo ratings yet
- Internet Connections: Big B or Little B?Document11 pagesInternet Connections: Big B or Little B?ajaycasperNo ratings yet
- Video Streaming395Document12 pagesVideo Streaming395sanathdNo ratings yet
- Internet ApuntesDocument5 pagesInternet ApuntesJimena YoNo ratings yet
- and Upload Speeds: InternetDocument3 pagesand Upload Speeds: InternetJohn Victor Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer NW Assingment (Presentation) Best PDFDocument44 pagesAdvanced Computer NW Assingment (Presentation) Best PDFJiru MuletaNo ratings yet
- U1l10 Data Exchange-2Document2 pagesU1l10 Data Exchange-2api-289547289No ratings yet
- What Is BluetoothDocument4 pagesWhat Is BluetoothArpit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Study Material Part-2Document10 pagesUnit-2 Study Material Part-2Himadri BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Fakultet Elektrotehnike U Tuzli: RTP-RTCP-RTSPDocument89 pagesFakultet Elektrotehnike U Tuzli: RTP-RTCP-RTSPMeša SelimovićNo ratings yet
- Internet ServicesDocument49 pagesInternet ServicesDexie Joy JaimeNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Networking: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesDocument95 pagesMultimedia Networking: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesMayank Raj BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Conjuntos Abstractos LogicaDocument18 pagesConjuntos Abstractos LogicaFreddy BeltranNo ratings yet
- DMC1935Document338 pagesDMC1935Kajendran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Networking: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesDocument48 pagesMultimedia Networking: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesStevan AdjieNo ratings yet
- NBN Speeds Explained: Factors Influencing SpeedDocument3 pagesNBN Speeds Explained: Factors Influencing SpeedFook NgoNo ratings yet
- MongalJyoti Saha - CA2 - WEBTECHNOLOGYDocument8 pagesMongalJyoti Saha - CA2 - WEBTECHNOLOGYRicky SahaNo ratings yet
- Introduction GifiDocument2 pagesIntroduction GifiTijo Emmanuel JosephNo ratings yet
- How To Fix Your Slow InternetDocument1 pageHow To Fix Your Slow InternetAmmar OdehNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology and Web DesignDocument33 pagesInternet Technology and Web DesignPooja GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dial Up NetworkingDocument4 pagesDial Up NetworkingAneesa JalilNo ratings yet
- Speed TestDocument1 pageSpeed TestYuli ChongNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Video Streaming Methods in Multihop Radio NetworksDocument5 pagesA Survey On Video Streaming Methods in Multihop Radio NetworksInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Serial Data CommunicationDocument28 pagesSerial Data Communicationameer hamzaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - ConnectivityDocument41 pagesUNIT 2 - ConnectivityZain BuhariNo ratings yet
- Online Potential Risks To Data and Personal InformationDocument67 pagesOnline Potential Risks To Data and Personal Informationezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Basic Python Programming - Part2Document14 pagesBasic Python Programming - Part2ezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- 3-Topic 3 Operating OnlineDocument8 pages3-Topic 3 Operating Onlineezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- 1-ICT Topic 3Document6 pages1-ICT Topic 3ezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- ICT - Topic 1 - LODocument4 pagesICT - Topic 1 - LOezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- 2-ICT - Environmental IssuesDocument3 pages2-ICT - Environmental Issuesezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Common FeaturesDocument1 pageCommon Featuresezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Information and Communication Technology For Examination From 2023Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Information and Communication Technology For Examination From 2023ezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesPython Cheat Sheetgr8ganesh4495100% (2)
- Digital Devices - : Audiences and Their Uses Wants and NeedsDocument37 pagesDigital Devices - : Audiences and Their Uses Wants and Needsezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- ICT Network SecurityDocument1 pageICT Network Securityezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Connectivity NotesDocument1 pageConnectivity Notesezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Routers Quick Study NotesDocument1 pageRouters Quick Study Notesezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument47 pagesComputer Softwareezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Information and Communication Technology 0417/02Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Information and Communication Technology 0417/02Thein ZawNo ratings yet
- Computer10to12 2008 PDFDocument72 pagesComputer10to12 2008 PDFA YoungeNo ratings yet
- Students Requiring Accommodations OnlyDocument4 pagesStudents Requiring Accommodations Onlyezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Gr11 Unit1 IO SheetsDocument16 pagesGr11 Unit1 IO Sheetsezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 10 To 12: Computer Studies, 2008 (Revised)Document4 pagesThe Ontario Curriculum, Grades 10 To 12: Computer Studies, 2008 (Revised)ezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Svcet: Introduction To Oop and Java FundamentalsDocument73 pagesSvcet: Introduction To Oop and Java Fundamentalsjames russell west brook100% (1)
- Outline of Course of Study: Faculty of Engineering Secondary School Department of EngineeringDocument4 pagesOutline of Course of Study: Faculty of Engineering Secondary School Department of Engineeringezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- ICS3U Unit 1 Test WorksheetDocument2 pagesICS3U Unit 1 Test Worksheetezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Simple Guide To Java PDFDocument24 pagesSimple Guide To Java PDFaarthi devNo ratings yet
- CS AnswersDocument27 pagesCS AnswersSova Sova33% (3)
- Gcse in Ict Unit 1 Sam-Ms-FinalDocument42 pagesGcse in Ict Unit 1 Sam-Ms-Finalezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Java TutorialDocument32 pagesJava Tutorialezzeddinezahra_55049No ratings yet
- Opps IntroductionDocument225 pagesOpps IntroductionPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Networking Igcse Cs Unit 3Document20 pagesData Communications and Networking Igcse Cs Unit 3PerduNo ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument22 pagesComputer Science NotesVrishinPatel100% (1)
- Apigateway DGDocument718 pagesApigateway DGhabriwwoNo ratings yet
- Should Students Get Limited Access To The InternetDocument2 pagesShould Students Get Limited Access To The InternetMark Landolf GoNo ratings yet
- First Sprint Demo Presentation - Group 4 (Default)Document19 pagesFirst Sprint Demo Presentation - Group 4 (Default)Gerald CaridoNo ratings yet
- Lookout Appendix A IocsDocument12 pagesLookout Appendix A IocsOlalekan Ibrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- 43i HL ManualDocument290 pages43i HL ManualJer HomeNo ratings yet
- Project Report 2021Document23 pagesProject Report 2021Ananmay Dixit40% (5)
- Top OSINT&Infosec Resources For You and Your Team100+ Blogs, PodcastsDocument24 pagesTop OSINT&Infosec Resources For You and Your Team100+ Blogs, Podcaststaha deghies100% (3)
- Installation & Configuration of LDAP+SAMBA On CentOS 5 PDFDocument15 pagesInstallation & Configuration of LDAP+SAMBA On CentOS 5 PDFRajeshSgssNo ratings yet
- Static Vs Dynamic RoutingDocument10 pagesStatic Vs Dynamic RoutingBijay LamaNo ratings yet
- Customer Request Form PDFDocument1 pageCustomer Request Form PDFMehmood ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Reddit Lamp TheoryDocument2 pagesReddit Lamp Theorygeorgekim04No ratings yet
- How Do You Remove Unused CSS From A Site - CSS-TricksDocument12 pagesHow Do You Remove Unused CSS From A Site - CSS-TricksARANIABDNo ratings yet
- 11 MIL PrelimDocument2 pages11 MIL PrelimSarah Mae MacarandanNo ratings yet
- 01-08 File ManagementDocument128 pages01-08 File Managementnaleonce02No ratings yet
- 10 Tips To Conserve Your Smartphone Battery PDFDocument6 pages10 Tips To Conserve Your Smartphone Battery PDFthonethoneNo ratings yet
- Books About Design: Every Founder Should ReadDocument9 pagesBooks About Design: Every Founder Should ReadAna BukvicNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist I Gcse Ice 0417Document42 pagesRevision Checklist I Gcse Ice 0417Amal Hayati Zali100% (1)
- Monitor b450Document24 pagesMonitor b450Enrique CarrilloNo ratings yet
- CSE-225 Midterm Question-Spring 2021Document2 pagesCSE-225 Midterm Question-Spring 2021Herbert M. HenryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Antconc by Tahir ShahDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Antconc by Tahir ShahTahir ShahNo ratings yet
- Archivetempad0900499362064200002035156 XMLDocument18 pagesArchivetempad0900499362064200002035156 XMLLois Andres Fuentes ChamorroNo ratings yet
- Mydraw User ManualDocument53 pagesMydraw User Manualmario rossiNo ratings yet
- Cot Motor 60HPDocument2 pagesCot Motor 60HPNelson BelloNo ratings yet
- Get Started With Synthetic Monitoring3Document2 pagesGet Started With Synthetic Monitoring3aravind.chinnaraj789No ratings yet
- 2PAA111693-610 A en System 800xa 6.1 Post InstallationDocument156 pages2PAA111693-610 A en System 800xa 6.1 Post Installationershivkumar2002No ratings yet
- Flyer - TDS Fiber PDFDocument2 pagesFlyer - TDS Fiber PDFseanNo ratings yet
- Git From Scratch: By: Eng. Mohamed Elemam EmailDocument61 pagesGit From Scratch: By: Eng. Mohamed Elemam EmailKuldeep Singh100% (4)
- Ulster Bank Interview Questions and Answers 40548Document11 pagesUlster Bank Interview Questions and Answers 40548qwertyNo ratings yet
- Hitachi NAS Platform 4000 Series: Petabyte-Scale File Sharing ChallengesDocument2 pagesHitachi NAS Platform 4000 Series: Petabyte-Scale File Sharing ChallengesJose AndresNo ratings yet
- Linking Aadhaar Mobile App GuideDocument8 pagesLinking Aadhaar Mobile App GuideSandeepNairNo ratings yet