Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHM1 Organic
Uploaded by
Hakim AbbasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHM1 Organic
Uploaded by
Hakim AbbasCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
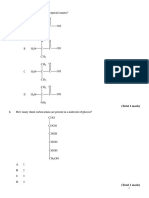
1. (a) But-2-ene, CH3CH=CHCH3, exists as geometric isomers.
(i) Draw the geometric isomers of but-2-ene.
(2)
(ii) Explain how geometric isomerism arises.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) (i) Draw the structural formula of a compound which is an isomer of but-2-ene but
which does not show geometric isomerism.
(1)
(ii) Explain why the isomer drawn in (i) does not show geometric isomerism.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 5 marks)
2. (a) A sample of 2-bromobutane was heated with potassium hydroxide in ethanolic solution.
A reaction occurred producing a mixture of but-1-ene and but-2-ene.
(i) Write an equation for the above reaction to show the production of either but-1-
ene or but-2-ene.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) State the type of reaction taking place.
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) Some bromine solution was shaken with a sample of but-2-ene, and a reaction occurred.
(i) State what would be seen during this reaction.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Draw the structural formula of the product of this reaction, and name this product.
Diagram:
Name ...............................................................................................................
(2)
(c) But-2-ene can exist as two stereoisomers.
(i) Draw the structural formula of the two stereoisomers of but-2-ene.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(2)
(ii) Explain why but-2-ene exists as two stereoisomers, and name this type of
isomerism.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
3. (a) Ethene and propene are in the same homologous series. Explain the term homologous
series.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(b) (i) Draw a representative length of the polymer chain of poly(propene).
(2)
(ii) State, with a reason, the empirical formula of poly(propene).
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(3)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(c) Poly(propene) does not have a sharp melting temperature, but softens over a range of
temperature. Suggest why this is so.
....................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(1)
(d) (i) Tetrafluoroethene, C2F4, also forms a polymer. Suggest why this polymer is very
inert.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give one use for poly(tetrafluoroethene).
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(e) Ethane and ethene both react with bromine. Ethane does not react at room temperature in
the dark, whereas ethene does so extremely quickly. Explain in terms of the bonding in
each molecule why this is so.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 14 marks)
4. Cracking is an important process in the petrochemical industry. Cracking the fraction of crude
oil with a boiling range of 200–300 °C produces a number of useful alkanes and alkenes.
(a) Why does the original fraction of crude oil have a boiling range rather than a single
boiling point?
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) The following equation represents one possible reaction which might occur during
cracking.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(i) Give the name of Product 1.
............................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give the molecular formula of Product 1.
............................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) Product 1 of this reaction is used as a component of petrol. Suggest ONE reason
why it is more suitable for this use than the original undecane.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(1)
(iv) State TWO necessary conditions used when cracking petroleum fractions.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(2)
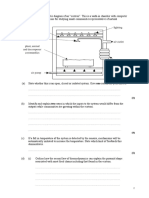
(v) Draw a labelled diagram showing suitable apparatus and materials for ‘cracking’
a liquid such as ‘light paraffin’ in the laboratory. You should indicate how a
gaseous product of the reaction could be collected.
(4)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(c) There are several isomers of Product 2. One of them, an alkene, can be made from
2-bromo-2-methylpropane, which has the following formula:
(i) Draw the structural formula of the alkene produced.
(1)
(ii) Name the type of reaction involved in the conversion of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane
to Product 2.
............................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) What reagent and conditions would be used to bring about this conversion?
Reagent ..............................................................................................................
Conditions ..........................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 14 marks)
5. (a) Bromine reacts with both ethane and ethene.
(i) Write the equations for the reactions below.
Ethane + bromine
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
......................................................................................................................
(1)
Ethene + bromine
......................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Classify the two reactions in terms of the type of reaction occurring.
Ethane + bromine
......................................................................................................................
(2)
Ethene + bromine
......................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Chloroethene (vinyl chloride), H2C==CHCl, can be polymerised in a similar type of
reaction to the polymerisation of ethene.
(i) Draw the full structural formula of the polymer poly(chloroethene), sufficient to
make the structure of the polymer clear.
(1)
(ii) State one use of poly(chloroethene).
......................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) State and explain one environmental problem arising from the disposal of
poly(chloroethene).
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
6. (a) Halogenoalkanes react with many nucleophiles.
Define the term nucleophile.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) (i) Identify the reagent and conditions necessary for the conversion of iodoethane to
ethylamine, C2H5NH2.
Reagent:.........................................................................................................
Conditions:.....................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(3)
(ii) State why the rate of reaction would be slower if bromobutane were used in place
of iodoethane, with all other conditions remaining the same.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) Iodoethane reacts with water to form ethanol and hydrogen iodide.
–1
C2H5I + H2O C2H5OH + HI Hf = +36 kJ mol
Use some or all of the data below to calculate the CI bond enthalpy.
Bond Bond enthalpy Bond Bond enthalpy
–1 –1
/ kJ mol / kJ mol
CH 413 HI 298
CC 347 CO 358
HO 464
(3)
(d) Ethanol was heated under reflux with an excess of a mixture of potassium dichromate(VI)
and dilute sulphuric acid. Draw the full structural formnula of the organic product.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(1)
(Total 10 marks)
7. One of the most important industrial uses of chlorine is in the production of poly(chloroethene),
usually called PVC. A sequence of reactions used to make PVC is set out below.
(a) (i) Name compound A.
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give the structural formula of chloroethene.
(1)
(iii) It is important that hydrogen chloride gas is not allowed to escape into the
atmosphere.
Suggest a way in which its escape could be prevented.
..........................................................................................................................
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) (i) Chloroethene is polymerised by a reaction involving free radicals. Explain what is
meant by a free radical.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give a necessary condition for the production of free radicals.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) (i) Ethane-1,2-diol, CH2OHCH2OH, is a useful compound which could be made from
compound A using a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Suggest a suitable nucleophile for this reaction.
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) The diagram below shows part of the formula of compound A. Use the diagram to
show how your suggested nucleophile attacks A.
C Cl
(2)
(iii) What is the leaving group in this reaction?
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(iv) Suggest a suitable chemical test you could use to confirm the identity of this
leaving group.
You should state the reagent you would use and give the observation expected.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
8. The reaction between chlorine and methane, in the presence of ultraviolet light, involves the
formation of free radicals and includes the following steps:
• ο –1
A Cl2 2Cl ΔΗ = +242 kJ mol
• • ο –1
B CH4 + Cl HCl + CH3 ΔΗ = +4 kJ mol
• • ο –1
C Cl2 + CH3 CH3Cl + Cl ΔΗ = –97 kJ mol
• •
D Cl + Cl Cl2
• •
E CH3 + CH3 CH3CH3
• • ο –1
F Cl + CH3 CH3Cl ΔΗ = –339 kJ mol
(a) (i) What is meant by a free radical? ....................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Draw a ‘dot-and-cross’ diagram, showing outer shell electrons only, for a chlorine
free radical.
(1)
(iii) What type of bond breaking occurs in step A?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) Which of the steps, A to F, are chain propagation steps?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) (i) Write the equation for the overall reaction between one mole of chlorine and one
mole of methane molecules.
(1)
ο
(ii) Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔΗ , for this reaction.
(2)
ο
(d) (i) What is the value of ΔΗ for step D? ................................................................
(1)
(ii) Would you expect step E to be exothermic or endothermic? Justify your answer.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(e) The overall reaction was repeated using bromine gas instead of chlorine gas.
Would you expect step A for bromine to be more or less endothermic than step A for
chlorine? Justify your answer.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
9. (a) Chlorine reacts with methane, CH4, to produce chloromethane.
(i) Write an equation for this reaction.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) State a necessary condition for this reaction.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) Chlorine can react with but-2-ene to form an addition product.
(i) Draw the structural formulae of the two geometric isomers of but-2-ene.
Isomer I Isomer 2
(2)
(ii) Explain why but-2-ene exists as two geometric isomers.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(iii) Name the addition product when chlorine reacts with but-2-ene.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 7 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
10. The industrial processes involved in the production of poly(chloroethene) are summarised in the
flow chart:
ethane ethene 1,2-dichloroethane chloroethene poly(chloroethene)
(a) (i) Ethane is converted to ethene by dehydrogenation.
Write a balanced equation, including state symbols, for this equilibrium reaction.
(1)
(ii) Explain why conditions of high pressure are less favourable for ethene production.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of an ethene molecule, showing the electron density distribution
in the and bonds between the carbon atoms.
(2)
(c) Give a chemical test which would distinguish between ethane and ethene.
State the result of your test with ethene.
Test ..............................................................................................................................
Result ...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(d) 1,2-dichloroethane is formed from ethene by reaction with chlorine.
State the type and mechanism of this reaction.
Type ...................................................................................................................................
Mechanism .........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
11. But-1-ene undergoes the following reactions:
(a) State the reagent and conditions needed for Reaction 1.
Reagent ........................................................................................................................
Conditions ....................................................................................................................
(3)
(b) (i) The reagent in Reaction 2 is gaseous hydrogen bromide.
Draw the full structural formula of compound A.
(1)
(ii) What type of reagent is hydrogen bromide in this reaction?
............................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) Identify the reagent needed for Reaction 3.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
......................................................................................................................................
(1)
(d) But-1-ene can be used to make an addition polymer.
Draw the repeating unit of the polymer.
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
12. Bromine reacts with both ethane, C2H6, and ethene, C2H4.
(a) The reaction of bromine with ethane occurs in ultraviolet light.
(i) By what type of mechanism does this substitution reaction occur?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Write the equation for a reaction of ethane with bromine.
(1)
(b) Bromine reacts rapidly with ethene without the need for light.
(i) Give the equation for this reaction using structural formulae.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(2)
(ii) Name the product. ...........................................................................................
(1)
(c) Explain, in terms of the bonding in the two hydrocarbons, why the reaction of bromine
with ethene occurs so much more readily than that with ethane.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 8 marks)
13. (a) (i) Draw the structural formulae of the two geometric isomers of but-2-ene, C 4H8.
(2)
(ii) Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why but-2-ene exists as two geometric
isomers whereas but-1-ene does not.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(iii) Draw the structural formula of another isomer with formula C 4H8.
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) Alkenes can be used to make polymers.
(i) Draw enough of the chain of poly(propene) to make its structure clear.
(2)
(ii) Explain why poly(alkenes) cause problems when they are disposed of in a
landfill site.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
14. (a) Name the homologous series to which the organic compound CH2=CHCH3 belongs.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) Write the structural formula of a member of the series named in (a) which contains four
carbon atoms.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 2 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
15. (i) Draw the displayed formula of propene, C3H6.
(1)
(ii) Draw a ‘dot and cross’ diagram for propene. You should show outer shell electrons only.
(1)
(Total 2 mark)
16. An addition polymer has the structure shown below.
CH3 H
C C
CH3 H n
Give the structural formula and the name of the monomer from which this polymer is made.
Structural formula
Name .....................................................................................................................................
(Total 2 marks)
17. Two reactions of a chloroalkane, X, are shown below.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Reaction1 Reaction2
Propanol-2-ol Chloroalkane X CH =CHCH
2 3
propene
(a) The chloroalkane X can be used to make propan-2-ol in Reaction 1.
(i) Name and draw the displayed formula of the chloroalkane X.
Name ...........................................................................................................
Displayed formula
(2)
(ii) Reaction 1 is an example of nucleophilic substitution. The nucleophile is the
hydroxide ion. Use the diagram below to show how it is able to attack the
chloroalkane X.
C Cl
(2)
(b) (i) What type of reaction is Reaction 2?
.............................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give the reagent and conditions needed for this reaction.
Reagent .............................................................................................................
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Conditions .........................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) Propan-2-ol has a higher boiling point than both the chloroalkane X and propene.
(i) Name the strongest intermolecular force between propan-2-ol molecules.
...........................................................................
(1)
(ii) Draw a diagram to show this force between two propan-2-ol molecules. Clearly
mark and label the bond angle between the molecules.
(2)
(d) Propene, CH2=CHCH3, can be polymerised forming poly(propene).
(i) Draw a section of the poly(propene) polymer chain formed from two monomer
units.
(2)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why poly(propene) is a solid at room
temperature.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 14 marks)
18. (a) The molecule isoprene has the displayed formula
H C H
H H
C C C C
H H H
(i) Give the systematic name of isoprene.
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) What colour change occurs when aqueous bromine solution is added to isoprene?
From ..................................................... to .......................................................
(1)
(iii) State the type and mechanism of this reaction.
Type ................................................ Mechanism .............................................
(2)
(iv) Suggest the displayed formula of the product formed when excess bromine reacts
with isoprene in the dark.
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) Compound Q, an isomer of isoprene, has the structural formula
CH2 =CHCH2CH=CH2.
(i) Give the name of the intermolecular force present in both isomers.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Which isomer would you expect to have the higher boiling point? Justify your
answer.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
19. (a) Draw the full structural formulae, showing all bonds, of:
(i) 2,4-dimethylpentane
(1)
(ii) 2-bromopropan-2-ol
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) Pent-2-ene shows geometric isomerism.
Draw the structures of the two geometric isomers.
Isomer 1 Isomer 2
(2)
(Total 4 marks)
20. Bromine needs ultraviolet radiation to react with ethane, C 2H6, but reacts with ethene, C2H4, in
the dark.
(a) Complete the equations.
(i) C2H6 + Br2 → ....................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) C2H4 + Br2 → ....................................................................................................
(1)
(b) (i) Identify and state the type of covalent bond in the hydrocarbon molecules that are
broken during these two reactions.
Ethane
bond broken ...................................... type ......................................
Ethene
bond broken ...................................... type ......................................
(2)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) Use your answer to (b)(i) to suggest why the reaction of bromine with ethene
occurs more readily than with ethane in the dark.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 5 marks)
21. This question is about some of the chemicals used in car engines and their reactions.
(a) Compound X, shown below, is one component of petrol.
H CH3 H H H
H— C— — C— — C— — C— — C— H
H CH3 H CH3 H
(i) Name X.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give the empirical formula of X.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) X can be made by cracking decane, C10H22.
Assuming only one other product forms in a cracking reaction, deduce the
molecular formula of this other product.
(1)
(iv) What is the sign of the enthalpy change for the reaction in which decane is
cracked? Give a reason for your answer.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(v) If the air supply in a car engine is poor, there is not enough air for carbon dioxide
to be produced.
Use this information to suggest ONE possible equation for the combustion of X in
this engine. Use the molecular formula of X in your equation.
(2)
(b) When air enters a car engine, as well as the fuel burning, nitrogen and oxygen can react to
form nitrogen(II) oxide.
–1
N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) ΔH = + 180 kJ mol
(i) What, if any, is the effect on the percentage of nitrogen(II) oxide in an equilibrium
mixture of these three gases if the pressure and temperature are increased?
Explain your answers.
Increase in pressure
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Increase in temperature
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) In a car exhaust pipe, nitrogen(II) oxide passes over a catalytic converter.
The following reaction occurs.
–1
2NO(g) + 2CO(g) → N2(g) + 2CO2(g) ΔH = –746 kJ mol
Explain why this reaction speeds up when the car engine has been running for a
few minutes.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(iii) A textbook says “The catalytic converter converts the gases coming out of the
engine into less harmful ones”.
State, with a reason, which of the four gases in the equation in (ii) you consider to
be least harmful.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iv) The diagram below shows the reaction profile for the change which occurs in the
catalytic converter.
E n erg y
2 N O (g ) + 2 C O (g )
N 2 (g ) + 2 C O 2 (g )
P rog ress o f reactio n
On the diagram, show the activation energy, EA.
Add a line showing the reaction profile if no catalyst is present.
(2)
(Total 12 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
22. This question concerns the compounds and reactions shown in the following reaction scheme.
CH3 H CH3 H CH3 H
S tep 5 S tep 1
— C— — C— C=C H— C— — C— H
H H n H H Cl H
E A B
S tep 4 S tep 2
CH3 H CH3 H
S tep 3
H— C— — C— H H— C— — C— H
Br H OH H
D C
(a) From the compounds, A to E, state
(i) which is a member of the same homologous series as pent-1-ene.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) which are described as secondary compounds.
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Give the systematic name for
(i) compound D ..........................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) compound E ............................................................................................................
(1)
(c) (i) What reagent and conditions would you use for step 4?
Reagent .............................................................................................................
Conditions .........................................................................................................
(2)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) What type of reaction is this? ................................................................................
(1)
(d) Compound B could be made from chlorine and propane in the presence of sunlight.
(i) Write an equation to represent the initiation step in this chain reaction.
(1)
(ii) Write an equation for the overall reaction to produce B in this way.
(1)
(iii) Another possible product of this reaction has the following structural formula.
H 3C — C H — C H 3
H 3C — C H — C H 3
Name this compound ........................................................................................
Suggest how this compound formed in the reaction mixture.
Name the type of step involved in its formation.
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 13 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
23. A gaseous hydrocarbon, W, is a product formed in the cracking of eicosane, C20H42.
W decolourises bromine, forming compound X.
When X is reacted with aqueous potassium hydroxide, compound Y is formed.
When a solution of Y is refluxed with an excess of acidified potassium dichromate(VI),
compound Z is formed.
Compound Z contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only.
3
(a) (i) On complete combustion, 0.10 g of Z produced 53 cm of carbon dioxide and
0.020 g of water at room temperature and pressure.
Calculate the empirical formula of compound Z.
3 –1
[Molar volume of a gas is 24 000 cm mol at room temperature and pressure]
(3)
–1
(ii) The molar mass of Z is 90 g mol . Find the molecular formula of Z.
(1)
(iii) A solution made by dissolving 0.900 g of compound Z in water is titrated with
3
sodium hydroxide solution. 20.0 cm of sodium hydroxide solution of
–3
concentration 1.00 mol dm is required for complete neutralisation.
Deduce the structural formula of compound Z.
(2)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(iv) Deduce the structural formulae of compounds W, X, and Y.
(3)
(v) Suggest a balanced equation for the cracking of eicosane.
(1)
(b) Compound Y can be made in one step from compound W.
State the reagents needed for this reaction.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 12 marks)
24. (a) Compound A, CH3CHBrCH2CH3, can be converted into butan-2-ol by reaction with
potassium hydroxide solution.
(i) Name compound A.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Write an equation for the conversion of compound A into butan-2-ol.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(iii) Identify the solvent required for this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iv) Classify this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) Compound A can also be converted into a mixture of the structural isomers but-1-ene and
but-2-ene by reaction with potassium hydroxide under different conditions.
(i) Write the ionic equation for the conversion of compound A into either but-1-ene
or but-2-ene.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) What is the solvent required for this reaction?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) Classify this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) But-2-ene exists as two geometric isomers.
(i) Draw the structural formulae of these TWO geometric isomers.
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) Explain why but-2-ene exists as two geometric isomers.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(d) Both but-1-ene and but-2-ene react with hydrogen, in the presence of a suitable catalyst,
to give the same product.
(i) Identify the catalyst.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Identify the product of this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 12 marks)
25. (a) Four reactions of but-1-ene are summarised on the chart below.
C H 3C H 2C H O H C H 3
R eactio n 1
K M n O 4 / d il H 2 S O 4
C H 3 C H 2 C H B rC H 3 C H 3C H 2C H CH 2 C om pound A
R eactio n 4 R eactio n 2
B r2 R ea ctio n 3
C o m p o un d B
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(i) Give the TWO reagents you would use for Reaction 1 in the laboratory.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) Give the name of the product, Compound A, of Reaction 2.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) Give the name of the product, Compound B, of Reaction 3.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iv) Suggest the reagent needed for Reaction 4.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) All four reactions are addition reactions. Explain what is meant by an addition reaction.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) (i) Explain what is meant by an electrophile.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give the formula of the attacking electrophile in Reaction 3.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(d) (i) Select ONE reaction from 1–4 which involves oxidation of but-1-ene.
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Reaction ...........................................
(1)
(ii) Explain what is meant by oxidation in this reaction.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(e) 1-chlorobutane can be made from but-1-ene in a two-step process. The but-1-ene is first
reduced and then a chlorine atom is substituted for a hydrogen atom.
CH3CH2CH=CH2 Reaction 5 Compound C Reaction 6 CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl
(i) Identify compound C.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Name the reagent and catalyst required for Reaction 5.
Reagent .............................................................................................................
Catalyst .............................................................................................................
(2)
(iii) Name the reagent and conditions for Reaction 6.
Reagent .............................................................................................................
Conditions .........................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 15 marks)
26. (a) (i) State TWO features that members of a homologous series have in common.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(2)
(ii) Name the homologous series to which propene belongs.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) Propene can be converted into a mixture of 2-chloropropane (as the major product)
and 1-chloropropane.
Classify the reaction involved and identify the reagent required.
Classification ....................................................................................................
Reagent .............................................................................................................
(2)
(b) Define the term structural isomers.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) 1-chloropropane and 1-bromopropane both react with ammonia to give 1-propylamine.
State and explain, in terms of bonding and kinetics, which of 1-chloropropane and 1-
bromopropane would react faster with ammonia.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(d) 1-chloropropene, CH3CH CHCl, can be polymerised to form poly(1-chloropropene).
Draw the repeat unit of poly(1-chloropropene).
(2)
(e) Explain why 1-chloropropene exists as two different geometric isomers, but propene does
not.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 14 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
27. This question is about four hydrocarbons with molecular formulae as shown.
A C2H2
B C3H6
C C3H8
D C4H10
(a) Which hydrocarbon has the same empirical formula as its molecular formula?
D
(1)
(b) Which has a molecular ion in the mass spectrum at mass/charge ratio = 58?
D
(1)
(c) Which is neither an alkane nor an alkene?
D
(1)
(d) Which could be 2-methylpropane?
D
(1)
(Total 4 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
28. This question is about the following organic compounds with skeletal formulae as shown:
D Br
Br
(a) Which compound could be made from one of the others in an addition reaction?
D
(1)
(b) Which compound has E–Z isomers?
D
(1)
(Total 2 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
29. Chemists investigating the mechanism of the reaction of ethene and bromine thought that the
first step was the addition of Br+. To test this, they reacted bromine with ethene in the presence
of sodium chloride.
If their theory about the first step of the reaction was correct, which product might form as well
as 1,2-dibromoethane?
A CH2BrCH2Na
B CH2BrCH2Cl
C CH2ClCH2Cl
D CH2NaCH2Na
(Total 1 mark)
30. Which of the following is the correct name for the compound below?
CH3 Cl
C C
H CH 3
A Z-3-chlorobut-2-ene
B E-3-chlorobut-2-ene
C E-2-chlorobut-2-ene
D Z-2-chlorobut-2-ene
(Total 1 mark)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
31. Propene can be used to make other important chemical products. The processes involved can be
summarised in the diagram:
C om poundA C H 2 (O H )C H (O H )C H 3
+H Br
R ea ction 1 R ea ction 2
C H 2 CH CH3
P rop en e
R ea ction 3
R ea ction 4
+ H 2 /N i
p o ly (p ro p en e)
P ro p an e
C H 3C H 2C H 2C l C H 3C H 2C H 3
R ea ctio n 5
(a) (i) Give the mechanism for Reaction 1.
(3)
(ii) Explain why compound A and not its structural isomer is the major product in
Reaction 1.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii) Name compound A formed in Reaction 1.
Name .................................................................................................................
(1)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) What is added in Reaction 2 to make the product CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH3?
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) Complete the balanced equation for the formation of poly(propene) in Reaction 3 using
displayed formulae.
n(CH2 CHCH3)
(2)
(d) Poly(propene) fibres can be used to make fleece which is used at several horse racing
courses to prevent the ground becoming frozen.
State one advantage of using poly(propene) instead of natural fibres of similar cost.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(e) (i) One stage in the mechanism of Reaction 5 is shown below.
• •
CH3CH2CH3 + Cl CH3CH2CH2 + HCl
What is this step?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give the name or formula of the trace product present in the final mixture which
gives evidence for this mechanism.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 11 marks)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Answers)
1. (a) (i)
CH 3 CH 3 H CH3
C C C C
H H CH 3 H 2
(ii) No rotation / restricted rotation around double bond(1) 1
(b) (i)
H C 2H5 H CH3
C C C C
H H H CH3
H H
CH 2 CH 2
C
H C C CH 3 CH 2 CH 2
H H 1
(ii) One end of C=C bond has 2 identical atoms / groups attached (1)
Or if cyclobutane –
no movement / no C=C (1) 1
[5]
2. (a) (i) e.g.
CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + KOH CH2=CHCH2CH3 + KBr + H2O
Or
CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + KOH CH3CH=CHCH3 + KBr + H2O
(1)
– –
allow ionic equation with OH and Br 1
(ii) Elimination (1) 1
(b) (i) brown / red-brown / orange / red-orange / yellow to colourless
/ fades / decolourises / gets paler (1) 1
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
H H
CH 3 C C CH 3
(ii) Br Br
2,3-dibromobutane (1) accept 3-bromobutan-2-ol if correct
structure drawn for hydroxy product 2
CH 3 CH 3 H CH 3
C C C C
H H CH3 H
(c) (1 mark for each)
allow: 2
H H H
CH 3 C C CH3 CH 3 C C CH 3
H
(ii) Restricted (or ‘no’) rotation about double bond /
2 different groups at each end of double bond (1)
geometrical / cis-trans (1) 2
[9]
3. (a) Group of compounds with the same general
formula (1) that
differ by –CH2- (1)
Same or similar chemical properties / same 3
functional group (1)
CH3 H
C C
(b) (i) H H
At least one repeat unit (1)
evidence of extension of chain (1) 2
consequential on correct repeat unit
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) CH2 (1)
empirical formula of propene/ the repeat unit (1)
since polymer made by addition reaction / no loss of
small molecules (1) 3
(c) Different chain lengths / areas of crystalline and amorphous structure (1) 1
(d) (i) C-F bond strong / high bond enthalpy / bond not 1
easily broken / steric hindrance by fluorine around carbon (1)
(ii) Non–stick coatings e.g. in saucepans, in pipes, on skis,
stain–proofing of fabrics, waterproof clothing. (1) 1
(e) Only single / sigma bonds in ethane (1)
Ethene also has bond (1)
bond weaker (and breaks) / electrons in bond 3
more accessible (1)
[14]
4. (a) It is a mixture / not a single compound 1
(b) (i) 2,4-dimethylpentane 1
(ii) C7H16 1
(iii) More volatile / lower boiling point / vaporises more readily / branched so
doesn’t knock / higher octane number 1
(iv) Heat / high temperature / 200 °C (1)
Silica / alumina (catalyst) /zeolites (1) 2
(v) Diagram should show:
Test tube containing paraffin absorbed on suitable absorbent – (1)
absorbent can be just shown in the diagram
Aluminium oxide catalyst (1)
Heat catalyst (1)
Recognition of collection of gas over water /gas syringe (1) 4
Penalties
–1 for poor diagram
(c) (i) (CH3)2C = CH2
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
ACCEPT (CH3)2CCH2 1
(ii) Elimination 1
(iii) Potassium hydroxide / KOH / NAQH (1)
Ethanolic / alcoholic solution + heat / reflux (1) 2
[14]
5. (a) (i) C2H6 + Br2 C2H5Br + HBr (1)
C2H4 + Br2 CH2BrCH2Br ALLOW C2H4Br2 (1) 2
IGNORE STATE SYMBOLS
(ii) (Free) radical / homolytic (1) substitution (1)
Electrophilic (1) addition (1) 4
H H
(C C )n
(b) (i) H Cl 1
(ii)
Water pipes
window or door frames
clothing
bottles Any one
coating on electricalcables
flooring
NOT plastic / PVC / carrier bags
1
(iii) Persists in the environment / persisting as litter
OR non-biodegradable / not broken down by bacteria (1)
because of strong C-Cl bond (1)
OR
combustion / burning (1)
produces toxic gases /acidic gases/HCI (1)
NOT chlorine 2
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
[10]
6. (a) A species with a lone pair / pair of electrons (1)
NOT “negative ion” alone or as an alternative
which it uses / donates to form a (dative) covalent bond (1) 2
(b) (i) Ammonia / NH3 (in ethanol) (1)
heat (1) NOT heat under reflux UNLESS in a sealed tube
If a temperature is quoted it must be greater than 100C
in sealed tube / under pressure / concentrated (1)
If a pressure is quoted it must be greater than 1 atm
Conditions are dependent on correct reagent.
If ammonia and an additional reagent max (1) for two correct conditions. 3
(ii) Carbon-bromine bond stronger / higher bond enthalpy than
carbon – iodine / Ea for C-Br is higher than C-I
IGNORE any extra explanations involving the alkyl groups 1
(c) Identify bonds broken and made (1)
e.g. Energy in + 464 or + 3340
AND Energy out (-) 656 or (-) 3532 (1)
Energy needed to break bonds – energy released to make bonds = 36 (1)
e.g. C-I + 464 – 656 = + 36
or C-I + 3340 – 3532 = + 36 (1)
Correct evaluation dependent on use of 36 (1)
–1
i.e. C-I = 228 kJ mol (1)
Correct answer with some correct working (3)
If final answer is negative max (2)
If 36 is on the wrong side, then 156 max 2 (-156 (1))
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
If miss out 36, then 192 max 1 3
H
O
H C C
O H ALLO W OH
H
(d) 1
[10]
7. (a) (i) 1,2-dichloroethane 1
(ii) CH2 = CHCl / CH2CHCl 1
(iii) e.g. dissolve / bubble HCl in water / absorb in an alkali / condense the
HCl(g) 1
(b) (i) Species having unpaired electron 1
(ii) Action of UV radiation/sunlight / named initiator / photoflood 1
–
(c) (i) Water / OH 1
(ii) Unshared / lone pair of electrons on a legitimate nucleophile
based on (c)(i) (1)
(c)(i) “nucleophile” attacks / forms bond with C of C – Cl (1) 2
–
(iii) Chloride ion / Cl 1
(iv) Add silver nitrate solution (1)
white ppt (1) 2
[11]
8. (a) (i) a particle / species /group with an unpaired electron /OWTTE 1
(ii) 1
(iii) homolytic 1
(b) B and C 1
(c) (i) C12 + CH4 CH3Cl + HCl 1
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
–1
(ii) +242 + 4 + –339 = –93 kJ mol
(A + B + F)
OR
–1
+4 – 97 = –93 kJ mol
(B + C)
Method (1)
answer with units (1) 2
–1
(d) (i) -242 kJ mol 1
(ii) Exothermic because a bond has been formed. 1
(e) Less endothermic (1)
the bond is weaker (1) 2
[11]
9. (a) (i) CH4 + C12 CH3Cl + HCl (1) 1
(ii) UV (radiation) / Sunlight (1) Not light 1
(b) (i)
H H H CH 3
C C C C
H 3C CH 3 H 3C H
(1 ) (1 ) 2
(ii) restricted rotation around double bond (1)
Allow no rotation at room temperature
two different groups on each double bonded carbon (1) 2
(iii) 2,3-dichlorobutane (1) 1
[7]
10. (a) (i) C2H6(g)/(I) C2H4(g) + H2(g)
If a state symbol is missing (0)
If (aq) (0) 1
(ii) At high pressure reaction goes in direction to reduce
pressure/to oppose change by Le Chatelier’s principle (1)
towards side with fewer molecules/moles (1) 2
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) Shapes of orbitals between and above carbon
If p orbitals drawn msut show overlapping
Shapes (1) ACCEPT crescents for bonds NOT lines for bond 2
Labels (1)
(c) Addition of bromine water/solution (1)
from yellow/brown/orange to colourless (1)
OR
acidified potassium manganate(VII) (1)
from pink/purple to colourless (1) 2
(d) Addition (1)
Elecrophilic/electrophile OR appropriate explanation (1) 2
[9]
11. (a) H2 / hydrogen NOT H (1)
Ni / nickel
OR platinum / Pt / palladium / Pd (1)
(Ni) 140 – 180 ° C / heat (1) 3
OR (Pt / Pd) room temperature
If no reagent but other parts correct (1)
Incorrect reagent (0)
(b) (i)
(ii) electrophile / electrophilic IGNORE any reference to addition 1
–
(c) potassium manganate(VII) / potassium permanganate / MnO 4 /
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
manganate(VII) ions IGNORE acid or alkali 1
ACCEPT name or formula
(d)
Correct structure (1) – only one repeat until identified
Continuation (1)
IGNORE ( )n 2
[8]
12. (a) (i) (Free) radical
ACCEPT homolytic radical
NOT radical ion 1
(ii) CH3CH3 + Br2 CH3CH2Br + HBr
OR
C2H6 + Br2 C2H5Br + HBr
ACCEPT multiple substitution only if the equation balances
Can be full structural formula
If H2 is one product then (0) 1
(b) (i) CH2 = CH2+Br2 → BrCH2CH2Br / CH2BrCH2Br /CH2–CH2
| |
Br Br
Ethene shown with double bond + Br2 (1)
product (1) 2
(ii) 1,2 (–) dibromoethane only – mark independently of (i)
IGNORE punctuation 1
QWC (c) Ethene has a π / double bond (1)
Ethane has σ only / single only / no π / no double bond (1)
π (in ethene) weaker than C–H (in ethane) / high electron
density in C=C relative to C–H bond (1) 3
[8]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
13. (a) (i)
H 3C CH3 H 3C H
C C C C
H H H CH3
Can show C in straight line if H’s clearly cis or trans.
If H is missing once but bond is shown, no penalty.
If all H’s missing then (1) only awarded for both structures
CH 3
ALLOW C– 2
(ii) (Both have) no/restricted rotation about C=C (rotation would
require π bond to break) (1)
but but-1-ene has two identical groups on a doubly
bonded carbon atom (1)
but-2-ene does not (1)
OR other way round 3
(iii)
H H H H
H
H C C C H C C H H C H
or or
H
H H C C H C H
H C H H H
H H C C
H
H H
ALLOW
H
H H H
C C
H C C H
H H
Do not need to show all bonds eg can be –CH3, –C2H5 1
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) (i)
CH 3 H
C C
H H
Skeleton (1)
Indication of continuation conditional on a two carbon
saturated chain in the skeleton. (1) 2
(ii) Unreactive OR non-biodegradable (1)
So occupies / fills site OR remains in the site OR causes visual pollution (1)
nd st
2 mark consequential on 1
st nd
NOT “Do not decompose/decay” for 1 mark but allow 2 mark 2
[10]
14. (a) Alkene 1
(b) CH2=CHCH2CH3 / CH3CH=CHCH3 / CH2 = C(CH3)2 / CH2=C(CH3)CH3
double bond need not be shown
ACCEPT displayed formula
Mark independently of a
Watch for incorrect numbers of H in the middle of the chain 1
[2]
15. (i)
H H H
H C C C
H H 1
(ii)
H H H
x x x
H x C C C
x x
H H
ALLOW all dots or crosses
ALLOW TE for a butene/pentene in (a)(i)
IGNORE circle 1
[2]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
16. (CH3)2C=CH2
ALLOW displayed formula (1)
ALLOW C(CH3)2=CH2
CH3C(CH3)=CH2
CH3CCH3=CH2
CCH3CH3=CH2
CH3CH3C=CH2
double bond need not be shown, but if single bond displayed (0)
(2-)methylpropene
2 - methylprop- 1 - ene IGNORE punctuation, spaces etc
2 - methylprop- 2 - ene
Mark independently
No transferred error allowed 2
[2]
17. (a) (i) 2(-)chloropropane
H Cl H
H C C C H
H H H No internal TE from name to structure
MUST be fully displayed 2
(ii)
(1)
+ –
IG N O R E rest o f m o le cu le C Cl
OH –
(1 )
Mark independently
Must attack the carbon
ALLOW attack by oxygen or negative charge or lone pair 2
ACCEPT OH – NOT OH –
NOT C+
(b) (i) Elimination
NOT in conjunction with additional incorrect information
eg “nucleophile” 1
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide / NaOH/potassium hydroxide / KOH (1)
Any additional incorrect reagent (0)
st
NOT alkali on its own for 1 mark
Alcoholic solution / ethanolic solution and heat / warm / reflux (1)
nd
2 mark is dependent on mention of correct reagent or “alkali”
nd
“aqueous” negates 2 mark eg KOH(aq) + heat (1) – ie reagent mark
NaOH(alc) + heat (2) 2
(c) (i) Hydrogen/H bonding 1
(ii)
CH 3
180º CH 3
C H 3C O H O CHCH3
H
H
H-bond and rest of molecule (1)
angle must be between 3 atoms for a correct H bond (1)
ALLOW HOH 106-108° 2
(d) (i)
H CH 3 H CH3
C C C C
H H H H IGNORE any “n” in this diagram
Brackets optional but continuation must be shown
4 carbon chain with 6Cs overall in structure (1)
methyl groups can be on C1 and C3, C1 and C4, C2 and C4, C2 and C3 (1)
H CH 3
C C
H H n 1 max 2
(ii) (big molecule) so large number of electrons (1)
Hence large/strong van der Waals’ forces
(to be overcome to change state)(1) 2
[14]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(2-)methylbut(a) -1,3 - diene
18. (a) (i) (1) (1)
IGNORE punctuation
ALLOW 1 max if correct answer is pre-fixed by cis / trans 2
(ii) From orange/yellow/brown to colourless (1)
NOT red NOT clear 1
(iii) addition (1)
electrophilic (1)
in either order 2
(iv)
H
H C H
H H H
H C C C C H
B r Br Br Br
Methyl group need not be displayed 1
(b) (i) Van der Waals’ (forces)
ACCEPT Van der Walls
NOT vdw 1
(ii) Q because (unbranched) so greater area of contact / closer packing
(between molecules) (1)
hence greater Van der Waals/vdw forces (1)
nd st
2 mark dependent on 1
Incorrect isomer chosen (0)
Fully correct reverse argument (2) 2
[9]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
19. (a) (i)
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H
H C H H C H
H H 1
Accept CH3 in branches
But do not allow bond directly to H
i.e.
C
C H 3
C C C C C
C C
Reject
(ii)
H Br H
H C C C H
H O H
H 1
H Br H
H C C C H
Accept H O H H
Reject bond pointing directly to H i.e.
in OH i.e.
C
H O
Reject Hs missing from carbons i.e.
Br
C C C
OH
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(b) Isomer 1
H CH 3
C C
C2 H5 H (1)
Isomer 2
C2H5
CH 3
C C
H H (1)
Accept 90° bond angles e.g
C C
OR
C C
ACCEPT
CH 3
C
C 2H5
C
If incorrect alkene eg but-2-ene, allow (1) for both cis and trans isomers 2
[4]
20. (a) (i) (C2H6 + Br2) → C2H5Br + HBr
OR
multiple substitution e.g.
C2H6 + 2Br2 → C2H4Br2 / CH3CHBr2/CH2BrCH2Br + 2HBr
C2H6 + 3Br2 → C3H3Br3 + 3HBr etc 1
Accept CH3C H2Br or full structural formula
Reject C2H6 + 3Br2 → 2C + 6HBr
(ii) (C2H4 + Br2) → CH2BrCH2Br 1
Reject C2H4Br2
(b) (i) ethane C– H bond and ethene C=C bond (1)
ALLOW carbon–carbon if double in type of bond
ethane type: σ/sigma and ethene type: π/pi (1)
OR mark horizontally 2
Reject σ and π for ethene
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) π/pi bond is weaker (than the σ/sigma bond) 1
Accept π/pi bond requires less energy to break
OR
π/pi bond has lower bond enthalpy
Reject π breaks more easily
Reject π bond is weak
OR
π/pi bond has higher electron density (than the σ/sigma bond)
Accept π/pi bond has more accessible electron density
[5]
21. (a) (i) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
Ignore punctuation (Commas and hyphens may be interchanged) 1
Accept 2,4,4 - trimethylpentane
Reject pentan for pentane
2-dimethyl-4
methylpentane
2,2-dimethyl-4-methyl
pentane
2-methyl-4,4-dimethyl
pentane
2,4-trimethylpentane
(ii) C4H9 1
Accept C8H18 → C4H9
(iii) C2H4 1
Reject CH2CH2
(iv) Positive because energy is required to break (C–C) bonds
(and not completely replaced (from new bonds made))
OR Positive because cracking requires (continuous) supply of
heat so must be endothermic 1
Accept two C–C bonds are broken and one C=C made
Reject positive because it only occurs at high temperature
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(v) C8H18 + 17/2 O2 → 8CO + 9H2O
OR 2C8H18 + 17 O2 → 16CO + 18H2O
OR C8H18 + 9/2 O2 → 8C + 9H2O (or doubled)
Oxygen on left and correct formulae of products (1)
balancing (1)
Second mark depends on first and a sensible hydrocarbon
formula must be used. 2
Accept balanced equations including CO and/or C with CO2
17/2 can be written 8.5 or 8½
Allow balanced equations based on C8H18 with a smaller
alkane in the products for 1 mark eg
C8H18 + O2 → CO + C7H16 +H2O (1)
(b) (i) Increase in pressure: No effect as number of
moles/molecules (of gas) doesn’t change during reaction (1)
Increase in temperature: more NO as forward reaction
endothermic OWTTE (1)
One mark for two correct predictions with incorrect explanations 2
Reject increase in temperature moves equilibrium to the right
(ii) Rate increases as converter gets hotter (as reaction is
exothermic) 1
(iii) N2 / nitrogen is (major) part of air/ N2 unreactive/ not
poisonous/ not a greenhouse gas / not acidic 1
Accept correct harmful properties of other 3 gases
(iv) Line from level of reactants to maximum labelled E A (1)
Curve of similar shape above existing curve, starting and
finishing at same levels, with maximum above original maximum (1) 2
[12]
22. (a) (i) A and/or propene 1
Accept prop-1-ene
Reject A and any other letter
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) B C and D (any order)
3 correct for 2 marks
2 correct for 1 mark
1 letter, correct or incorrect O eg B
2 letters both correct 1 BC
2 letters 1 correct 1 wrong O BE
3 letters, all correct 2 BCD
3 letters, 2 correct 1 wrong 1 BCE
3 letters, 1 correct 2 wrong O ABE
4 letters, 3 correct 1 wrong 1 BCDE
4 letters, 2 correct 2 wrong O ABDE
5 letters O ABCDE 2
(b) (i) 2–bromopropane 2 (–) bromo (–) propane
2 Bromo Propane 2, bromopropane 1
Reject bromopropane
Reject bromo-2-propane
Reject 2-bromopropene
(ii) poly(propene) or polypropene 1
Accept polly(propene)
Accept polypropylene
Reject poly porpene
Reject polypropane
(c) (i) potassium/sodium hydroxide (1)
(concentrated)
ethanol(ic)/alcoholic AND heat/reflux 2
Accept KOH/NaOH
Reject alkali on its own
Reject any mention of water/aqueous/pressure (–1)
(ii) Elimination (reaction) 1
Reject any qualification of elimination e.g nucleophilic /
electrophilic cracking
•
(d) (i) Cl2 2Cl
Ignore state symbols 1
Reject not 2 Cl(g)
Reject Cl2 →2Cl
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) C3H8 + Cl2 C3H7Cl + HCl
Ignore state symbols 1
Reject 2Cl° + C3H8 → C3H7Cl + HCl
(iii) 2 (,) 3 (–)dimethyl butane (1) Ignore punctuation
Reaction between two
CH3CHCH3 (1) dot must be shown on central
carbon atom
Termination (1) 3
Accept C3H7° + C3H7° → C6H14
Accept chain termination
Reject 2,3 methylbutane
Reject CH3CHCH3°
[13]
53
23. (a) (i) Amount of CO2 = 24000
= 0.0022 (mol)
Accept 0.002 with working
0.020
Amount of H2O= 18
= 0.0011 (mol) 3
Amount of C = 0.0022 mol = 0.0265(g)
Amount of H = 0.0022 mol = 0.0022(g)
st
Any one of above needed for 1 mark (1)
Mass of O in Z = 0.0714 (g)
OR amount of O in Z = 0.0045 (mol)
Some clear indication they have done it correctly (1)
Empirical formula CHO2 (1)
(ii) (CHO2)y = (12 + 1 + 2 × 16)y = 90
Y=2
Molecular formula C2H2O4
Allow TE from (i)
Allow C2H2O4 with no working
Allow any indication they know how to do it
eg ‘n × empirical mass = molar mass’ 1
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Reject C4H10O only (no connection with (i))
20.0 1.00
(iii) (0.01 mol Z contain 1000 =) 0.02 (mol) (1)
Accept formula alone for Z
CO2H
|
CO2H (1) 2
Accept fully/partially displayed formula
(iv) W CH2=CH2 (1)
X CH2BrCH2Br (1)
Y CH2OHCH2OH (1)
Look out for TE and internal TE
Eg W CH3CHCH2
X CH3CHBrCH3
Y CH3CHOHCH3
is worth 1 max 3
Accept full credit for consistent answers based on other gaseous
alkenes eg CH3CHOHCH2OH etc
(v) C20H42 C18H38 + C2H4 (1)
Allow C17H36 + C3H6 OR C16H34 + C4H8 1
Accept TE for W
Accept any balanced equation including ethane
(b) Potassium manganate((VII))/KMnO4 (1)
Sulphuric acid/H2SO4 consequential on potassium manganate (1)
ALLOW ‘acidified potassium manganate((VII))’ for both marks 2
Accept TE for W alkene and corresponding monohydric alcohol
1. H2SO4/sulphuric acid
2. H2O/water
Reject other Roman numerals after managate
[12]
24. (a) (i) 2-bromobutane
the “2” must be in front of “bromo”
Ignore punctuation and capitals 1
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + KOH → CH3CHOHCH2CH3 + KBr
OR
– –
CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + OH → CH3CHOHCH2CH3 + Br 1
Accept C2H5 instead of CH2CH3
+
Allow K as spectator ion
Reject eqns with NaOH
(iii) water / H2O / aqueous ethanol 1
Accept C2H5OH (aq) / aqueous alcohol/KOH(aq)/aqueous
Do not penalise use of NaOH(aq) again
Reject just “ethanol / ethanolic / alcoholic (KOH)”
(iv) nucleophilic substitution (both needed) 1
Accept reasonable phonetic spelling
– –
(b) (i) CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + OH → CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2O + Br
OR
– –
CH3CHBrCH2CH3 + OH → CH2=CHCH2CH3 + H2O + Br
Double bond need not be shown 1
Accept C2H5 instead of CH2CH3
Ignore spectator ions
(ii) Ethanol / C2H5OH / CH3CH2OH /
H H
H C C OH
H H 1
Accept alcohol OR Ethanolic/alcoholic
Accept KOH/NaOH
Reject C2H6O
Reject any mention of water/aqueous
(iii) elimination
ignore “nucleophilic” 1
Reject electrophilic elimination
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(c) (i) 1
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 H
C C C C
H H H CH 3
bond to H of CH3 on left carbon
structure with 90° bond angles
(c) (ii) no / restricted rotation around double
bond / C=C /π – bond (1)
has two different groups joined to
each C (of double bond) OR each (carbon of C=C) has a CH 3
and a H (1) 2
limited rotation
on the carbon
(d) (i) nickel / Ni
OR platinum / Pt
OR palladium / Pd 1
(d) (ii) butane / CH3CH2CH2CH3 1
C2H5 for CH3CH2
JUST “C4H10”
[12]
25. (a) (i) (Concentrated) sulphuric acid/H2SO4 (1)
Water/H2O (1)
Any order 2
Accept phosphoric acid
1 HBr 2 NaOH/KOH (2)
H2SO4 + NaOH/KOH (1max)
H2O and high T and P and catalyst (1 max)
Reject dilute/aq sulphuric acid
H2SO4 + Na2Cr2O7 (0)
H2O alone (0)
H2O + × (eg H2O2) (0)
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) Butan(e) -1,2-diol 1
Ignore punctuation
1,2-butan(e)diol
1,2-dihydroxybutane
Reject buta-1,2-diol
Reject but-1,2-diol
Reject 1,2-diolbutan(e)
Reject any formula
(iii) 1,2-dibromobutane 1
Ignore punctuation
Reject any formula
(iv) Hydrogen bromide/HBr
Ignore (aq) 1
Accept KBr + H2SO4/H3PO4
Accept any other metal
Accept bromides
(b) Two reactants come together to make one product 1
Accept one reagent added across double bond
Accept use judgement but in general look for ‘two…become
one’
Accept ‘two or more reactants give one product’
Reject ‘adding 1 atom’
Reject just ‘unsaturated becomes saturated’
Reject just ‘the double bond breaks’
Reject ‘2 molecules are joined’
(c) (i) A species/molecule/ion with a space for/which can accept (a pair of)
electrons (to make a dative covalent bond) 1
Accept an electron deficient entity
Accept electron deficient ion
Reject just ‘a lover of negative charge’
Reject positive ion
Reject electron deficient element
δ+ δ– δ+
(ii) Br – Br / Br 1
+
Accept Br
Be generous on symbols for delta
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
Reject Br2
(d) (i) Reaction 2 1
Reject two answers
(ii) Oxidation number of carbon increases
or
oxygen is added (to the organic compound) 1
Reject loss of electrons alone / loss of electrons and addition of
oxygen
(e) (i) Butane/CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 1
Accept displayed formulae
Accept C2H5 instead of CH3 CH2
Reject C4H10
(ii) Hydrogen (1)
Nickel (1) 2
Accept H2
Accept Ni
Accept platinum/Pt or palladium/Pd
Reject H
(iii) Chlorine (1)
UV/ultraviolet/sunlight (1) 2
Accept Cl2
Accept visible light
Reject just ‘light’
[15]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
26. (a) (i) Any two of
• (same) general formula
Accept (Same) general molecular formula
Reject (Same) molecular formula
• (successive) members differ by CH2
• (same) functional group/ (similar/same) chemical
properties/reactions
• regular trend in physical properties
Reject same physical properties
Reject reference to a specific reaction e.g. same reaction with
chlorine
IGNORE “same properties” 2
(ii) alkene(s) 1
Reject C=C
Reject alkane
(iii) electrophilic addition (1) both needed
IGNORE heterolytic and penalise homolytic
hydrogen chloride/HCl (1) 2
Reject (Dilute) hydrochloric acid/dilute HCl /HCl(aq)
(b) same molecular formula (1)
Accept same numbers of each atom
different structural formulae/displayed formulae/
arrangement of atoms (1) 2
Accept different structure
Reject different arrangement in space
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(c) 1-bromopropane faster (1)
Stand alone
Accept reverse statement
Any answer which gives 1-chloropropane as faster scores zero
overall
because C–Br bond weaker (than C–Cl) (1)
Accept reverse argument
Reject if no reference to carbon-halogen bond
IGNORE attempted explanations of why C–Br bond weaker
therefore lower activation energy/Eact (1)
[Lower Eact must be related to C–X bond] 3
Accept reverse argument
(d)
H H
C C
CH 3 Cl
2 carbon chain with continuation bonds in repeat unit (1)
All other atoms correct (1)
IGNORE subscript n
IGNORE where the bond to the CH3 goes e.g.
CH3 is fine 2
If more than one repeat unit given and number of repeat units
stated or the repeat unit identified (2)
nd
If repeat unit not stated or identified can score 2 mark only
Reject 3 carbon chain
Or
Any repeat unit containing a double bond scores zero
(e) Restricted rotation around double bond (1)
Accept no rotation/double bond cannot rotate (at room
temperature)
1-chloropropene has two different groups on both carbons/each
carbon (in the double bond)(but propene does not) (1) 2
Accept propene has two identical groups on one carbon (of the
double bond) (but 1-chloropropene does not)
[14]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
27. (a) C 1
(b) D 1
(c) A 1
(d) D 1
[4]
28. (a) A 1
(b) C 1
[2]
29. B
[1]
30. C
[1]
31. (a) (i)
(1) Intermediate
H H H H H H H H H
C C C H H C C C H H C C C H
H +
H H H H Br H
H
Br Br–
(1) for curly arrow
(1) for two curly arrows 3
Reject inaccurate placing of curly arrows
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
Topic 2 – Organic Chemistry (Questions)
(ii) The secondary carbocation/carbonium ion is more stable
+
than the primary (so forms when H adds)
OR
The secondary carbocation/carbonium ion is
stable because the methyl groups are electron donating 1
(iii) 2-bromopropane 1
(b) Acidified potassium manganate(VII) / potassium
permanganate / KMnO4((aq)) 1
(c)
H H
n (C H 2 = C H C H 3 ) C C
n
HH C H
H
balanced and double bond broken (1)
CH3 on side chain (1) 2
Reject CH3 in unbranched chain
(d) Poly(propene) is non-biodegradable / won’t break down in wet conditions (1) 1
(e) (i) propagation 1
(ii) C6H14 / hexane /
Structural, displayed or skeletal formulae of hexane 1
[11]
As Chemistry - Paper 1 hakimabbas31site
You might also like
- Ligand Coupling Reactions with Heteroatomic CompoundsFrom EverandLigand Coupling Reactions with Heteroatomic CompoundsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CHM1 Organic3Document72 pagesCHM1 Organic3Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Organic QDocument20 pagesCHM1 Organic QGM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature 3 QPDocument11 pagesNomenclature 3 QPklaksmanan1No ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument14 pagesCombinepdfBee Jay JayNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocument11 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksAlia ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Chapters 22-26 Past Papers QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapters 22-26 Past Papers QuestionsHehe Haah100% (1)
- Topic 7 TestDocument11 pagesTopic 7 Testab9652378No ratings yet
- June 2003Document8 pagesJune 2003paolo maldiniNo ratings yet
- Compounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsDocument69 pagesCompounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsmarvellousadenugaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanisms 4 QPDocument9 pagesReaction Mechanisms 4 QPklaksmanan1No ratings yet
- Halogenalkanes Elimination and OzoneDocument88 pagesHalogenalkanes Elimination and Ozone22S48 SUNDARAM RAMASUBBU RAKSHANo ratings yet
- 3.3.4 Alkenes FullDocument39 pages3.3.4 Alkenes FulllfcluishoughtonNo ratings yet
- Isomerism 2 QPDocument9 pagesIsomerism 2 QPPragna AnanthNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions For 2.8 Haloalkanes 1Document18 pagesExtra Questions For 2.8 Haloalkanes 1Younes AlahmadNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Assessed HomeworkDocument13 pagesTopic 1 Assessed HomeworkBest ProgressNo ratings yet
- WS 4 (18.07.22)Document4 pagesWS 4 (18.07.22)Micheelle JeannethNo ratings yet
- Halogenoalkanes Alcohol and Spectra Unit 2Document8 pagesHalogenoalkanes Alcohol and Spectra Unit 2Barminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Practice TestDocument7 pagesTopic 7 Practice Test5IB12 GANGWANI LAKSHMI AJAYNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1a N C Principles of Chemistry State of Matter Atoms Atomic StructureDocument25 pagesChemistry 1a N C Principles of Chemistry State of Matter Atoms Atomic StructuresechosNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanisms 3 QPDocument7 pagesReaction Mechanisms 3 QPSiti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 HWDocument14 pagesTopic 7 HWShirmara Pile-fordeNo ratings yet
- Y13 Biology Christmas Exam TechniqueDocument35 pagesY13 Biology Christmas Exam TechniqueSimon AwberyNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Qualitative ChemistryDocument216 pagesCHM1 Qualitative ChemistryHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Structure TestDocument10 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Structure TestJuiloNo ratings yet
- Q1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeDocument56 pagesQ1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeZaksd100% (1)
- IB Set 4 Topic 2Document4 pagesIB Set 4 Topic 2DaNo ratings yet
- Cells-Microscopes-Cell-Cycle-and-Immunity-Questions GRADE 12 HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENTDocument36 pagesCells-Microscopes-Cell-Cycle-and-Immunity-Questions GRADE 12 HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENTAsha justin joseph100% (1)
- Atp QPDocument10 pagesAtp QPJainam MehtaNo ratings yet
- A2 Organic Book 1 2020Document231 pagesA2 Organic Book 1 2020bookworm12045No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Assessed HomeworkDocument13 pagesTopic 1 Assessed Homeworksteve jobsNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.3 Particles Antiparticles and PhotonsDocument34 pages3.2.1.3 Particles Antiparticles and Photonsmax.duxburyNo ratings yet
- Chem Mock Test IG A Paper I (2023)Document18 pagesChem Mock Test IG A Paper I (2023)pyae157163No ratings yet
- A-Level Paper 2 pp1Document20 pagesA-Level Paper 2 pp1Amaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Kinetics ExamproDocument33 pages1.5 Kinetics Examproannonymous oneNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 WorksheetDocument7 pagesTopic 1 WorksheetBhaswati BharNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Assessed HWDocument5 pages2.8 Assessed HWlilaNo ratings yet
- 3.3.3 Halogenoalkanes FullDocument41 pages3.3.3 Halogenoalkanes FulllfcluishoughtonNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomerism QDocument8 pagesStereoisomerism Q장채윤No ratings yet
- Alkene Extra Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlkene Extra Exam QuestionsJenessaNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Particle Physics - 2Document12 pages4.5 Particle Physics - 2Mozammel AnowarNo ratings yet
- AS Level Topic 6A TestDocument14 pagesAS Level Topic 6A TestMorvan BarnesNo ratings yet
- IAS Chemistry Atomic Structure Question Bank and MSDocument32 pagesIAS Chemistry Atomic Structure Question Bank and MSAthenaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionDocument23 pagesMixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionYaakkwNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Biology - Year 10Document24 pagesPractice Questions - Biology - Year 10thomasNo ratings yet
- Practice Examination Questions For 1.6 Alkanes (Includes Some Questions From 1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistry)Document12 pagesPractice Examination Questions For 1.6 Alkanes (Includes Some Questions From 1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistry)Маша ЖуковскаяNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Structure & Bonding QDocument115 pagesCHM1 Structure & Bonding QGoutham SivagnanamNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocument10 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Edexcel IGCSEDocument32 pagesChemistry: Edexcel IGCSEkianloongtNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Document20 pagesA-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Jesus ChristNo ratings yet
- 10 -შემაჯამებელი -1alfaDocument9 pages10 -შემაჯამებელი -1alfaPresident David MattheinouNo ratings yet
- Organic RevisionDocument6 pagesOrganic RevisionEllson LinNo ratings yet
- B.2 QPDocument4 pagesB.2 QPYuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet (Topic - Plants and Food)Document22 pagesWork Sheet (Topic - Plants and Food)ananafra861No ratings yet
- Particle Physics QuestionsDocument8 pagesParticle Physics QuestionsMartinNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Mechanical Systems: Structural ElementsFrom EverandModelling of Mechanical Systems: Structural ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Homogenization of Coupled Phenomena in Heterogenous MediaFrom EverandHomogenization of Coupled Phenomena in Heterogenous MediaNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Transition Metal Chemistry: Molecules, Supramolecular Assemblies and MaterialsFrom EverandChirality in Transition Metal Chemistry: Molecules, Supramolecular Assemblies and MaterialsNo ratings yet
- moleProblemsWkst PDFDocument2 pagesmoleProblemsWkst PDFChong Xue ErNo ratings yet
- WS15 Calculating Moles Mass and MR Bronze Activity SheetDocument4 pagesWS15 Calculating Moles Mass and MR Bronze Activity SheetHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS14 Net Ionic Equation WorksheetDocument1 pageWS14 Net Ionic Equation WorksheetHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS15C Moles Solutions Practice Questions 2Document1 pageWS15C Moles Solutions Practice Questions 2Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WSBalancing21 PDFDocument2 pagesWSBalancing21 PDFkeenahbernadette100% (1)
- Moles PacketDocument11 pagesMoles PacketCaslyn Campbell0% (1)
- Stoichiometry-Chemical Equations: Part A: Write Balanced Chemical Equation For Following Word EquationsDocument2 pagesStoichiometry-Chemical Equations: Part A: Write Balanced Chemical Equation For Following Word EquationsFoxy world 152No ratings yet
- WS5 Mole Calculation Practice MassDocument2 pagesWS5 Mole Calculation Practice MassHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS15C Moles Solutions Practice Questions 2Document1 pageWS15C Moles Solutions Practice Questions 2Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS9 Moles, ReactionsDocument1 pageWS9 Moles, ReactionsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Compound Names and Formulas Tutorial and WorksheetDocument20 pagesCompound Names and Formulas Tutorial and Worksheetapi-262326666100% (1)
- Worksheet Chemistry Calculations ks4Document5 pagesWorksheet Chemistry Calculations ks4Chaterine AdiwinotoNo ratings yet
- WS8 Moles, Molecules and GramsDocument2 pagesWS8 Moles, Molecules and GramsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS15G Moles Practice Questions 3Document1 pageWS15G Moles Practice Questions 3Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Moles Worksheet: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesMoles Worksheet: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedJon KlementNo ratings yet
- 5.electricity and Chemistry PDFDocument15 pages5.electricity and Chemistry PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- WS3 Chemical Equations OldDocument2 pagesWS3 Chemical Equations OldHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 3.atoms, Elements and Compounds - QPDocument40 pages3.atoms, Elements and Compounds - QPHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- WS5 Mole Calculation Practice Mass MsDocument2 pagesWS5 Mole Calculation Practice Mass MsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Anic Chemistry QPDocument78 pagesAnic Chemistry QPHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry-Chemical Equations: Part A: Write Balanced Chemical Equation For Following Word EquationsDocument2 pagesStoichiometry-Chemical Equations: Part A: Write Balanced Chemical Equation For Following Word EquationsFoxy world 152No ratings yet
- 6.chemical Changes QPDocument25 pages6.chemical Changes QPHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 12 Sulfur PDFDocument3 pages12 Sulfur PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Anic Chemistry PDFDocument30 pagesAnic Chemistry PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Table of Contents-ChemDocument1 page0.1 Table of Contents-ChemHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 4 Stoichiometry PDFDocument8 pages4 Stoichiometry PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Force - Scalars & VectorsDocument10 pages3.4 Force - Scalars & VectorsHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 10 ElectricityDocument26 pages10 ElectricityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 6.1 States of MatterDocument11 pages6.1 States of MatterHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- LightDocument12 pagesLightHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 22 Feb Goc 1 - OneDocument19 pages22 Feb Goc 1 - OneShreyaNo ratings yet
- HGJJHDocument4 pagesHGJJHsugindavidrajNo ratings yet
- Redox Polymerization: A.S. SaracDocument56 pagesRedox Polymerization: A.S. SaracJavier David Ruiz GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Chapter No. 1Document11 pagesNtroduction: Chapter No. 1Noman AslamNo ratings yet
- Alkane Dehydrocyclization MechanismDocument74 pagesAlkane Dehydrocyclization MechanismStefany CNo ratings yet
- KIMED - HSA ANALGESIKvDocument21 pagesKIMED - HSA ANALGESIKvKuni RofiatyNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of BenzeneDocument11 pagesNomenclature of BenzeneNajwa ZhafiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Chemical Principles and Applications Ii Module 1: The Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsDocument23 pagesUnit 2: Chemical Principles and Applications Ii Module 1: The Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Organic Acids From Fermentation BrothsDocument20 pagesRecovery of Organic Acids From Fermentation BrothsLCteyNo ratings yet
- Alkene - Alkynes 1Document39 pagesAlkene - Alkynes 1Hajar MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon-05-Assignments (New)Document20 pagesHydrocarbon-05-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Class 11 Che CH 12Document12 pagesNcert Sol For Class 11 Che CH 12KishoreNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDocument20 pagesReduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDhewi LayNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Crash Reviewer PDFDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Crash Reviewer PDFmaganda akoNo ratings yet
- By R. K. Malik by R. K. Malik by R. K. Malik by R. K. MalikDocument7 pagesBy R. K. Malik by R. K. Malik by R. K. Malik by R. K. Malikshubham vithalkarNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Information Engineering (Eie) : Staff ListDocument32 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Information Engineering (Eie) : Staff ListtemitopefunmiNo ratings yet
- Types of Fatty AcidDocument3 pagesTypes of Fatty AcidDrbee10No ratings yet
- Group Transfer Polymerization: ConceptDocument7 pagesGroup Transfer Polymerization: Conceptcuongtran_siegenNo ratings yet
- MEK IntroductionDocument4 pagesMEK IntroductionEllie Rose Aple BanawaNo ratings yet
- LANXESS - Bitterfeld - HQC (Sertifikat Halal)Document3 pagesLANXESS - Bitterfeld - HQC (Sertifikat Halal)Widiyanto Dwidie PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 13 - Esters88Document4 pagesLecture Notes 13 - Esters88Surendra RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- MCAT Molecules List 1.1Document6 pagesMCAT Molecules List 1.1Rania AbdusamadNo ratings yet
- Lead Acetate TestDocument1 pageLead Acetate TestLea Angela Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Amination by ReductionDocument43 pagesAmination by ReductionShreyashNo ratings yet
- Use of Functionalized Poly (Ethylene Glycol) S For Modification of PolypeptidesDocument24 pagesUse of Functionalized Poly (Ethylene Glycol) S For Modification of PolypeptidesFranciscoNo ratings yet
- The Molecules of LifeDocument13 pagesThe Molecules of LifeZen Garcia100% (1)
- Lucas TestDocument9 pagesLucas Testcleahis cruz100% (1)
- Review Article The Thiol-Ene (Click) Reaction For The Synthesis of Plant Oil Derived PolymersDocument14 pagesReview Article The Thiol-Ene (Click) Reaction For The Synthesis of Plant Oil Derived PolymersAdnanNo ratings yet
- Enol ContentDocument13 pagesEnol Contentsally gomaa100% (2)
- Flammability Characteristics of Common Gases and LiquidsDocument1 pageFlammability Characteristics of Common Gases and LiquidsNeme VasquesNo ratings yet