Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellular Respiration 2
Uploaded by
Naledi Noxolo Bhengu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesOriginal Title
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesCellular Respiration 2
Uploaded by
Naledi Noxolo BhenguCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Cellular Respiration
Identify Main Ideas What You’ll Learn
■ the role of electron carriers in cellular
As you read, underline or
respiration
highlight the main ideas in ■the difference between alcoholic
each paragraph. fermentation and lactic-acid
fermentation
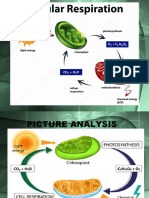
Overview of Cellular Respiration
Organisms get energy through cellular respiration.
Electrons from carbon compounds such as glucose are collected, and the energy is used to make
ATP.
ATP is used by cells. The equation for respiration, shown below, is the
opposite of the equation for photosynthesis.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ➞ 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis, a process in which glucose is broken down into
pyruvate. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not need oxygen.
Glycolysis is followed by aerobic processes, which require
the presence of oxygen. During aerobic respiration, pyruvate
is broken down and ATP is made. Aerobic respiration occurs
in two parts: the Krebs cycle and electron transport.
Glycolysis
During glycolysis, two phosphate groups are joined to glucose, using two molecules of ATP. The
6-carbon molecule is then broken down into two 3-carbon compounds. Two phosphates are
added, and electrons and protons combine with two NAD+ molecules to form two NADH
molecules.
The two 3-carbon molecules are changed into two molecules of pyruvate. Four molecules of ATP
are made.
1-Answer the following questions.
a.The process by which glucose is converted to pyruvate is ……………..
b. Which organisms do glycolysis?.............................
c. What are reactants of glycolysis?.......................&…………………….
d. At end of glycolysis glucose is converted to…………………….
e. How many ATP molecules does glycolysis YIELD?..............
f. Where does glycolysis take place in the cell?........................
Krebs Cycle
Next, the pyruvate, made during glycolysis, is transported into the mitochondria. There
it is converted into carbon dioxide in a series of reactions called the Krebs cycle.
What are the steps of the Krebs cycle?
Before the pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle, it reacts with coenzyme A (CoA) to form a 2-
carbon intermediate called acetyl CoA. Carbon dioxide is released, and NAD is changed
to NADH. Acetyl CoA then moves to the mitochondria, where it combines with a 4-
carbon molecule to form citric acid. Citric-acid is then broken down, releasing two
molecules of carbon dioxide and making one ATP, three NADH, and one FADH2.
Acetyl CoA and citric acid are made, and the cycle continues. Two pyruvate molecules
are made during glycolysis, resulting in two turns of the Krebs cycle for each glucose
molecule.
2-Complete the figure by writing the location of each stage of cellular
respiration.
5-Answer the following questions.
a.In the Krebs cycle, what is pyruvate converted to?.....................................
b. How many ATP molecules are gotten from cellular respiration?.............
c. Which step of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP?......................
d. What are the reactants of cellular respiration?.......................&…………….
e. What are the products of cellular respiration?............, …………….&…………..
f. Where does Krebs cycle take place?.....................................
g. electron transport chain takes place along………………………………………..
h. The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis use the high-energy
.……………………electrons to produce
i. NAD+ is ……….. carrier in cellular respiration.
Do prokaryotes use cellular respiration?
Some prokaryotes also undergo aerobic respiration.
Since they have no mitochondria, electron transport occurs in the cellular membrane instead.
Pyruvate does not move to mitochondria, saving the prokaryotic cell two ATP. Prokaryotes make
38 molecules of ATP from one molecule of glucose.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration takes place when oxygen is low. Some prokaryotes that do not need oxygen
use anaerobic respiration all the time. Other cells use anaerobic respiration when
oxygen levels are low.
How does ATP store energy?
ATP is the most abundant energy-storing molecule. It is found in all kinds of organisms. The
structure of ATP is shown below. It is made of an adenine base, a ribose sugar,
and three phosphate groups. ATP releases energy when the bond between the second and third
phosphate groups is broken, forming a molecule called adenosine diphosphate (ADP). ADP can be
changed back into ATP by adding a phosphate group.
How is ATP made during anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration, or fermentation, follows glycolysis when oxygen is absent. Glycolysis
makes two ATP from each glucose molecule.
Fermentation makes a small amount of ATP and regenerates the cell’s supply of NAD_ so
glycolysis can continue.
Two important types of fermentation are lactic-acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation.
What are the types of fermentation?
Lactic-acid fermentation changes pyruvate into lactic acid.
It takes place in skeletal muscle cells during strenuous exercise, when the body cannot supply
enough oxygen. It is also used to make foods like cheese, yogurt, and sour cream.
Yeast and some bacteria undergo a type of fermentation known as alcohol fermentation. These
organisms use pyruvate to make ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
6.Answer the following questions.
a. The release of energy from food molecules in the absence of oxygen is ……….respiration.
b. What is the name for the anaerobic breakdown of glucose?........................
c. many ATP molecules do you get from anaerobic respiration?.....................................
d. What are the two main types of fermentation?.......................&……………………….
e. What is the purpose of fermentation?.............................................................................
f. What kind of organism performs alcoholic fermentation?........................
g. Where does lactic acid fermentation occur in animals?................................
h. What substance is given off during alcoholic fermentation?.............................
i. What kind of fermentation do animal cells do if oxygen is not available?...................
Done by:……………………………………………….
Class:11/……………………………
Make a three-tab Venn diagram Foldable from one sheet of paper to
compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
You might also like
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration G2 1Document5 pagesCellular Respiration G2 1tibigarcarizaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Q2 ELS L4 Cellular RespirationDocument30 pagesQ2 ELS L4 Cellular RespirationJoshNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesCellular RespirationGwen SteffanyNo ratings yet
- Notes CELLULAR RESPDocument6 pagesNotes CELLULAR RESPela ravenaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideDocument7 pagesAP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideVal HathiramaniNo ratings yet
- 8 3Document22 pages8 3lianneNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument19 pagesGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Katriel Ziv Batutay - Refective QuestionsDocument2 pagesKatriel Ziv Batutay - Refective QuestionsKatriel Ziv LasNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Gen Bio 1 Week 2Document12 pages2nd Quarter Gen Bio 1 Week 2Jonela BesaresNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDJ ISAACS25% (4)
- How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy: Chapter ObjectivesDocument12 pagesHow Cells Harvest Chemical Energy: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesCampbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manualkevinrodriguezcnytfpaskx100% (23)
- Ebook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesEbook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (13)
- Gen Bio W3-5Document9 pagesGen Bio W3-5Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Introduction To Cellular RespirationDocument14 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To Cellular Respirationbabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Study Guide 2015Document7 pagesCH 9 Study Guide 2015dickbeater73No ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 13 To 15: Energy TransformationDocument8 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 13 To 15: Energy Transformationkent ignacioNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Ange EeeeeDocument4 pagesAnge EeeeeHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Introduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. CycleDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. Cycleمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Biology - Respiration in PlantsDocument13 pagesClass 11 - Biology - Respiration in PlantsDivyansheeNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular RespirationJethroNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document6 pagesQ2 Module 5joseantoniolcastro408No ratings yet
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Document14 pagesLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Andre NesbethNo ratings yet
- Reading Material - Cellular-RespirationDocument7 pagesReading Material - Cellular-RespirationechaNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Lesson 5.4 and 5.5 How Organisms Obtain and Utilize Energy Organisms Require Energy To Carry Out Functions Required For LifeDocument33 pagesLesson 5.4 and 5.5 How Organisms Obtain and Utilize Energy Organisms Require Energy To Carry Out Functions Required For Liferandyturajr21No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ExplanationDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Explanationvestermail50% (2)
- PS and CRDocument34 pagesPS and CRErika MatiasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis TEST REVIEWDocument2 pagesANSWERS Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis TEST REVIEWGen Li Togy100% (3)
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition Starr Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition Starr Solutions Manual DownloadGraham Hissem100% (24)
- Biochemical Pathways: Chapter 6 and 7 From Text BookDocument46 pagesBiochemical Pathways: Chapter 6 and 7 From Text BookSnehal SinghNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint To Accompany Concepts in Biology: Twelfth Edition Enger - Ross - BaileyDocument24 pagesPowerpoint To Accompany Concepts in Biology: Twelfth Edition Enger - Ross - BaileyAndika HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDocument4 pagesMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesCellular Respiration NotesSwayam SakpalNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument100 pagesRespirationColin RiddellNo ratings yet
- Revision Session 2011Document11 pagesRevision Session 2011glenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Cellular RespirationDocument57 pagesCellular RespirationAlyana Grace GuquibNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell EnergyDocument4 pagesWorksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell Energyclaryl alexaNo ratings yet
- 7e's - Cellular RespirationDocument5 pages7e's - Cellular RespirationVea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 7Document4 pagesBiology Class 7Jon Williams100% (4)
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Unit Five Last One Grade 11 Biology Energy TransformationDocument55 pagesUnit Five Last One Grade 11 Biology Energy TransformationaxumfunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Cellular RespirationCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationDocument2 pagesC6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationHarleen BalNo ratings yet
- Biology Anual Exam Detailed Answer PDFDocument12 pagesBiology Anual Exam Detailed Answer PDFAnsha NasarNo ratings yet
- Hope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessDocument11 pagesHope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessMark Johnson San JuanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 00 Burl U of TDocument612 pagesGeneral Biology 00 Burl U of TAndreiClaudiuNo ratings yet
- UW Infectious Diseases + Microbiology Educational Objectives PDFDocument75 pagesUW Infectious Diseases + Microbiology Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- Molecular Classification of Breast CancerDocument9 pagesMolecular Classification of Breast CancerKarlaMaldonadoMonsalveNo ratings yet
- Congenital Nephrotic SyndromeDocument44 pagesCongenital Nephrotic Syndromeaad81kolrenmed50% (2)
- Malaria JournalDocument8 pagesMalaria JournalArmaina TanjungNo ratings yet
- 3 Agarose Gel Electrophoresis & Ames TestDocument4 pages3 Agarose Gel Electrophoresis & Ames TestNurulNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Endemicity of Chilimo Forest, Central EthiopiaDocument4 pagesDiversity and Endemicity of Chilimo Forest, Central Ethiopiaasmeraamde21No ratings yet
- Marocmolecule Review Worksheet - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesMarocmolecule Review Worksheet - Answer KeyBecka RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PowernotesDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom Powernotessheikhanzar643No ratings yet
- Making DNADocument5 pagesMaking DNADaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Rev Ahara PakaDocument5 pagesRev Ahara PakaMSKCNo ratings yet
- Abstractbook Nsctls-2021 FinalDocument141 pagesAbstractbook Nsctls-2021 Finalijarbn editorNo ratings yet
- Technical Session 6 11.00 AM-1.00 PM: Consolidation and Compendium PreparationDocument2 pagesTechnical Session 6 11.00 AM-1.00 PM: Consolidation and Compendium PreparationkarpanaiNo ratings yet
- BIOCONDocument11 pagesBIOCONAravind SairamNo ratings yet
- BCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20Document31 pagesBCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20AmyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Biological Molecules: at The End of The Lesson, You Are Expected ToDocument4 pagesStructure and Functions of Biological Molecules: at The End of The Lesson, You Are Expected ToFrancinne MartinNo ratings yet
- Zoogeographical DistributionDocument17 pagesZoogeographical DistributionSoumya Ranjan SwainNo ratings yet
- Health - Diabetes Research PaperDocument7 pagesHealth - Diabetes Research Paperapi-299727107No ratings yet
- Plant Structure Lab Report 3 PDFDocument4 pagesPlant Structure Lab Report 3 PDFVermilah Ann Despi67% (6)
- GEd 109 BiodiversityDocument30 pagesGEd 109 BiodiversityArisNo ratings yet
- Using BioeditDocument3 pagesUsing BioeditHanna KaruniaNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 823) Stacy M. Cowherd (Auth.), Virginia Espina, Lance A. Liotta (Eds.) - Molecular Profiling - Methods and Protocols (2012, Humana Press)Document462 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 823) Stacy M. Cowherd (Auth.), Virginia Espina, Lance A. Liotta (Eds.) - Molecular Profiling - Methods and Protocols (2012, Humana Press)ashutosh pandey100% (1)
- IB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionDocument19 pagesIB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionikaNo ratings yet
- BhilawaDocument12 pagesBhilawaSurendra Kumar SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- GCSE Week 09 InheritanceDocument36 pagesGCSE Week 09 InheritanceFrankie BarnesNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The WIV Databases That Were Taken OfflineDocument26 pagesAn Investigation Into The WIV Databases That Were Taken OfflineDrastic ResearchNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTDocument8 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTavik sadhuNo ratings yet
- v4n2 9pdfDocument10 pagesv4n2 9pdfissaninNo ratings yet