Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23 Hints and Solutions
Uploaded by
Light MayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Matrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23 Hints and Solutions
Uploaded by
Light MayCopyright:
Available Formats
MATRIX SCIENCE ACADEMY
Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23
Time : 60 Min Chem : Groupwise Paper Marks : 50
Hints and Solutions
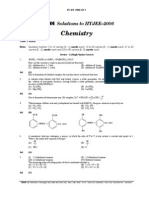
01) Ans: D) both (a) and (b) therefore, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Sol: Carbinol is CH3OH. Hence, ethanol
CH3 CH2 OH is called methyl carbinol
02) Ans: D) 7
Sol: Since the solution is acidic, pH < 7. This is 2
For the complex ion Ni CN4 , In the complex
because [H ] from H2O [107 ] cannot be
2
neglected in comparison to 1012 M. ion Ni CN4 , there are four CN ligands
which are strong field ligands.
03) Ans: A) C2O24 Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
Sol: C2O24 Ni28 4s2 3d8 Ni2 3d8 .
The hybridisation involved is dsp3 and the
04) Ans: A) Ammoniacal silver nitrate complex ion is square planar with no unpaired
electrons therefore it is diamagnetic in nature.
05) Ans: A) neutral Figure
06) Ans: D) one secondary and two primary OH 12) Ans: C) CsOH
groups. Sol: C5OH is strong base undergoes complete
CH2 OH
ionization.
|
Sol: C H OH
| 13) Ans: A) Current
CH2 OH Sol: Current has no effect the degree of ionization.
i.e. one secondary and two primary alcoholic
14) Ans: C) C2H5OH
groups.
Sol: C2H5OH
07) Ans: B) salicylic acid.
15) Ans: D) anomeric carbon
2
c
08) Ans: C) K a 16) Ans: B) 1.0 m
1
Sol: This is the mathematical form of Ostwald's [salt]
Sol: pOH pKa log
dilution law. [Acid]
[Salt] [salt]
09) Ans: B) acetic acid. 5.5 4.5 log log 5.5 4.5 1
K Cr O 0.1 0.1
Sol: CH3CH2OH
2 2 7
CH3COOH
[salt]
i.e. antilog 1 10 [salt] 1
0.1
10) Ans: B) B2H6 and alkaline H2O2
Sol: Hydroboration oxidation i.e. industrial 17) Ans: C) primary alcohol.
preparation of alcohol is as Sol:
1 Dry
3CH3CH CH2 B2H6 (CH3CH2CH3 )3 B
2 ether
HO
(CH3CH2CH3 )3 B
2 2
3CH3CH2CH2 OH
11) Ans: B) 2,0
Sol: In the complex ion NiCl4
2
, the oxidation 18) Ans: C) 4
state of Ni is + 2.
19) Ans: B) amminepentachloroplatinate (IV) ion
Ni28 4s2 3d8 Ni2 3d8
The hybridisation involved is sp3 and the complex 20) Ans: A) Water
ion is tetrahedral. It has two unpaired electrons,
JEE-MAIN, MHT-CET, NEET/AIPMT, MHT-CET-XI - New Syllabus (MH)
MATRIX SCIENCE ACADEMY
Sol: H2O H OH 34) Ans: D) K4 Ni CN2 (Ox)2
Acid
[Acid because of donation of proton] Sol: K4 Ni CN2 (Ox)2 by IUPAC rule.
H2O H H3O
Base
35) Ans: B) glucosidic linkage
[Basic because of gaining of proton]
36) Ans: C) sp3
21) Ans: C) sp3d2
Sol: sp3
Sol: [CoF6 ]3 is an outer complex containing
sp3d2 hybridisation. 37) Ans: D) 4 105
Sol: c = 0.1, 0.02
22) Ans: D) CH3CHOHCH3
Kb 2.c 0.1 4 104 4 105
Sol: CH3CHOHCH3
38) Ans: B) 8 103
23) Ans: B) H2SO4 , HSO4
Sol: HgSO4 of Ksp S2 S Ksp
Sol: Here, H2SO4 H HSO4
i.e. S 6.4 105 8 103 m/l
24) Ans: A) dyes.
Sol:
39) Ans: B) Ag CN2
Sol: EAN rule states that for a stable complex the
EAN - atomic number of noble gas. If not so, the
complex does not follow EAN rule. The EAN values
for the given four complex ions are as follows.
4
(a) Fe CN6 : Fe26 ,Fe2 24 electrons, 6CN
25) Ans: A) triammine diaquachloro cobalt (III)
chloride. ligands contributing 6 2 12 electrons
Sol: From IUPAC rule. EAN = 24 + 12 = 36 (At. No. of Kr).
(b) Ag CN2 : Ag 47 , Ag 46 electrons. 2CN
26) Ans: B) basic a mino acid
Sol: Out of two lone pairs of electrons on two ligands contributing 2 2 4 electrons
nitrogen atoms, one is involved in Resonance and EAN = 46 + 4 = 50 (Not At. No. of any noble gas).
the other is available for protonation therefore Does not follow EAN rule
Histidine is a basic a mino acid. 3
(c) Co NH3 6 : Co27 ,Co3 24 electrons 6NH3
27) Ans: B) 6.3 103 ligands contributing 6 2 12 electrons
EAN = 24 + 12 36 (At. No. of Kr
Sol: Here, Ksp 4s3 2
(d) ). PtCl6 : Pt78 ,Pt4 74 electrons. 6Cl
Ksp 6
1.0 10
S 3 3 S 6.3 103 ligands contributing 6 2 12 electrons.
4 4 EAN = 74 + 12 = 86 (At. No. of Rn).
28) Ans: D) 13 40) Ans: B) Secondary alcohol
Sol: [OH ] 101M , so pOH 1
3
We know, pH pOH 14 p H 1 4 1 1 3 41) Ans: C) CO H2O6
3 3
29) Ans: D) quinol Sol: Fe CN6 and Co NH3 6 are low-spin
30) Ans: B) cellulose complexes involving d2sp3 hybridisation, while
3
31) Ans: D) NO3
Co H O
2 6
is a high-spin complex involving
Sol: Those compounds which accept H are sp3d2 hybridisation (outer orbital complex).
known as Bronsted base, NO3 accepts H and
form HNO3 . So it is a base. 42) Ans: D) BF3
Sol: BF3
32) Ans: D) lysine
43) Ans: D) 1, 4
33) Ans: C) aldehydic and alcoholic.
44) Ans: B) intra-molecular hydrogen bonding
JEE-MAIN, MHT-CET, NEET/AIPMT, MHT-CET-XI - New Syllabus (MH)
MATRIX SCIENCE ACADEMY
Sol:
45) Ans: D) sp3 to dsp2
Sol: In the complex ion NiCl4
2
, the
3
hybridisation involved is sp and the molecular
geometry is tetrahedral. When the weak-field
ligands Cl , change to strong-field ligands CN ,
2
the complex ion formed is Ni CN 4 which
involves dsp2 hybridisation and the molecular
geometry is square planar.
46) Ans: D) B2H6 .H2O2 NaOH
Sol: In this reaction addition of H2O has taken
place according to Anti-Markownikoff rule; hence,
the reaction must be B2H6 reaction.
47) Ans: C) coordination number
48) Ans: B) 3.0
Sol: Here, [H ] 103 M, pH log[103 ] i.e. pH 3
49) Ans: B) Cr H2O4 Cl2 Cl
Sol: Cr H2O4 Cl2 Cl
50) Ans: A) Myoglobin
JEE-MAIN, MHT-CET, NEET/AIPMT, MHT-CET-XI - New Syllabus (MH)
You might also like
- Matrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L1 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsDocument2 pagesMatrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L1 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsLight MayNo ratings yet
- UnityDocument2 pagesUnityLight MayNo ratings yet
- A BF3 B IOv Solvw 5 ZL WDB2Document6 pagesA BF3 B IOv Solvw 5 ZL WDB2arindamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12th CBSE Sample PaperDocument9 pagesChemistry Class 12th CBSE Sample PaperSiddhi GoplanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2018Document4 pagesChemistry 2018Shubhankar ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- JEE (Adv) 2012 - Paper-1 - Q +solnDocument8 pagesJEE (Adv) 2012 - Paper-1 - Q +solnJanmedra Kumar TripathyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PHD - Set 1 - Questions PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry PHD - Set 1 - Questions PDFvksumanthNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Chemistry - 2019: Version Code: D-5Document7 pagesKcet - Chemistry - 2019: Version Code: D-5Manoj CNo ratings yet
- Matrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23Document4 pagesMatrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- MHT CET CHEMISTRY P2 SolDocument2 pagesMHT CET CHEMISTRY P2 SolLight MayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Sample Question Paper - 9Document6 pagesChemistry - Sample Question Paper - 9Mohd AdilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, BT-2, SET-IDocument6 pagesChemistry, BT-2, SET-ISoham NagNo ratings yet
- Kcet Chemistry 2017 Key AnswersDocument7 pagesKcet Chemistry 2017 Key AnswersKumar HanumanthaiahNo ratings yet
- Gate Chemistry 2007Document21 pagesGate Chemistry 2007uvir iitmNo ratings yet
- KCET 2019 Question Paper ChemistryDocument7 pagesKCET 2019 Question Paper ChemistryDarshan LNo ratings yet
- KVPY SA 2017 Chemistry Question Answerkey SolutionsDocument11 pagesKVPY SA 2017 Chemistry Question Answerkey SolutionsPRITHISH HAZRANo ratings yet
- Part - I (Chemistry) 80 Marks Section - I Single Correct Answer TypeDocument14 pagesPart - I (Chemistry) 80 Marks Section - I Single Correct Answer TyperajeshNo ratings yet
- APPLIED SCIENCE-1 (Chemistry)Document9 pagesAPPLIED SCIENCE-1 (Chemistry)Anonymous nIcSGEwNo ratings yet
- 2018 A Level H2 CM Suggested SolutionDocument19 pages2018 A Level H2 CM Suggested SolutionabishekksivarajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QP2Document6 pagesChemistry QP2Jinendra UvarajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1009) - PaperDocument13 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1009) - PaperIshan AgnohotriNo ratings yet
- SP Print OutDocument39 pagesSP Print Outbruno we dont talk aboutNo ratings yet
- Etea 2019Document7 pagesEtea 2019Izhar RahmanNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - M.Sc. Chemistry HyderabadDocument22 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - M.Sc. Chemistry HyderabadYocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- GUJCET - D22 Mar 2024Document13 pagesGUJCET - D22 Mar 20249bshrutiyadav16No ratings yet
- Final Step-A SolutionsDocument58 pagesFinal Step-A SolutionsHalfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Comp2021 Grand Btest - 2 ChemistryDocument11 pagesComp2021 Grand Btest - 2 Chemistrypivig90932No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument10 pagesChemistrydivyagarwal101No ratings yet
- Term-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDocument6 pagesTerm-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDarshan NayakNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) Chemistry GsebDocument8 pages(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) Chemistry GsebmjdNo ratings yet
- PU Board Model Paper With Water MarkDocument12 pagesPU Board Model Paper With Water MarkNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Rits-21 1Document13 pagesRits-21 1Muhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives PDFDocument32 pagesHalogen Derivatives PDFRaju Singh100% (1)
- HC DPP Ak 2 PDFDocument6 pagesHC DPP Ak 2 PDFJannaki PvNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Chemistry Feb 25 Shift 2Document17 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Chemistry Feb 25 Shift 2S085 Pranav HNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides and Aryl HalidesDocument16 pagesAlkyl Halides and Aryl Halidesvardesh100% (1)
- Coordination Compounds 109 QuestionsDocument19 pagesCoordination Compounds 109 QuestionsAnkit kumarNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Solved Chemistry 2006Document9 pagesIIT-JEE Solved Chemistry 2006Abhinav93% (15)
- 1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalDocument7 pages1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalShudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Probleme IiDocument16 pagesProbleme IisorinikloveNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - Iii: General InstructionsDocument5 pagesSample Paper - Iii: General Instructionssuchetha manjunthaNo ratings yet
- First Semester Diploma Examination in Engineering Technology-October, 2012Document9 pagesFirst Semester Diploma Examination in Engineering Technology-October, 2012Anonymous nIcSGEwNo ratings yet
- P-Block Group - 15-18Document59 pagesP-Block Group - 15-18lokesh swastikNo ratings yet
- Time: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHDocument5 pagesTime: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHlakshmi.vedanarayanan7785No ratings yet
- Home Assignment-3Document32 pagesHome Assignment-3ansh guptaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Prelims Revision PaperDocument6 pagesPre-Prelims Revision PaperaaaaNo ratings yet
- 0109 Chemistry Paper With Solution EveningDocument6 pages0109 Chemistry Paper With Solution EveningTheManASHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ADocument2 pagesChemistry ASparKY NIghtcoreNo ratings yet
- Chem Prepa 1Document10 pagesChem Prepa 1Kubra KhanNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry Sample Paper 1 Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument16 pagesClass Xii Chemistry Sample Paper 1 Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 70 General InstructionsAnmol PawateNo ratings yet
- EM Chem 2007Document8 pagesEM Chem 2007commonsensec88No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Pre BoardDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY Pre BoardRUDRANo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - (13th) (POI) Paper-1Document8 pagesCHEMISTRY - (13th) (POI) Paper-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- My Faculty Is Downloading Question Paper Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesMy Faculty Is Downloading Question Paper Alkyl HalidesanskritiNo ratings yet
- SL Paper 1 MsDocument14 pagesSL Paper 1 MsKali stringsNo ratings yet
- TPJC H2 Chem 08prelim Ans AllDocument10 pagesTPJC H2 Chem 08prelim Ans AllRonald McdonaldNo ratings yet
- DPP Qualitative AnalysisDocument5 pagesDPP Qualitative AnalysisNagendra BharadwazNo ratings yet
- 2011 Chemistry Question PapersDocument4 pages2011 Chemistry Question Papersalex scottNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Matrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsDocument3 pagesMatrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsLight MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsDocument2 pagesMatrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsLight MayNo ratings yet
- DocScanner 27 Mar 2023 10-05 AmDocument1 pageDocScanner 27 Mar 2023 10-05 AmLight MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23Document3 pagesMatrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23Document3 pagesMatrix Academy: JEE-MAIN 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- CC Physical Chem Test PaperDocument4 pagesCC Physical Chem Test PaperLight MayNo ratings yet
- MHT CET CHEMISTRY P2 SolDocument2 pagesMHT CET CHEMISTRY P2 SolLight MayNo ratings yet
- Chem Marks CC 11-04Document1 pageChem Marks CC 11-04Light MayNo ratings yet
- MAJcc TriDocument2 pagesMAJcc TriLight MayNo ratings yet
- UntifyDocument91 pagesUntifyLight MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Academy: MHT-CET-XII - New Syllabus (MH) 2022-23Document4 pagesMatrix Academy: MHT-CET-XII - New Syllabus (MH) 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- Title Phy MbsDocument4 pagesTitle Phy MbsLight MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Academy: MHT-CET-XII - New Syllabus (MH) 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsDocument4 pagesMatrix Academy: MHT-CET-XII - New Syllabus (MH) 2022-23 Hints and SolutionsLight MayNo ratings yet
- ExportQuiz SBCREDOXDocument4 pagesExportQuiz SBCREDOXLight MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L1 2022-23Document3 pagesMatrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L1 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- Matrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23Document4 pagesMatrix Science Academy: Chemistry MHT CET L2 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document22 pagesLecture 1Sameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Design For RC Flat SlabsDocument70 pagesDesign For RC Flat SlabsAil AafaaqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Love PoemDocument1 pageChemistry Love PoemMohd FarisNo ratings yet
- Novolastic Subsea Thermal InsulationDocument3 pagesNovolastic Subsea Thermal InsulationCarloBardoliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Discharge Through GasesDocument4 pagesElectrical Discharge Through GasessambhuNo ratings yet
- Phase Rule Class 2ND Sem NotesDocument6 pagesPhase Rule Class 2ND Sem NotesAmartya PraharajNo ratings yet
- Seminar-Machining Centers and Machine Tool StructuresDocument20 pagesSeminar-Machining Centers and Machine Tool StructuresniteshwanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process SyllabusDocument4 pagesManufacturing Process SyllabusRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Anne Marie Helmenstine, PH.D.: Black Powder Composition Chemical Composition of Black Powder or GunpowderDocument5 pagesAnne Marie Helmenstine, PH.D.: Black Powder Composition Chemical Composition of Black Powder or GunpowderRara Aoi100% (1)
- RC Lecture 11 - ColumnsDocument19 pagesRC Lecture 11 - ColumnsShean Berwin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesClass X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2019 PDFApex Institute100% (1)
- Bill of Material: 103PW2 - PL5/16"X4" - 1'-3" - 2 REQ'DDocument1 pageBill of Material: 103PW2 - PL5/16"X4" - 1'-3" - 2 REQ'Dai ambaraNo ratings yet
- Module in Magnetic Properties of MaterialsDocument14 pagesModule in Magnetic Properties of MaterialsFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Elems 13Document101 pagesElems 13Reynald de VeraNo ratings yet
- Elementary Inorganic Nomenclature PDFDocument2 pagesElementary Inorganic Nomenclature PDFPrecious Mae Cuerquis BarbosaNo ratings yet
- All in One - 10th Class em - Fa-2Document35 pagesAll in One - 10th Class em - Fa-2sai ramxeroxNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument12 pagesCorrosiontabaNo ratings yet
- Handbook Best Practice Dropped Object Management - Engelsk - GodkjentDocument108 pagesHandbook Best Practice Dropped Object Management - Engelsk - Godkjentmiguel angelNo ratings yet
- Endalkachew AbrhameDocument93 pagesEndalkachew Abrhamelibanhaji25No ratings yet
- Mullion Transom Connector BS-EN-1991-1-1 V2.0Document2 pagesMullion Transom Connector BS-EN-1991-1-1 V2.0Giri DharanNo ratings yet
- Processing of Oil SeedsDocument20 pagesProcessing of Oil SeedsRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- 1-Polo - MSDSDocument5 pages1-Polo - MSDSSaad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document20 pagesLecture 5يوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Fino ClassicDocument2 pagesFino ClassicRicette FaciliNo ratings yet
- 4024q1 Specimen PaperdocxDocument12 pages4024q1 Specimen PaperdocxLeses MayNo ratings yet
- Obele Ifenna PDFDocument197 pagesObele Ifenna PDFGuomin JiNo ratings yet
- Gunstone 61 eDocument0 pagesGunstone 61 esusu222000No ratings yet
- RC1 - Chapter 3BDocument30 pagesRC1 - Chapter 3BKhoi DuongNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Its Applications: For General Chemistry 2/grade 12 (STEM) Quarter 3/week 1.a-DDocument19 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Its Applications: For General Chemistry 2/grade 12 (STEM) Quarter 3/week 1.a-DSherwin Jay PalaspasNo ratings yet
- Methods and Techiniques in PathologyDocument15 pagesMethods and Techiniques in PathologyKiran100% (1)