Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Function Generators
Uploaded by
sushilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Function Generators
Uploaded by
sushilCopyright:
Available Formats
Function Generators:-
A function generator is a signal source that has the capability of producing different
types of waveforms as its output signal. The most common output waveforms are sine-
waves, triangular waves, square waves, and sawtooth waves. The frequencies of such
waveforms may be adjusted from a fraction of a hertz to several hundred kHz.
Actually, the function generators are very versatile instruments as they are capable of
producing a wide variety of waveforms and frequencies.
Many function generators are also capable of generating two different waveforms
simultaneously (from different output terminals, of course). This can be a useful feature
when two generated signals are required for a particular application. For instance, by
providing a square wave for linearity measurements in an audio-system, a simultaneous
sawtooth output may be used to drive the horizontal deflection amplifier of an
oscilloscope, providing a visual display of the measurement result. For another example,
a triangular-wave and a sine-wave of equal frequencies can be produced simultaneously.
If the zero crossings of both the waves are made to occur at the same time, a linearly
varying waveform is available which can be started at the point of zero phase of a sine-
wave.
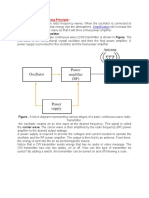
Function Generator Working & Block Diagram
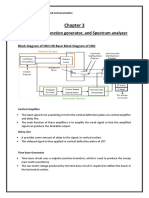
Function Generator Block Diagram
The block diagram of a function generator is given in the figure. In this instrument, the
frequency is controlled by varying the magnitude of the current that drives the integrator.
This instrument provides different types of waveforms (such as sinusoidal, triangular and
square waves) as its output signal with a frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 100 kHz.
The frequency controlled voltage regulates two current supply sources. Current supply
source 1 supplies a constant current to the integrator whose output voltage rises linearly
with time. An increase or decrease in the current increases or reduces the slope of the
output voltage and thus controls the frequency.
The voltage comparator multivibrator changes state at a predetermined maximum level,
of the integrator output voltage. This change cuts-off the current supply from supply
source 1 and switches to the supply source 2. The current supply source 2 supplies a
reverse current to the integrator so that its output drops linearly with time. When the
output attains a predetermined level, the voltage comparator again changes state and
switches on to the current supply source. The output of the integrator is a triangular wave
whose frequency depends on the current supplied by the constant current supply
sources. The comparator output provides a square wave of the same frequency as
output. The resistance diode network changes the slope of the triangular wave as its
amplitude changes and produces a sinusoidal wave with less than 1% distortion.
o )
o (1)
You might also like
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- RF-382A Remote ControllerDocument8 pagesRF-382A Remote ControllerΒΕΗΣ ΣΤΕΛΙΟΣ Veis SteliosNo ratings yet
- X Ray GeneratorDocument70 pagesX Ray Generatorub17075% (4)
- EMI Signal GeneratorsDocument10 pagesEMI Signal GeneratorsNaga HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Frequency Multipliers PDFDocument22 pagesFrequency Multipliers PDFduymanhhusNo ratings yet
- High Frequency X-RayDocument8 pagesHigh Frequency X-RayAshish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Generation and Analysis of Non-Linear LoadsDocument20 pagesHarmonic Generation and Analysis of Non-Linear Loadsue06037No ratings yet
- 1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-413-651Document239 pages1 Electrical - and - Electronics - Measurment. McGraw Hill, 2013-413-651Andrea Acuña100% (1)
- DP950XB REV2.0 2019-08-16 CN - ZH-CN - enDocument10 pagesDP950XB REV2.0 2019-08-16 CN - ZH-CN - enSunu Pradana0% (1)
- Function Generator: Triangular Waves Square Waves Sawtooth WavesDocument3 pagesFunction Generator: Triangular Waves Square Waves Sawtooth WavesPriyanka AroraNo ratings yet
- DP 1Document7 pagesDP 1meena__devendrakumarNo ratings yet
- RF Sweep Generator & Function GeneratorDocument4 pagesRF Sweep Generator & Function GeneratorRohit Rosan- 026No ratings yet
- Function Generator Waveform GuideDocument34 pagesFunction Generator Waveform GuideanantNo ratings yet
- SIGNAL GENERATORS Unit 3Document49 pagesSIGNAL GENERATORS Unit 3Murali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Function Generator GuideDocument4 pagesFunction Generator GuidemansurNo ratings yet
- Inverter (Electrical) : TypesDocument16 pagesInverter (Electrical) : Typesramkrishna01No ratings yet
- OSCILLATORS AND GENERATORSDocument20 pagesOSCILLATORS AND GENERATORSswetha bagadi it's good but how it will workNo ratings yet
- EMI-Signal GeneratorsDocument7 pagesEMI-Signal GeneratorsVineela ThonduriNo ratings yet
- Harmonic DistortionDocument5 pagesHarmonic Distortionnarendra.pathakNo ratings yet
- Signal GeneratorsDocument4 pagesSignal GeneratorsPriyanka AroraNo ratings yet
- SweepDocument2 pagesSweepSantoshbabu Kesanakurthi100% (1)
- WaveDocument13 pagesWaveBipasna RaiNo ratings yet
- Variable AF generator produces audio signalsDocument12 pagesVariable AF generator produces audio signalsAditi KumariNo ratings yet
- Signal GeneratorsDocument15 pagesSignal GeneratorsSobhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document6 pagesUnit 3S ManikandanNo ratings yet
- High Frequency X-RayDocument8 pagesHigh Frequency X-RayAshish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Generator 1 4Document11 pagesGenerator 1 4Utkarsh PariharNo ratings yet
- Micro Inverter For CFL LampsDocument27 pagesMicro Inverter For CFL LampsHamed RazaNo ratings yet
- Unit-III-Signal Generators & Wave Analyzers PDFDocument33 pagesUnit-III-Signal Generators & Wave Analyzers PDFsumalathaNo ratings yet
- Distortion: Any Deviation From The Original Signal Waveform Is Called DistortionDocument22 pagesDistortion: Any Deviation From The Original Signal Waveform Is Called DistortionPrashanth PerumallaNo ratings yet
- FUNCTION GENERATOR: PRODUCING ELECTRICAL WAVEFORMS FOR TESTING AND DEVELOPMENTDocument3 pagesFUNCTION GENERATOR: PRODUCING ELECTRICAL WAVEFORMS FOR TESTING AND DEVELOPMENTcsaproNo ratings yet
- Function GeneratorsDocument4 pagesFunction GeneratorsVarunKumarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Instrument Assessment 2Document10 pagesElectronic Instrument Assessment 2Ashish JhaNo ratings yet
- Electrical MetersDocument5 pagesElectrical MetersRameez Ali100% (1)
- Chap 3 Notes.Document13 pagesChap 3 Notes.Mohit kaduNo ratings yet
- Emi Unit2Document21 pagesEmi Unit2m.srinivasa raoNo ratings yet
- SSBC Systems and Angle Modulation DefinitionsDocument30 pagesSSBC Systems and Angle Modulation DefinitionsRalph Reyes SantelicesNo ratings yet
- Oscillator Noise Analysis: Cyclostationary NoiseDocument12 pagesOscillator Noise Analysis: Cyclostationary Noisedeepakvaj25No ratings yet
- Inductance Meter With 1nH ResolutionDocument3 pagesInductance Meter With 1nH Resolutionharry75700No ratings yet
- Function GeneratorDocument2 pagesFunction GeneratorChimaraoke NdubuezeNo ratings yet
- 300 274 ReportDocument7 pages300 274 ReportHuzaifa AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Signal GeneratorDocument2 pagesSignal GeneratorNaantagam Blur DafuusNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Oscilloscope X-Y Mode, Function Generator and Lissajous Polar (2012)Document13 pagesExp 5 Oscilloscope X-Y Mode, Function Generator and Lissajous Polar (2012)usmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Power InvertersDocument13 pagesPower InvertersCaHyaUTamaPNNo ratings yet
- InverterDocument22 pagesInvertersetsindiaNo ratings yet
- Oscillator BasicsDocument3 pagesOscillator BasicsRam Krishan SharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Signal Analyzers: AF Wave AnalyzerDocument15 pagesUNIT-2 Signal Analyzers: AF Wave Analyzersonuchary100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Frequency StabilityDocument24 pagesLecture 2 - Frequency StabilityDushani MunasingheNo ratings yet
- PWM InverterDocument2 pagesPWM InverterMandavi Nagar KotasthaneNo ratings yet
- Feedback Amplifiers?: in Electronics, Coupling Is Passing Energy From One Part of The Circuit To Some OtherDocument6 pagesFeedback Amplifiers?: in Electronics, Coupling Is Passing Energy From One Part of The Circuit To Some Othervadlamudi TharunNo ratings yet
- Voltage Controlled Oscillator - Usage of VCO, Working and ApplicationDocument6 pagesVoltage Controlled Oscillator - Usage of VCO, Working and ApplicationseemabNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis Lab - An Introduction To Lab EquipmentDocument3 pagesCircuit Analysis Lab - An Introduction To Lab EquipmentBrandon SimonNo ratings yet
- Study function generator labDocument11 pagesStudy function generator labGarima SarafNo ratings yet
- Function GeneratorDocument12 pagesFunction Generatordineshpadhiyar0% (1)
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1Rasha HashimNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Single-Phase SPWM Inverter: Sandeep PhogatDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Single-Phase SPWM Inverter: Sandeep PhogatPraneeth MutnuruNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Signal GeneratorsDocument31 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Signal Generatorsumar_khalif100% (3)
- Notes On Signal GeneratorsDocument3 pagesNotes On Signal GeneratorsAdrian PostavaruNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Continuous Wave Transmitter: Radio Transmitter Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesContinuous Wave Transmitter: Radio Transmitter Working PrinciplesushilNo ratings yet
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument4 pagesCathode Ray OscilloscopesushilNo ratings yet
- Digital Storage OscilloscopeDocument4 pagesDigital Storage OscilloscopesushilNo ratings yet
- M3 Training NotesDocument64 pagesM3 Training NotessushilNo ratings yet
- Ata 31-Indicating & RecordingDocument36 pagesAta 31-Indicating & RecordingRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 300C CounterDocument3 pages300C CounterHạnh NhânNo ratings yet
- Features Description: Low Cost Green-Mode PWM Controller For Flyback ConvertersDocument13 pagesFeatures Description: Low Cost Green-Mode PWM Controller For Flyback ConvertersfjfjgkNo ratings yet
- Infineon ICE1PCS02 DS v01 02 enDocument18 pagesInfineon ICE1PCS02 DS v01 02 enZulfiqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Touchscreen and Zigbee Assistant in AirlinesDocument69 pagesTouchscreen and Zigbee Assistant in Airlinesk_snova67% (3)
- Isl24837 PDFDocument2 pagesIsl24837 PDFPaulo Roberto s freireNo ratings yet
- DS005671Document43 pagesDS005671WilliamWillyFNo ratings yet
- Over Load and Short Circuit Protection Strategy For Voltage Source Inverter Based UPSDocument27 pagesOver Load and Short Circuit Protection Strategy For Voltage Source Inverter Based UPSAkshay PotekarNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Based Active Power CalculationDocument12 pagesTime Domain Based Active Power CalculationFrank CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Smart Automation in Railway System: Arundas M H, Nikhil Babu T S, Lijo K JDocument5 pagesSmart Automation in Railway System: Arundas M H, Nikhil Babu T S, Lijo K JerodeiframeNo ratings yet
- Dual Synchronous Buck Pseudo Fixed Frequency Power Supply ControllerDocument27 pagesDual Synchronous Buck Pseudo Fixed Frequency Power Supply ControllerManish BaghelNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Low Power, High Speed 4 - Bit Magnitude ComparatorDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Low Power, High Speed 4 - Bit Magnitude ComparatorChilaka JayaramNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits II Lab ManualDocument47 pagesAnalog Circuits II Lab ManualParesh SawantNo ratings yet
- Mic 2282Document10 pagesMic 2282mariusz sNo ratings yet
- L6565 DatasheetDocument17 pagesL6565 DatasheetJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- 1.adc DacDocument35 pages1.adc DacGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- ECE Pulse and Digital CircuitsDocument2 pagesECE Pulse and Digital CircuitsGautam ReddyNo ratings yet
- DBATU UG EXTC Engg Syllabus With Cover Page 1Document155 pagesDBATU UG EXTC Engg Syllabus With Cover Page 1Sudhirkumar DhotreNo ratings yet
- BQ24196 TexasInstrumentsDocument41 pagesBQ24196 TexasInstrumentsNoel Alejandro Cordova RangelNo ratings yet
- UC3842 current mode controller application noteDocument7 pagesUC3842 current mode controller application noteCui BapNo ratings yet
- Analysis, Design, and Implementation of A High-Efficiency Full-Wave Rectifier in Standard CMOS TechnologyDocument11 pagesAnalysis, Design, and Implementation of A High-Efficiency Full-Wave Rectifier in Standard CMOS TechnologymohsinmanzoorNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion Utilizing The AT89CX051 MicrocontrollersDocument6 pagesAnalog-to-Digital Conversion Utilizing The AT89CX051 MicrocontrollersJuan Jose MendozaNo ratings yet
- Adc0801 PDFDocument36 pagesAdc0801 PDFroi_sihombingNo ratings yet
- Automatic Three Phase Induction Motor Star - Delta Starter: A Project Report Submitted at D N Polytechnic MeerutDocument31 pagesAutomatic Three Phase Induction Motor Star - Delta Starter: A Project Report Submitted at D N Polytechnic MeerutDeepanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- EEL203-Analog Electronics LabDocument3 pagesEEL203-Analog Electronics LabAthira SivanandhanNo ratings yet
- 16F1939Document508 pages16F1939strek1No ratings yet
- General Description Features: High Performance Current Mode PWM ControllerDocument11 pagesGeneral Description Features: High Performance Current Mode PWM ControllerPhạm Tấn HảiNo ratings yet
- MIT Op-Amp Lab ReportDocument20 pagesMIT Op-Amp Lab ReportcrackintheshatNo ratings yet
- At 30 IcDocument9 pagesAt 30 IcCristina AntohiNo ratings yet