Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood
Blood
Uploaded by
RECTO ERL WYN BEE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThis document discusses various filarial parasites that can infect humans, including Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Loa loa, Onchocerca volvulus, and Mansonella species. It addresses the life cycles, vectors, tissues involved, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of different filarial infections. Key points covered include the use of blood smears and skin snips to identify microfilariae, tissues parasites reside in, symptoms of different stages of lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis, and eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various filarial parasites that can infect humans, including Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Loa loa, Onchocerca volvulus, and Mansonella species. It addresses the life cycles, vectors, tissues involved, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of different filarial infections. Key points covered include the use of blood smears and skin snips to identify microfilariae, tissues parasites reside in, symptoms of different stages of lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis, and eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesBlood
Blood
Uploaded by
RECTO ERL WYN BEEThis document discusses various filarial parasites that can infect humans, including Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Loa loa, Onchocerca volvulus, and Mansonella species. It addresses the life cycles, vectors, tissues involved, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of different filarial infections. Key points covered include the use of blood smears and skin snips to identify microfilariae, tissues parasites reside in, symptoms of different stages of lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis, and eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
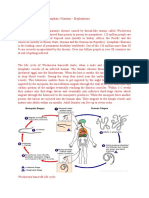
1. Blood-sucking arthropod vector such as ______, ______, ________.
2. filarial nematodes infect the_____________, ______________, ____________, and____________.
3. Where does the infective larval stage reside?
4. The infective larvae grow and develop into the adult gravid worm in the human host in how many months?
5. Where does the female and male adult worms’ mate?
6. The female worm produces large numbers of larvae called?
7. Parasites can reside in the host for many years and cause what?
8. The identification of various species is based on?
9. It is a physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle.
10. What do you call the study of circadian rhythms?
11. Filariae inhabit a variety of tissue, give 5
12. What is the diagnosis of microfilariae?
13. What diagnosis is considered as sensitive procedure?
14. Adult worms are often sequestered in?
15. Microfilariae may be seen moving in what?
16. In Knotts concentration, what will you need?
17. How many mL of heparinized blood you will be using under the membrane filter test?
18. Size of the nucleopore filter used in the membrane filter?
19. What microfilariae spp displays a nocturnal periodicity?
20. What microfilariae spp diurnal a nocturnal periodicity?
21. What microfilariae spp displays non periodic?
22. In W. bancrofti and B. malayi filariae, blood should be draw in what time?
23. In Loa loa filariae, blood should be draw in what time?
24. What microfilariaes are found in skin?
25. These microfilariae can be detected trough skin snips or punch biopsies
26. It is the most common filariaris to infect humans
27. Severe involvement of the lower extremities and genitalia may result in____________.
28. Vectors of Wuchereria bancrofti?
29. It is a sheathed microfilaria, pointed tail and the cephalic space is not long as it is wide and has distinct nuclei in
the nuclear column.
30. Adults exhibit microfilariae in their blood without experiencing symptoms, what do you call this filariasis?
31. Pts exhibit moderate generalized enlargement of lymph nodes, especially in the ______ region.
32. Blood examination discloses numerous microfilariae and ___________________.
33. Recurrent attacks are characterized by___________, ____________, ___________and localized areas of swelling
and redness of the arms and legs
34. They experience acute lymphanngitis of spermatic cord, epididymitis, orchitis, and scrotal edema.
35. This is the result from the worms and their toxic products
36. It is the dramatic result of filariasis
37. Obstructive filariasis develops__________, usually follows years of continuous filarial infection, and is preceded
by chronic edema and often by repeated acute inflammatory attacks.
38. In chronic stage the cellular reaction and edema are replaced by _______________
39. mcf is generally ___________ in patients with elephantiasis
40. Rupture of the lymphatics of the kidney may produce______________?
41. It is similar to that of W. bancrofti, although it is often milder and more frequently involves the lymphatics of the
upper extremities.
42. What parasite stains well with Giemsa stain?
43. The tail of the parasite has a swelling at the tip and has two solitary nuclei located beyond the end of the nuclear
column (termed subterminal and terminal nuclei) and the cephalic space is long that it is wide
44. Microfilariae are very similar to those of B. malayi, although somewhat larger, what is being described?
45. Also known as the African eye worm, eye worm
46. Where does loa loa lives?
47. Loa loa migrate continuously, producing transient (2-3 days) local inflammatory reactions known as
_____________________?
48. It is caused by parasitic worm Loa loa?
49. What is the periodicity of loa loa?
50. Loa loa does not stain in what stain?
51. Nuclei in the tail extend to the rounded tip, the nuclear column is distinct, and the cephalic space is short.
52. It is a leading cause of blindness in endemic areas, which include central Africa, Central America (Mexico and
Guatemala), and northern South America.
53. What is the vector of O. volvulus?
54. Adult worms live in ____________________in subcutaneous and deeper tissues that can grow to be 40 mm in
diameter.
55. Movement of microfilariae through the surface of the eye may result in__________, ____________,
and______________________________, thus leading to blindness with repeated infections over time.
56. It lacks both a sheath and nuclei in the tail tip.
57. Give the 3 Mansonella spp that infects humans
58. What disease is caused by M. ozzardi?
59. Infections are often assymptomatic but may produce____________, ___________, and___________.
60. Mcf is present in _______ and in the ________ (no cutaneous pathology)
61. Disease caused by M. perstans
62. Former name of M. perstans
63. What is the infective and definitive host of M. perstans?
64. What are the symptoms of M. perstans?
65. What are the diagnosis of M . perstans?
66. The unsheathed mcf found in the skin of humans and chimpanzees have the appearance of a
________________________ (with nuclei extending to the tip).
67. What is the intermediate host of M. streptocerca
68. It is non pathogenis but may cause ___________ and ___________.
69. What is the treatment of M. streptocerca
70. What other filarial infections that may infect humans? Give 4
71. Mature parasite of Angiostrongylus cantonensis and Angiostrongylus costaricensis is normally found in where?
72. This Angiostrongylus spp migrate to the brain and spinal cord (producing eosinophilic meningoencephalitis.
73. This Angiostrongylus spp cause acute abdominal syndrome with inflammatory lesion of the ileocecal region.
74. The (female) nematodes is known by their typical barber’s pole appearance, which results from spiral disposition
of the blood-filled intestine and the white uterine tubes in fully developed female worms, what Angiostrongylus
spp is this
75. How humans acquire infection of Angiostrongylus cantonensis?
76. Where did the infective stage of Angiostrongylus spp develops?
77. What type of meningoencephalitis is produced by Angiostrongylus cantonensis?
78. How to diagnose the Angiostrongylus cantonensis?
You might also like
- EcoHealth Whistleblower Andrew Huff Provides Evidence That COVID-19 Was Created in Wuhan LabDocument54 pagesEcoHealth Whistleblower Andrew Huff Provides Evidence That COVID-19 Was Created in Wuhan LabJim Hoft100% (11)
- BIP Student WorksheetDocument4 pagesBIP Student WorksheetFitra Arif MustofaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964From EverandProceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964Augusto CorradettiNo ratings yet
- Filarial NematodeDocument18 pagesFilarial NematodeHawre NajmaddinNo ratings yet
- 20-21 QuestionnaireDocument3 pages20-21 QuestionnaireRhoma Mae IsoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Filariasis: Disease ManagementDocument10 pagesLymphatic Filariasis: Disease ManagementamyNo ratings yet
- Parasitology - Blood & Tissue - W Bancrofti B Malayi - PresentationDocument43 pagesParasitology - Blood & Tissue - W Bancrofti B Malayi - PresentationNicole ManogNo ratings yet
- BN Filarial WormDocument137 pagesBN Filarial WormCherenet TomaNo ratings yet
- Man Bahadur Rana BPH, Acas, NepalDocument34 pagesMan Bahadur Rana BPH, Acas, NepalDipankar NathNo ratings yet
- Man Bahadur Rana BPH, Acas, NepalDocument34 pagesMan Bahadur Rana BPH, Acas, NepalDipankar NathNo ratings yet
- Filariasis: Tropmed Block Faculty Medicine USU 2016Document26 pagesFilariasis: Tropmed Block Faculty Medicine USU 2016Tiurma SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 84Document38 pagesChapter 84Naimon Kumon KumonNo ratings yet
- Helemnth ReportDocument15 pagesHelemnth ReportHawre NajmaddinNo ratings yet
- FILARIASISDocument57 pagesFILARIASISadekayo100% (6)
- Microfilariae: Presented byDocument26 pagesMicrofilariae: Presented byyudhisthir panthiNo ratings yet
- FilariaDocument85 pagesFilariaRajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- 4.3. Blood and Tissue NematodesDocument89 pages4.3. Blood and Tissue NematodesRediat GossayeNo ratings yet
- Report PARA Lymphatic Filarial Nematodes Group 2 Adalid Asug AustriaDocument28 pagesReport PARA Lymphatic Filarial Nematodes Group 2 Adalid Asug AustriaDaniel AustriaNo ratings yet
- Printable Flashcard On Biology 104 Test #1 Chapters 20-22Document9 pagesPrintable Flashcard On Biology 104 Test #1 Chapters 20-22cskjain100% (1)
- Onchocerca Volvulus Onchocerca Ochengi Litomosoides Sigmodontis Brugia Malayi Wuchereria Bancrofti Litomosoides SigmodontisDocument2 pagesOnchocerca Volvulus Onchocerca Ochengi Litomosoides Sigmodontis Brugia Malayi Wuchereria Bancrofti Litomosoides SigmodontisCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Revision: Types of Life Cycle in Trematoda and CestodaDocument54 pagesRevision: Types of Life Cycle in Trematoda and CestodaMicroscopeGeekNo ratings yet
- 42 National Science Olympiad: 9 March 2006 Questions and Solutions: BiologyDocument55 pages42 National Science Olympiad: 9 March 2006 Questions and Solutions: Biologymartynapet100% (2)
- Blood and Tissue Nematods 2015Document109 pagesBlood and Tissue Nematods 2015sinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Micropara Lab Parasites Gr123456Document99 pagesMicropara Lab Parasites Gr123456Mary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Lesson 1 VirusDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 4 Lesson 1 VirusKreizel FajaNo ratings yet
- Wuchereria BancroftiDocument6 pagesWuchereria BancroftiAinur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Filarial Nematodes: Wuchereria BancroftiDocument8 pagesFilarial Nematodes: Wuchereria BancroftiMegumi TadokoroNo ratings yet
- Filarial NematodesDocument15 pagesFilarial NematodesOpi SaNg MadRidistasNo ratings yet
- 14-15 QuestionnaireDocument5 pages14-15 QuestionnaireRhoma Mae IsoNo ratings yet
- Biology 1002 Exam 1 Fall 2018Document11 pagesBiology 1002 Exam 1 Fall 2018Jashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON Topic: Pox Viridae General Properties, Dna Replication & Cow Pox DiseaseDocument8 pagesAssignment: ON Topic: Pox Viridae General Properties, Dna Replication & Cow Pox DiseaseVinayak ChuraNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue NematodesDocument60 pagesBlood and Tissue NematodesDanielle Pecson100% (1)
- Bio-Zoology - 1516 EMDocument45 pagesBio-Zoology - 1516 EMVinoth MNo ratings yet
- Tissue Nematodes: 49.1 IntoductionDocument8 pagesTissue Nematodes: 49.1 IntoductionAileen LuzonNo ratings yet
- Wuchereria BancroftiDocument13 pagesWuchereria Bancroftiumeshchandralenka09No ratings yet
- Filaria N Tissue NematodeDocument27 pagesFilaria N Tissue NematodeLanny Margaretha BarutuNo ratings yet
- Filaria & Other Tissue Nematodes: BBS-PR 2017 Parasitology DeptDocument27 pagesFilaria & Other Tissue Nematodes: BBS-PR 2017 Parasitology DeptOktaviani Karo SekaliNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document11 pagesLect 2Sara AliNo ratings yet
- Love Surgeon Bio102 Past QuestionsDocument9 pagesLove Surgeon Bio102 Past QuestionsTechnob StudioNo ratings yet
- 7 Module 6 Nematodes Part 2Document100 pages7 Module 6 Nematodes Part 2Luke Jovanni TAOCNo ratings yet
- Para Lec FinalsDocument3 pagesPara Lec FinalsVanessa May BlancioNo ratings yet
- Wuchereria BancroftiDocument19 pagesWuchereria BancroftiMayuri VohraNo ratings yet
- Onchocerciasis FullDocument10 pagesOnchocerciasis FullChidera EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Nematodes Part 3Document50 pagesModule 9 - Nematodes Part 3Arnold GarcinesNo ratings yet
- Filaria - A Comprehensive StudyDocument63 pagesFilaria - A Comprehensive StudyDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Wuchereria Bancrofti: Aby Elijah L. BernardinoDocument22 pagesWuchereria Bancrofti: Aby Elijah L. BernardinoAby Brr100% (1)
- Biol 1002 Exam 2Document5 pagesBiol 1002 Exam 2Jashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- Week 2. Learning Module Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic OrganismDocument25 pagesWeek 2. Learning Module Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic OrganismFezaret Jerome C.No ratings yet
- 1 Lec HistoryDocument10 pages1 Lec Historycharizepascual110899No ratings yet
- Filariasis Report (NCM 55 - B3)Document21 pagesFilariasis Report (NCM 55 - B3)Jette Charmae OlboNo ratings yet
- Wu C Here Ria Bancroft IDocument3 pagesWu C Here Ria Bancroft IMariamNo ratings yet
- Blood Tissue NematodesDocument27 pagesBlood Tissue NematodesAfif Mamen100% (1)
- Brugia MalayiDocument8 pagesBrugia MalayiROn Ace DancelNo ratings yet
- Micro AssignmentDocument3 pagesMicro AssignmentClement GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Filariasis Elimination IndiaDocument108 pagesGuidelines Filariasis Elimination IndiaegalivanNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiolog1Document226 pagesMedical Microbiolog1gardenya100% (5)
- Microorganisms: Compulsory TextDocument8 pagesMicroorganisms: Compulsory TextAna CecansciucNo ratings yet
- BIO102 Lesson 1Document66 pagesBIO102 Lesson 1Esther OgelekaNo ratings yet
- Viro Final 6Document10 pagesViro Final 6Muhammad Arslan UsmanNo ratings yet
- The Filariae: Lymphatic System, Subcutaneous and Deep Connective TissueDocument17 pagesThe Filariae: Lymphatic System, Subcutaneous and Deep Connective TissueKaranja GitauNo ratings yet
- The War Within Us: Everyman's Guide to Infection and ImmunityFrom EverandThe War Within Us: Everyman's Guide to Infection and ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Address: Phone Number: Email Address: Date: April 2023Document16 pagesAddress: Phone Number: Email Address: Date: April 2023RECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- GEC 103 (Globalization)Document1 pageGEC 103 (Globalization)RECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- DRAFTDocument5 pagesDRAFTRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Cestodes Self TestDocument2 pagesCestodes Self TestRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Eric YuanDocument2 pagesEric YuanRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Cavite MutinyDocument50 pagesCavite MutinyRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Infant CareDocument4 pagesInfant CareRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument3 pagesBusiness PlanRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Basic SurvivalDocument5 pagesBasic SurvivalRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- 4.6 Signal Communication 1Document7 pages4.6 Signal Communication 1RECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Basic Signal CommunicationDocument8 pagesBasic Signal CommunicationRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- 1.1 Gender and DevelopmentDocument7 pages1.1 Gender and DevelopmentRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- 1.2 Personality DevelopmentDocument8 pages1.2 Personality DevelopmentRECTO ERL WYN BEENo ratings yet
- Sample Speech Blood Drive PDFDocument5 pagesSample Speech Blood Drive PDFNil PunadiyaNo ratings yet
- Who Immunization-Routine-Table2Document11 pagesWho Immunization-Routine-Table2Frances Jean T. DoblasNo ratings yet
- IMNCI - 6th SemDocument32 pagesIMNCI - 6th SemAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 151 - Cellulitis and ErysipelasDocument8 pagesChapter 151 - Cellulitis and ErysipelasDorothy BullecerNo ratings yet
- Dataset On Child Vaccination in Brazil From 1996 To 2021: Data DescriptorDocument9 pagesDataset On Child Vaccination in Brazil From 1996 To 2021: Data DescriptorlaireneNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument24 pagesCommunicable DiseasesJanus de LeonNo ratings yet
- Small RuminantDocument296 pagesSmall RuminantSadaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Field Visit ReportDocument6 pagesField Visit ReportDr.Mohammed MahsoubNo ratings yet
- PT Sprint 2023 Social Issuse @upsc - Success - Time1Document92 pagesPT Sprint 2023 Social Issuse @upsc - Success - Time1Nitin SinghNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Primary Care Art and Science of Advanced Practice Nursing 4th Edition Dunphy Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Primary Care Art and Science of Advanced Practice Nursing 4th Edition Dunphy Test Bank PDFsangpaulina100% (11)
- Chapter 8 Blood DonationDocument55 pagesChapter 8 Blood DonationCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- Prometric Notes3Document133 pagesPrometric Notes3Majid KhanNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure For Health PromotionDocument3 pagesInfrastructure For Health PromotionLuo MiyandaNo ratings yet
- Worm Infestation: Ms Alisha TalwarDocument82 pagesWorm Infestation: Ms Alisha TalwarSumon Kumar biswasNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapMersiya SarapuddinNo ratings yet
- RespiratorychempowerpointDocument10 pagesRespiratorychempowerpointapi-252255196No ratings yet
- Drug Study CEFAZOLINDocument6 pagesDrug Study CEFAZOLINAicelle Love Sampat LapenaNo ratings yet
- VIRUS Biology Mindmap Biological ClassificationDocument1 pageVIRUS Biology Mindmap Biological ClassificationE-KARTNo ratings yet
- "Bioterrorism": Delhi Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research UniversityDocument6 pages"Bioterrorism": Delhi Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research UniversityNeeru ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Simple Guide Identification Bacteria: Dr. Khalil AlkuwaityDocument18 pagesSimple Guide Identification Bacteria: Dr. Khalil AlkuwaitySaid IsaqNo ratings yet
- The Pharmacist - S Role in Preventing Antibiotic Resistance PDFDocument8 pagesThe Pharmacist - S Role in Preventing Antibiotic Resistance PDFalfox2000No ratings yet
- COA of Maitake Mushroom ExtractDocument1 pageCOA of Maitake Mushroom ExtractPan EmmaNo ratings yet
- Menu Plan ForTuberculosisDocument3 pagesMenu Plan ForTuberculosisgandhialpitNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: School Contingency Plan For Covid-19 ResurgencesDocument22 pagesDepartment of Education: School Contingency Plan For Covid-19 ResurgencesReal Talk / Music '20100% (1)
- COVID-19 Vaccination Acceptance and Its Associated Factors Among The Iraqi Population: A Cross Sectional StudyDocument13 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccination Acceptance and Its Associated Factors Among The Iraqi Population: A Cross Sectional StudyJijesh NambiarNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Its TypesDocument3 pagesImmunity and Its TypesBenazir SheikhNo ratings yet
- CV - Microbiology Infection ControlDocument14 pagesCV - Microbiology Infection ControlDrRahul KambleNo ratings yet
- Lloyd Rice - Distribution - of - Heartwater - in - Cattle - in - Gokwe North District ZimbabweDocument32 pagesLloyd Rice - Distribution - of - Heartwater - in - Cattle - in - Gokwe North District ZimbabweLloyd RiceNo ratings yet
- Com. Medicine Scheme of Exam 08-11-22Document39 pagesCom. Medicine Scheme of Exam 08-11-2260-K NileshNo ratings yet