Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How An Induction Machine Works Part 5
How An Induction Machine Works Part 5
Uploaded by
JohanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How An Induction Machine Works Part 5
How An Induction Machine Works Part 5
Uploaded by
JohanCopyright:
Available Formats
Great question! So, let's imagine you have a toy car with wheels that can spin.
Now, imagine you have a battery that can make the wheels spin by sending
electricity to them through wires.
Now, let's say you want to make a bigger version of this toy car that can carry
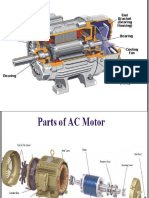
people. You would need a bigger motor to make the car move. In a bigger motor,
there is a part called the rotor that rotates when electricity is applied to it.
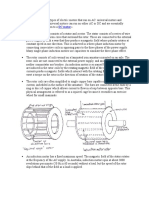
In an induction machine, the rotor has a bunch of wires wrapped around it. These
wires are called rotor bars. But, unlike the wires in the toy car, the rotor bars
are not connected to a battery or power source. Instead, they are left "floating"
or "unconnected".
Now, here's the interesting part. When electricity is applied to the stator, it
creates a magnetic field that spins around the rotor. This magnetic field induces a
current in the rotor bars, even though they are not connected to a power source.
If the rotor bars were not shorted, this induced current would cause the rotor to
heat up and could damage the motor. So, to prevent this from happening, the ends of
the rotor bars are connected together with metal rings. This creates a closed loop
for the induced current to flow through, which helps to reduce the heat and protect
the motor.
So, in summary, the rotor bars in an induction machine are shorted together to
create a closed loop for the induced current to flow through, which helps to
protect the motor from damage.
You might also like
- How Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- How Alternator WorksDocument8 pagesHow Alternator WorksRsjBugtongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Magnet Power: Shenhe Wang'S Permanent Magnet MotorDocument52 pagesChapter 1: Magnet Power: Shenhe Wang'S Permanent Magnet MotorMayki ChiNo ratings yet
- How Electric Motors WorkDocument8 pagesHow Electric Motors WorkJennifer ElliottNo ratings yet
- What Is An AlternatorDocument16 pagesWhat Is An AlternatorSanrasni100% (1)
- 1 Free-Energy Devices - Power From MagnetsDocument79 pages1 Free-Energy Devices - Power From MagnetsGoran ŠtetinNo ratings yet
- Brushed DC Electric Motor - WikipediaDocument63 pagesBrushed DC Electric Motor - WikipediaKISHORE PERUMALLANo ratings yet
- LUTEC AUSTRALIA PTY LTD Displays Prototypes That Amplifying Electricity by 5 TimesDocument1 pageLUTEC AUSTRALIA PTY LTD Displays Prototypes That Amplifying Electricity by 5 TimesyodifoyorNo ratings yet
- Construct Electric MotorDocument15 pagesConstruct Electric MotorcontrasterNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC MachineDocument10 pagesConstruction of DC MachineMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Eddy Current Brakes: Found in Cars As WellDocument7 pagesBasic Structure of Eddy Current Brakes: Found in Cars As Wellpseudo networkNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorsDocument2 pagesElectric MotorsPopa Elena MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Slip Ring and Split RingDocument5 pagesSlip Ring and Split RingboltuNo ratings yet
- Basic Motor TheoryDocument48 pagesBasic Motor Theoryantoniogh2No ratings yet
- Learning Electric Motor and It's ComponentDocument4 pagesLearning Electric Motor and It's Componentandrey tinoh100% (1)
- What Is An Alternator?: Battery Voltage Regulator AlternatorDocument5 pagesWhat Is An Alternator?: Battery Voltage Regulator AlternatorNeverhhhNo ratings yet
- How Electric Motors WorkDocument7 pagesHow Electric Motors WorkBrian FanelliNo ratings yet
- Induction, Squirrel Cage Motor - Torque CalculationDocument10 pagesInduction, Squirrel Cage Motor - Torque CalculationAlexandra100% (1)
- Ex 3Document7 pagesEx 3Feras Al-AzzehNo ratings yet
- Toy Motor Lab Nikki TomblinDocument7 pagesToy Motor Lab Nikki Tomblinapi-316460888No ratings yet
- Electrical SectionDocument3 pagesElectrical SectionVivek BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- What Is A Solar Motor?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Solar Motor?D K SHARMANo ratings yet
- Principles of DC MotorsDocument14 pagesPrinciples of DC MotorsAravind Raj PandianNo ratings yet
- How Alternator WorksDocument10 pagesHow Alternator Worksanimesh907100% (1)
- DC MotorDocument1 pageDC Motorkarizmatic_kushNo ratings yet
- How Does An AC Motor Work?: Stator Squirrel CageDocument4 pagesHow Does An AC Motor Work?: Stator Squirrel CageQuen EscletoNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: Rotor (Document3 pagesElectric Motor: Rotor (qwert qwertNo ratings yet
- eCARS2x 2018 T1-3 Types Electric Motors-Conferencia4Document4 pageseCARS2x 2018 T1-3 Types Electric Motors-Conferencia4EulerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Document4 pagesIntroduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current and Applications ProjectDocument7 pagesEddy Current and Applications Projectअभिषेक मान67% (3)
- History: Electric Motor Alternating Current Stator RotorDocument14 pagesHistory: Electric Motor Alternating Current Stator RotorManas NagNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC MachineDocument10 pagesConstruction of DC MachineMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Basics of AC Electric Motors and PartsDocument3 pagesBasics of AC Electric Motors and PartsPankaj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Motor TheoryDocument39 pagesBasic Motor Theoryarfat_ahmad_khanNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic MotorDocument21 pagesUltrasonic Motorjyothsna123456100% (1)
- Magnetism: Systems Operation - FundamentalsDocument10 pagesMagnetism: Systems Operation - Fundamentalsrigoberto otinianoNo ratings yet
- 4 AdvDocument13 pages4 AdvHemanth SaiNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument7 pagesElectrical Machinesusama jabbarNo ratings yet
- AC Motor WikipediaDocument10 pagesAC Motor WikipediasmeenaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ac DCDocument10 pagesAssignment Ac DCKamil KhairiNo ratings yet
- Single PhasingDocument22 pagesSingle PhasingAakarsh Rastogi100% (2)
- Electro 3 Finals Task PerformanceDocument23 pagesElectro 3 Finals Task PerformanceJuan Miguel TorresNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument8 pagesAC MotorSmai HondoNo ratings yet
- Basic Motor TheoryDocument26 pagesBasic Motor TheoryRoberth Salsr LpzNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument71 pagesAC Motorstallone21No ratings yet
- L1 ElectromagnetDocument12 pagesL1 ElectromagnetelizaclassroomNo ratings yet
- How Electric Motors WorkDocument2 pagesHow Electric Motors Workankush2020No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductiongalihwidiastoNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors-Abdulla AlhashmiDocument3 pagesElectric Motors-Abdulla AlhashmiAbdulla Al HashmiNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument4 pagesInduction MotorSenjuti DeNo ratings yet
- Spinning Homopolar Motor With Magnet TrifoldDocument2 pagesSpinning Homopolar Motor With Magnet TrifoldJorell lapatingNo ratings yet
- AC MotorDocument22 pagesAC MotorMoise CristinaNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors and Generators: Schematics of Some Types of MotorDocument16 pagesElectric Motors and Generators: Schematics of Some Types of MotorterranohrNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Induction MotorDocument1 pageWorking Principle of Induction Motormuhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Why Polyphase Induction Never Attains Synchronous SpeedDocument2 pagesWhy Polyphase Induction Never Attains Synchronous SpeedKaruppu SamyNo ratings yet
- Mr. Mohanbir Singh: TopicDocument6 pagesMr. Mohanbir Singh: TopicGagan BoparaiNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Systems Operation - FundamentalsDocument9 pagesMagnetism: Systems Operation - FundamentalsWellington FrançaNo ratings yet
- Science Project - Generators and MotorsDocument4 pagesScience Project - Generators and MotorsApril GonzalesNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 4Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 4JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 3Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 3JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 2Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 2JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 3Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 3JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 1Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 1JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 5Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 5JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 2Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 2JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 1Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 1JohanNo ratings yet
- How An Induction Machine Works Part 4Document1 pageHow An Induction Machine Works Part 4JohanNo ratings yet