Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer
Uploaded by
Kwinn EspinosaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer
Uploaded by
Kwinn EspinosaCopyright:
Available Formats
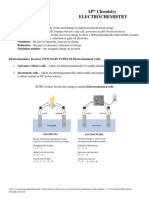
BATTERY TWO TYPES OF CELLS
- Device that converts chemical energy Primary cell
contained within its active materials
• irreversibly that transform chemical
directly into electric energy by means of
energy to electrical energy.
an electrochemical oxidation-reduction
(redox) • When the initial supply of reactant is
exhausted, energy cannot be readily
- ELECTROCHEMICAL OXIDATION- restored to the battery by electrical
REDUCTION is type of reaction that means.
involves the transfer of electrons from Advantage
one material to another via an electric • Has only one chemical reaction
circuit.
Disadvantage
FIRST BATTERY • Can be only used once.
- Invented by ALESSANDRO VOLTA in
1799 Types of Primary Cell
• Mercuric Oxide 1.35 V
- 1780 in building on Galvani’s, the • Carbon –zinc (Leclanche) 1.5 V
discovery of how a circuit of two metal’s • Zinc Chloride 1.5 V
frog leg can cause the frog’s leg • Manganese Dioxide (Alkaline) 1.5 V
respond. • Zinc air 1.5 V
- 1791 Volta demonstrated when two • Silver Oxide 1.5 V
metals and brine-soaked doth or • Lithium 3.0 V
cardboard are arranged in a circuit they
produce an electric current. - Lead- Acid Cell
- 1800 Volta stacked several pairs of - Nickel-Cadmium cell
alternating copper (silver) and zinc discs - Solar Cell
(electrodes) separated by cloth or
cardboard soaked in brine (electrolyte)
to increase the electrolytic conductivity.
Secondary Cell
BATTERY VS. CELL
- Can be recharged.
Cell - Chemical reactions reversed by
• Is a self contained compartment supplying electrical energy to the cell,
• Is unit which includes Two restoring their original composition.
electrodes and one electrolyte Advantage
Battery • Can be used multiple times.
• Two or more cells are connected Disadvantage
together, the combination is called • Has 2 chemical processes
battery.
Types of Secondary Cell - Batteries that successfully traverse the
• Solar Cell 0.5 V esophagus are unlikely to lodge to any
• Silver Cadmium 1.1 V location.
• Nickel-Cadmium 1.2 V - Liquefaction necrosis may occur
• Nickel-metal hydride 1.2 V because sodium hydroxide is generated
• Nickel iron (Edison Cell) 1.2 V by the current produced by the battery.
• Nickel Zinc 1.6 V - Perforation has occurred as rapidly as
• Lead-acid 2.1 V 6hrs after ingestion.
• Lithium-Ion 3.7 V
SWITCHES
HYDROMETER
- Flick it one way to go on and the other
- A device used to check the state of way to go off.
charge of a cell within a lead- acid
TWO STATES OF A SWITCH
battery.
Open
EXPLOSIONS
- No electrical connection
- Caused by misuse or malfunction of a
- There is a very high resistance between
battery, such as attempting to recharge
a wire coming into the switch and the
a primary battery.
wire going out of the switch.
- Car batteries, explosions occur when a
short circuit generates very large Closed
currents.
- Car batteries liberate hydrogen when - There is an electrical connection.
they are overcharged (because of - There is a very low resistance between a
electrolysis of the water in the wire coming into a switch and the wire
electrolyte). coming out of the switch.
3 IMPORTANT FEATURES TO CONSIDER WHEN
ENVIRONMENTAL CONCERNS SELECTING A SWITCH
- Widespread batteries can cause toxic - Contacts (single pole, double throw)
metal pollution. - Ratings (maximum voltage and current)
- Consumes resources and often involves - Method of operation (toggle, slide, key)
hazardous chemicals. SWITCH CONTACTS
- Contributes electronic waste.
Pole- number of switch contact sets.
INGESTION AND DEATH Throw- number of conducting positions, single
or double.
- Small button/ disk batteries can be
swallowed by kids. Way- Number of conducting positions, three or
- Battery electrical discharge can burn the more.
tissues and can be serious enough to Momentary- switch returns to its normal
lead to death. position when released.
Open- off position, contacts not conducting.
Closed- on position, contacts conducting, there
may be several on positions.
ON-(OFF)Push-to-break = SPST Momentary
SWITCH CONTACTS RATINGS
- A push-to-break switch returns to its
- Switch contacts are rated with normally closed (on) position when you
maximum voltage and current, and release the button.
there may be different ratings for AC
and DC. The AC values are higher
because the current falls to zero many
times each second and an arc is less
likely to form across the switch
contacts.
- For low voltage electronics projects the ON -ON Single Pole, Double Throw = SPDT
voltage rating will not matter - This switch can be on in both positions,
- The maximum current is less for switching on a separate device in each
inductive loads (coils and motors) case. It is often called a changeover
because they cause more sparking at switch. For example, a SPDT switch can
the contacts when switched off. be used to switch on a red lamp in one
position and a green lamp in the other
STANDARD SWITCHES position.
- A SPDT toggle switch may be used as a
ON-OFF Single Pole, Single Throw = SPST simple on -off switch by connecting to
COM and one of the A or B terminals
- A simple on-off switch. This type can be
shown in the diagram. A and B are
used to switch the power supply to a
interchangeable, so switches are usually
circuit. When used with mains
not labeled.
electricity this type of switch must be in
the live wire, but it is better to use a
DPST switch to isolate both live and
neutral.
ON -OFF -ONSPDT Centre Off A special version
(ON)-OFF Push-to-make = SPST Momentary of the standard SPDT switch.
- A push-to-make switch returns to its - It has a third switching position in the
normally open (off) position when you center which is off. Momentary (ON) -
release the button, this is shown by the OFF -(ON) versions are also available
brackets around ON. This is the where the switch returns to the central
standard doorbell switch. off position when released.
Dual ON-OFF Double Pole, Single Throw = DPST SPECIAL SWITCHES
- A pair of on-off switches which operate Push-Push Switch (e.g. SPST = ON-OFF)
together (shown by the dotted line in
- This looks like a momentary action push
the circuit symbol). A DPST switch is
switch but it is a standard on-off switch:
often used to switch mains electricity
push once to switch on, push again to
because it can isolate both the live and
switch off. This is called a latching
neutral connections.
action.
Micro switch (usually SPDT = ON-ON)
- Micro switches are designed to switch
fully open or closed in response to small
movements. They are available with
levers and rollers attached.
Key switch
Dual ON-ON Double Pole, Double Throw =
- A key operated switch. The example
DPDT
shown is SPST.
- A pair of on-on switches which operate
Tilt Switch (SPST)
together (shown by the dotted line in
the circuit symbol). - Tilt switches contain a conductive liquid
- A DPDT switch can be wired up as a and when tilted these bridges the
reversing switch for a motor as shown in contacts inside, closing the switch. They
the diagram. can be used as a sensor to detect the
position of an object. Some tilt switches
contain mercury which is poisonous.
Reed Switch (usually SPST)
- The contacts of a reed switch are closed
by bringing a small magnet near the
switch. They are used in security
circuits, for example to check that doors
are closed. Standard reed switches are
SPST (simple on-off) but SPDT
(changeover) versions are also available.
Warning: reed switches have a glass
body which is easily broken
Multi-pole Switch Relays
- The picture shows a 6-pole double - An electrical switch that opens and
throw switch, also known as a 6-pole closes under the control of another
changeover switch. It can be set to have electrical circuit. The switch is operated
momentary or latching action. Latching by an electromagnet to open or close
action means it behaves as a push-push one or many sets of contacts.
switch, push once for the first position, - Relays enable a low voltage circuit to
push again for the second position etc. switch on a high voltage or high current
circuit.
Multi-way Switch
- Multi-way switches have 3 or more
conducting positions. They may have
several poles (contact sets). A popular
type has a rotary action and it is
available with a range of contact
arrangements from 1-pole 12-way to 4-
pole 3 way. Solenoid
- The number of ways (switch positions) - Electromagnetic are used in solenoids
may be reduced by adjusting a stop to activate a plunger. When the solenoid
under the fixing nut. For example, if you is switched on, the plunger is attached
need a 2-pole 5-way switch you can buy to the coil.
the 2-pole 6-way version and adjust the
stop.
- Contrast this multi-way switch (many
switch positions) with the multi-pole
switch (many contact sets) described
above.
Motor
Tactile switch
- Motors are often used to turn wheels,
- This is a type of momentary pushbutton gears, cams, or pulleys. Motors have
switch. Tactile switches are rated by the two terminals that connect to a battery.
amount of force needed to push the The direction of the turning depends on
button and are often flat so that they the way the battery wires are connected
can be easily inserted within a surface to the terminals.
without protruding.
Stepper Motor
- Stepper motors are very precise motors
that can be made to turn through an
exact number of steps.
You might also like
- Electronics For Absolute BeginnersDocument17 pagesElectronics For Absolute Beginnersvladadj_1603No ratings yet
- Low Volatge and BatteryDocument74 pagesLow Volatge and BatteryOladokun Sulaiman OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument95 pagesChapter IIJohnfer AquinoNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument48 pagesElectrical Safetyvidya_artiNo ratings yet
- KU1202 Battery - 2022Document52 pagesKU1202 Battery - 2022Brian GilchristNo ratings yet
- Ece ReviewerDocument4 pagesEce ReviewerKwinn EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry BatteriesDocument11 pagesElectrochemistry BatteriesswazNo ratings yet
- Medical PhysicsDocument26 pagesMedical PhysicshayaNo ratings yet
- 17 Electrochemistry With Answers PDFDocument15 pages17 Electrochemistry With Answers PDFFirdausia Rahma Putri100% (1)
- Basic Electricity 1Document6 pagesBasic Electricity 1Joanna Fe JaimNo ratings yet
- 6 - Electric Potential Voltage For WeeblyDocument26 pages6 - Electric Potential Voltage For WeeblyPAYNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science & Technology University: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument37 pagesAddis Ababa Science & Technology University: Department of Chemical EngineeringdagmawiNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- Half-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarDocument3 pagesHalf-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarKirstie ImeldaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics I ReviewerDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics I ReviewerAyana Nylazir BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesForm 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsJu Li TanNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Electronic DC Conduction - ElectrochemistryDocument27 pagesIonic and Electronic DC Conduction - ElectrochemistryWilliam Sin Chau WaiNo ratings yet
- Cfe Bu2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCfe Bu2 ReviewerMaria Katrina Ilumin VersozaNo ratings yet
- Electrical System - Part1Document36 pagesElectrical System - Part1LARA JOANNE DORIANo ratings yet
- Batteries PDFDocument24 pagesBatteries PDFkaviyavikashini kaviyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in ElectrochemistryDocument19 pagesBasic Concepts in Electrochemistrynoor saqibNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Power Sources: BatteriesDocument31 pagesElectrochemical Power Sources: BatteriessudhaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation: Transducers and SensorsDocument36 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation: Transducers and SensorsAkhil WaliaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellDocument11 pagesElectrochemical CellssssNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument34 pagesElectricityPpppNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Electrochemistry R0 - 220830Document34 pages2.3 Electrochemistry R0 - 220830Kelly Roxelle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument12 pagesSeminarANKURNo ratings yet
- MP Lec 5 (3158)Document39 pagesMP Lec 5 (3158)Fateh RaufNo ratings yet
- 17 Electrochemistry With AnswersDocument15 pages17 Electrochemistry With AnswersAgam MittalNo ratings yet
- Ece LectureDocument5 pagesEce LecturechibiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell Project FileDocument16 pagesElectrochemical Cell Project Filevabhay22435No ratings yet
- Robotics Reviewer Quarter 1Document16 pagesRobotics Reviewer Quarter 1Dane Gian Angelo TanNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument9 pagesElectrochemistryFabian AvilaNo ratings yet
- Energy SystemsDocument73 pagesEnergy SystemsajayNo ratings yet
- (18530) Sheet 1 Electrochemistry B PDFDocument99 pages(18530) Sheet 1 Electrochemistry B PDFAnuragPandey100% (1)
- Batteries: Engr. Noornabi ShaikhDocument37 pagesBatteries: Engr. Noornabi ShaikhAyeshaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument27 pagesElectrochemistrymanishaNo ratings yet
- Lecture#02Document31 pagesLecture#02Sarmad AsadNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument153 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYSTUDY GRINDNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellDocument12 pagesElectrolytic CellabcNo ratings yet
- B U - Reviewer-1Document41 pagesB U - Reviewer-1Harvey MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- 2019-2020 Electrical Principles BookletDocument33 pages2019-2020 Electrical Principles Bookletthomaskm1327No ratings yet
- Batteries-B.tech First YearDocument7 pagesBatteries-B.tech First YeartifinNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free UNIT 2Document12 pagesWuolah Free UNIT 2javiosto3010No ratings yet
- RT4 - Reviewer For Comprehensive Exam 1Document11 pagesRT4 - Reviewer For Comprehensive Exam 1Aj PlacidoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocument4 pagesChemical Effects of Electric CurrentJayden DcostaNo ratings yet
- InterruptersDocument8 pagesInterruptersrichierichNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Electrical Energy Production LESSONS (22-23) 2Document45 pagesChapter 12 Electrical Energy Production LESSONS (22-23) 2irum qaisraniNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell: Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Chemistry For Grade 12Document8 pagesElectrochemical Cell: Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Chemistry For Grade 12Farhan Pranadarmesta MerchNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument26 pagesElectrochemical CellsNeveroy ReidNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument6 pagesFundamentals of ElectricityGABUAT, KIRK STEVEN P.No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument32 pagesElectrochemistrySHOBHIT GAUTAM 2K21/A12/72No ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument15 pagesChem ProjectAPARNA GANGWARNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers (Lec) - For MergeDocument10 pagesChemistry For Engineers (Lec) - For MergeCleofe Jane P. CasasNo ratings yet
- Electricity..class 7thDocument4 pagesElectricity..class 7thAyush Soni 7:- परिश्रम 3678No ratings yet
- Chemical EffectDocument12 pagesChemical EffectMohan LalNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and CircuitsDocument33 pagesElectric Current and CircuitssatikantNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Electricity and Circuits - Science Class 6 PDF DownloadDocument5 pagesStudy Notes - Electricity and Circuits - Science Class 6 PDF DownloadruchikaNo ratings yet
- Direct Current (DC) : Content of DC Sources of DC Impact of Different Cell ConnectionDocument5 pagesDirect Current (DC) : Content of DC Sources of DC Impact of Different Cell Connectionfmtt100% (1)