Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 He PDF
Uploaded by
Mervi Sarsonas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document discusses Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives which divides objectives into three domains: cognitive, psychomotor, and affective. It also discusses the importance of formulating clear objectives using the SMART criteria (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time-bound). Finally, it outlines steps for planning instruction including selecting content, choosing teaching methods, and evaluating learning.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 6 HE.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives which divides objectives into three domains: cognitive, psychomotor, and affective. It also discusses the importance of formulating clear objectives using the SMART criteria (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time-bound). Finally, it outlines steps for planning instruction including selecting content, choosing teaching methods, and evaluating learning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesChapter 6 He PDF
Uploaded by
Mervi SarsonasThis document discusses Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives which divides objectives into three domains: cognitive, psychomotor, and affective. It also discusses the importance of formulating clear objectives using the SMART criteria (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time-bound). Finally, it outlines steps for planning instruction including selecting content, choosing teaching methods, and evaluating learning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
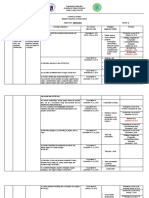
CHAPTER 6 Educational objectives suggested by Bloom (1984) are
PLANNING AND CONDUCTING CLASSES divided into 3 domains:
1. Cognitive (Knowing)
The Planning Sequence 2. Psychomotor (Doing)
1. Formulate objectives 3. Affective (Feeling, Valuing)
2. Select and organize content
3. Choose teaching methods Cognitive Domain
4. Design assignments ▪ factual knowledge, conceptual knowledge,
5. Evaluate learning procedural knowledge, metacognitive knowledge
▪ Measures knowledge by using oral and written tests
Course Outline or Syllabus Original subcategories:
▪ Include the following: knowledge, comprehension, application,
1. The name of the course analysis, synthesis and evaluation
2. The name of the instructor Revised subcategories (by Krathwohl):
3. A one-paragraph course description remember, understand, apply, analyze,
4. A list of course objectives evaluate and create
5. Teaching methods to be used
6. Textbook or other readings Psychomotor Domain
7. Methods of evaluation ▪ Teacher observes what the learners are actually
▪ Helps the learners to gauge what is to be learned and doing when performing skills
expected of them ▪ Learners demonstrate what they have learned
▪ Learning contract between teacher and learners Example: The learner will correctly mix two types of
▪ It should be followed insulin in one syringe.
▪ If there are changes in the course outline, the
learners should be notified Affective Domain
▪ Not so easy to write and measure—related to beliefs,
Formulating Objectives attitudes and values
▪ Written in a way that it has meaning for the learners Example: Asking the student to defend in writing the
▪ Reflect what the learner is supposed to do with what refusal of the nurse to divulge confidential
is taught information given by the patient. Demonstrates
positive attitudes towards the elderly while giving
Value of Objectives care
▪ Selection and handling of course materials
▪ Determine that learners in class have learned what is Wording of Objectives
taught ▪ Course Objectives are broadly stated
▪ Learners need to know more about a course Example: Recognize the parameters of effective
hemodialysis
Taxonomy of Objectives ▪ Class Objectives are usually few; written and
▪ Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (1956) distributed to the learners on a weekly basis
▪ Brainchild of several measurement specialists under
Benjamin Bloom Objective Characteristics:
▪ It was conceived as a means of facilitating the S = SPECIFIC
exchange of test items among faculty at various M = Measurable
universities in order to create bank of items, each A = Achievable
measuring the same educational objectives R = Realistic
(Krathwohl, 2002) T = Time Bounded
The essential components of instructionally sound Organizing Content, Headings, Subheadings
learning objectives can be organized into a mnemonic— ▪ Follow a logical sequence (moving from general to
ABCD, which represents: specific) or (from Simple to complex)
A = audience
B = behavior Selecting the Teaching Method
C = condition ▪ It depends on the following factors:
D = degree 1. Objective and type of learning one is trying to
achieve
The condition 2. Abilities of the teacher
▪ Part of an objective specifies the circumstances, 3. Compatibility of the teacher and the teaching
commands, directions, etc., that the student is given method
to initiate the behavior 4. Compatibility of the learner and the teaching
▪ diagram, given a map, after a lecture or method
demonstration, after completing the reading 5. Capabilities and the background level of the
learners
The behavior 6. Number of students
▪ A verb denotes an overt, observable action 7. Resources of the institution/school
(behavior), such as identify, name, list, describe, etc.
Choosing teaching Method
The degree ▪ Effectiveness of teaching methods depend on the
▪ Known as criteria, is a set of descriptions that outcome criterion
describe how well the behavior must be performed ▪ If it’s an acquisition of knowledge, lecture would be
to satisfy the intent of the behavioral verb useful—can be used in training sessions
The criterion Objective and Type of Learning One is Trying to Achieve
▪ Describing how well the learner must perform in ▪ Presentation of facts or rules (lecture with handouts)
order to be considered competent ▪ Molding attitude (case studies, discussion, role
▪ It answers the question, what do you expect the playing)
learner to be able to do in achieving an acceptable ▪ Motivating learners (gaming)
performance?
▪ Within a given period of time, such within 20 Methods in Evaluating Learning
minutes; or, according to the information given in the ▪ Placement evaluation (preassessment)
text, lab manual, lecture; or, in accordance with ➢ done before instruction
recommendations of some external source ▪ Diagnostic evaluation
➢ attempts to discover the causes of student’s
learning problems
▪ Formative evaluation
➢ monitors progress during the learning
process
▪ Summative evaluation
➢ takes place at the end of an instructional unit
or course
You might also like
- DVK Book Research Resilence Workbook Exercises For ChaptersDocument14 pagesDVK Book Research Resilence Workbook Exercises For ChaptersDeirdre25% (4)
- Richards, Jack C. Reflective Teaching in Second Language ClassroomsDocument35 pagesRichards, Jack C. Reflective Teaching in Second Language ClassroomsMelisaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocument6 pagesModule 7 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingSheila Mae Paltep100% (9)
- Getting Started with Teacher Clarity: Ready-to-Use Research Based Strategies to Develop Learning Intentions, Foster Student Autonomy, and Engage StudentsFrom EverandGetting Started with Teacher Clarity: Ready-to-Use Research Based Strategies to Develop Learning Intentions, Foster Student Autonomy, and Engage StudentsNo ratings yet
- Facility Management Professional: Ifma'S FMP CredentialDocument5 pagesFacility Management Professional: Ifma'S FMP Credentialsanthosh kumar t mNo ratings yet
- FCI Management TraineeDocument2 pagesFCI Management TraineeVijay Kumar100% (2)
- High Quality AssessmentDocument7 pagesHigh Quality AssessmentCRISTIANDION YBANEZNo ratings yet
- Method - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Document90 pagesMethod - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Dr. Tapan Kr. Dutta100% (1)
- Instructional Planning and DevelopmentDocument27 pagesInstructional Planning and DevelopmentEiram Flores100% (2)
- ICT Level 2 Practice Test PDFDocument15 pagesICT Level 2 Practice Test PDFSalih Anwar93% (15)
- 4k1zx C S I U T U S T S I H eDocument147 pages4k1zx C S I U T U S T S I H eleandromacnNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Math 7 Q3Document3 pagesCurriculum Map Math 7 Q3richard alicawayNo ratings yet
- Elements or Components of A Curriculum DesignDocument5 pagesElements or Components of A Curriculum DesignErrol CatimpoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Learning OutcomesDocument36 pagesAssessing Learning OutcomesAllison Yambao CastroNo ratings yet
- Instructional PlanningDocument15 pagesInstructional Planningniksolehin82% (11)
- Lesson Plan 7es and 4asDocument61 pagesLesson Plan 7es and 4asdudzkie angelo100% (1)
- Calawag Vs Up VisayasDocument1 pageCalawag Vs Up VisayasEileen Eika Dela Cruz-LeeNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation Tool-Rpms: Teacher I-IiiDocument12 pagesClassroom Observation Tool-Rpms: Teacher I-IiiRandyllan BantuganNo ratings yet
- Lte 1 Asc 1Document9 pagesLte 1 Asc 1Cyrus CortezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Unit 1Document14 pagesAssessment Unit 1Jhazz Gabieta100% (2)
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2Judelyn Alfonte ReladorNo ratings yet
- Assessment Unit 111Document14 pagesAssessment Unit 111Jhazz GabietaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Model of Teaching - BDocument51 pagesTopic 2 - Model of Teaching - Bg-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- 01 TCUR111 Course Unit 5Document8 pages01 TCUR111 Course Unit 5Sunako ClaesNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewernicole.goco7No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Instructional DesignDocument21 pagesTopic 2 - Instructional DesignHamizah ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- PSTM Group 3 ReportingDocument4 pagesPSTM Group 3 Reportingcheska cNo ratings yet
- Tefl-Lesson PlanDocument30 pagesTefl-Lesson PlanMaulidea PutriNo ratings yet
- CED106 ReviewerDocument3 pagesCED106 ReviewerNana's StrawberryNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثامنةDocument41 pagesالمحاضرة الثامنةalpha academyNo ratings yet
- Less0n Plan by AhmedDocument29 pagesLess0n Plan by AhmedashrafalisqNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes and KPIsDocument74 pagesLearning Outcomes and KPIsKRISTINo ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Teachinghataki878No ratings yet
- Educator AS Assessor . Name: PamellaDocument12 pagesEducator AS Assessor . Name: PamellapamellaNo ratings yet
- SAS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Basic Concepts and Principles of AssessmentDocument86 pagesSAS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Basic Concepts and Principles of AssessmentJade SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Title of The Lesson Time Required To Complete The LessonDocument4 pagesTitle of The Lesson Time Required To Complete The LessonAustine TangNo ratings yet
- GN - Shindume GuideDocument35 pagesGN - Shindume Guideeddypnd.ngNo ratings yet
- Guidelines: Nursing DepartmentDocument33 pagesGuidelines: Nursing DepartmentIvanah Mae AcloNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Lesson PlansDocument29 pagesSession 2 - Lesson PlansHussein AlwaseefNo ratings yet
- 5 Instructional Objectives and Sessionl PlanningDocument18 pages5 Instructional Objectives and Sessionl Planningfaridkhan100% (5)
- Anne Davies Assessment Course NotesDocument8 pagesAnne Davies Assessment Course Notesapi-504234130No ratings yet
- All 1 Lesson 2Document22 pagesAll 1 Lesson 2Reynoel CaneteNo ratings yet
- Cy Lte1Document9 pagesCy Lte1Cyrus CortezNo ratings yet
- Health Education NotesDocument13 pagesHealth Education NotesZEPHANNY ANNE TABBAYNo ratings yet
- ORANGE TEAM - Written ReportDocument6 pagesORANGE TEAM - Written ReportAlyssa Ashley A. ImamNo ratings yet
- Lesson IX Approaches Strategies and Methods in Teaching Science in The Elementary GradesDocument35 pagesLesson IX Approaches Strategies and Methods in Teaching Science in The Elementary GradesGracelyn Alcaraz RoxasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning: Mark Lawrence A. FernandezDocument40 pagesLesson Planning: Mark Lawrence A. FernandezAssej Mae Pascua villaNo ratings yet
- Gchs Alta Vista - How We Plan 2Document9 pagesGchs Alta Vista - How We Plan 2api-242583573No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - April 18, 20223Document42 pagesLesson Plan - April 18, 20223JADE THERESE RAMOSNo ratings yet
- PED 4 Methods and Strategies of TeachingDocument20 pagesPED 4 Methods and Strategies of TeachinglorylainevalenzonatorresNo ratings yet
- Planning and Conducting ClassesDocument23 pagesPlanning and Conducting ClassesjehzamudioNo ratings yet
- Basics of Assessment of Learning 1Document23 pagesBasics of Assessment of Learning 1Ay BanNo ratings yet
- Smithsonian Stcms Assessment FlyerDocument4 pagesSmithsonian Stcms Assessment FlyercontactsikhiaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 30083 - Chapter 2Document48 pagesEDUC 30083 - Chapter 2Kirstin VeronicaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 90 Task 1Document6 pagesEDUC 90 Task 1Gliecy OletaNo ratings yet
- A. High Quality Assessment in Retrospect - 075547Document8 pagesA. High Quality Assessment in Retrospect - 075547ghela0511No ratings yet
- archLESSON PLAN SCIENCEDocument4 pagesarchLESSON PLAN SCIENCEANGELIKA ABORITANo ratings yet
- Planning and Organizing For Instruction: Prepared By: Group 2 Flordela Sanchez Maria Leonora Patriarca Jherilyn ObcianaDocument21 pagesPlanning and Organizing For Instruction: Prepared By: Group 2 Flordela Sanchez Maria Leonora Patriarca Jherilyn ObcianaAmeil OrindayNo ratings yet
- C10 Behavioral ObjectivesDocument8 pagesC10 Behavioral ObjectivesChloe CatibudNo ratings yet
- Compiled PSSIM MODULE 1 16Document20 pagesCompiled PSSIM MODULE 1 16Glyde Maye BostonNo ratings yet
- ESP Course DesignDocument12 pagesESP Course DesignDesy Liliani HusainNo ratings yet
- Health Education 2 2Document13 pagesHealth Education 2 2simbulanrhaiza2No ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanNhico BryanNo ratings yet
- Aol Lesson 1, Topic 1Document7 pagesAol Lesson 1, Topic 1Nicole Dennise NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- EDUC 202 Assessment in Learning 1 Lesson 1Document21 pagesEDUC 202 Assessment in Learning 1 Lesson 1Janzen A. GabioNo ratings yet
- Assessment in EnglishDocument25 pagesAssessment in EnglishjeromeNo ratings yet
- How to Practice Before Exams: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Study Techniques, Time Management, and Stress Relief for Exam SuccessFrom EverandHow to Practice Before Exams: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Study Techniques, Time Management, and Stress Relief for Exam SuccessNo ratings yet
- O Estudo Acompanhado: Como Ensinar e Auxiliar um Estudante a Aprender com AutonomiaFrom EverandO Estudo Acompanhado: Como Ensinar e Auxiliar um Estudante a Aprender com AutonomiaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ndwu1012 English I Updated 15jan2015Document4 pagesSyllabus Ndwu1012 English I Updated 15jan2015Nur Amalina SyahindahNo ratings yet
- ESP Module 1 Unit 4Document9 pagesESP Module 1 Unit 4Kristine YalunNo ratings yet
- Ms. Shipra JainDocument2 pagesMs. Shipra JainDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Raising The Reading Skills of Grade 3 Students of Bagumbayan Central School - 070307Document6 pagesRaising The Reading Skills of Grade 3 Students of Bagumbayan Central School - 070307Elizabeth NocilladoNo ratings yet
- Cornell Student-Alumni Mentor Program HandbookDocument10 pagesCornell Student-Alumni Mentor Program HandbookAniAceNo ratings yet
- How Education System Has Changed in The PastDocument10 pagesHow Education System Has Changed in The Pasta bdusta lsNo ratings yet
- Cristo Rey Central Elementary School: Edukasyon Sa PagpapakataoDocument1 pageCristo Rey Central Elementary School: Edukasyon Sa PagpapakataoElla DavidNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Persuasive Strategies in English Social and Commercial AdvertisementsDocument37 pagesComparative Analysis of Persuasive Strategies in English Social and Commercial AdvertisementsJOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN LINGUISTICSNo ratings yet
- Ellie Espiritu - Resume WsDocument1 pageEllie Espiritu - Resume Wsapi-510163231No ratings yet
- BSBCMM401 Learner Workbook V1.1 - Shortened Version - TMSSDocument58 pagesBSBCMM401 Learner Workbook V1.1 - Shortened Version - TMSSAryan Singla100% (1)
- Flow Chart English Courses 2019 Dec 9-2Document1 pageFlow Chart English Courses 2019 Dec 9-2A HughesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Ed 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan Ed 1zachharveyneilNo ratings yet
- Anderson & Otalora - 2010 - Designing A Course On CLIL For In-Service Teacher Education PDFDocument32 pagesAnderson & Otalora - 2010 - Designing A Course On CLIL For In-Service Teacher Education PDFcarlazNo ratings yet
- Traning and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesTraning and Developmentpeace.missileNo ratings yet
- Emt203 Assessment 2Document8 pagesEmt203 Assessment 2api-354631612No ratings yet
- RPH Year 1,2,4Document11 pagesRPH Year 1,2,4Ieka ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLAN MATHEMATICS-6 Q1 W9-DemoDocument3 pagesLESSON-PLAN MATHEMATICS-6 Q1 W9-DemoMini DachshundNo ratings yet
- Programmes and Courses in EnglishDocument175 pagesProgrammes and Courses in EnglishCarlos EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Hereth EslDocument60 pagesHereth Eslapi-308547775No ratings yet
- Simple Vak QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesSimple Vak Questionnairer3belzNo ratings yet
- DLL RWS Week 6Document4 pagesDLL RWS Week 6lorenzo corulloNo ratings yet
- Twenty Tips For Developing Positive Relationships With ParentsDocument3 pagesTwenty Tips For Developing Positive Relationships With Parentssaema_pNo ratings yet