Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control Lec 1
Uploaded by
Asfand Haroon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesControl SS and TS
Original Title
Control lec 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentControl SS and TS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesControl Lec 1
Uploaded by
Asfand HaroonControl SS and TS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
4 MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A CONTROL SYSTEM
ELEC207 - Control Theory [Lecture 1: Introduction]
Prof Simon Maskell, <s.maskell@liverpool.ac.uk>
January 27, 2023
1 Lecture Learning Objectives
Function, architecture, history and applications of a control system
Open-loop and closed-loop systems
Mathematical model of a control system
2 Function, architecture, history and applications of a con-
trol system
Control is making machines do what they are supposed to do. It was arguably the first multi-
disciplinary subject.
Control has had and continues to have many applications, for example:
Manufacturing Processes;
Autonomous systems (eg Unmanned Air Vehicles).
3 Open-loop and closed-loop systems
The use of a sensor to provide feedback is the crucial idea:
Open-loop control systems (with no feedback) are very hard to design.
Closed-loop control systems (with feedback) are much easier to get to work.
4 Mathematical model of a control system
An open-loop control system is depicted in figure 1. A common decomposition of the plant is shown
in figure 2. A closed-loop control system is shown in figure 3.
ELEC207 Lecture Notes: Lecture 1 (Introduction), Page 1
4 MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A CONTROL SYSTEM
Figure 1: Open Loop Control System
Figure 2: Plant
ELEC207 Lecture Notes: Lecture 1 (Introduction), Page 2
4 MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A CONTROL SYSTEM
Figure 3: Closed Loop Control System
ELEC207 Lecture Notes: Lecture 1 (Introduction), Page 3
You might also like
- Control Systems U1 (TEL306)Document77 pagesControl Systems U1 (TEL306)Ruvenderan SuburamaniamNo ratings yet
- Dorfch1 PDFDocument36 pagesDorfch1 PDFA6427531100% (1)
- Principles of Automatic ControlDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Automatic ControlMesut OzilNo ratings yet
- Design & Simulation of Electro-Pneumatic SystemDocument54 pagesDesign & Simulation of Electro-Pneumatic SystemSaravanan Mathi0% (2)
- DCSDocument57 pagesDCSRanjita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Abiyot egataNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 - Control SystemDocument25 pagesModule - 1 - Control SystemRonitNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MergedDocument209 pagesModule 1 MergedDivyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Control EngineeringDocument29 pagesControl EngineeringJonathan PereaNo ratings yet
- Me2009 - Control System Technology Lab Assignment 3: Hochiminh City University of Technology Mechatronics DepartmentDocument10 pagesMe2009 - Control System Technology Lab Assignment 3: Hochiminh City University of Technology Mechatronics DepartmentPhan Dương KhiemNo ratings yet
- Design & Simulation of Electro-Pneumatic System Using PLC Automation StudioDocument54 pagesDesign & Simulation of Electro-Pneumatic System Using PLC Automation StudiomikostovNo ratings yet
- Prelim-MODULE 1Document11 pagesPrelim-MODULE 1Celimen, John Renz C.No ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument16 pagesControl Systemmsm158No ratings yet
- From - Control System Design - by Karl Johan Åström, 2002Document38 pagesFrom - Control System Design - by Karl Johan Åström, 2002VigneshRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Control System 2Document36 pagesControl System 2RajeevSangamNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechatronics - Control - DevicesDocument40 pages1 Mechatronics - Control - DevicesAdrian GCNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control Systems: Theme 1Document16 pagesIntroduction To Control Systems: Theme 1Murphy's LawNo ratings yet
- 01-Introduction To Control SystemsDocument14 pages01-Introduction To Control SystemsAhmed JouleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument68 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionNtiyisoColbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OneDocument31 pagesChapter 1 OneKibrom MenasboNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument70 pagesLecture NotesPrathamraj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 35 MT227 Modern and Optimal ControlDocument2 pages35 MT227 Modern and Optimal ControlBrenyi Zanabria ConchaNo ratings yet
- Power System StabilityDocument9 pagesPower System StabilityMyScribdddNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bottle Filling and Capping Control SystemDocument41 pagesAutomatic Bottle Filling and Capping Control SystemoscarNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - LECTURE NOTESDocument132 pagesControl Systems - LECTURE NOTESgutha manikantaNo ratings yet
- IEC 1499 (Funciones)Document10 pagesIEC 1499 (Funciones)Marcos RosenbergNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Compressed WatermarkDocument71 pagesControl Engineering Compressed WatermarkBasava RajNo ratings yet
- Information Sciences: Yufeng Chen, Zhiwu Li, Kamel BarkaouiDocument17 pagesInformation Sciences: Yufeng Chen, Zhiwu Li, Kamel BarkaouiitzgayaNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV Distributed Control System: SyllabusDocument19 pagesUnit - IV Distributed Control System: SyllabusRandom ManNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document41 pagesUnit 1Rudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument7 pagesUnit IanandhNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Model-Based Development of Control Systems For Forestry CranesDocument16 pagesResearch Article: Model-Based Development of Control Systems For Forestry Cranesgil lerNo ratings yet
- Control in Nonlinear SystemsDocument11 pagesControl in Nonlinear Systemsdiego ivan perea montealegreNo ratings yet
- System Modeling: PRESSENTED BY:-Er. Saurabh MalpotraDocument36 pagesSystem Modeling: PRESSENTED BY:-Er. Saurabh MalpotraCr ZyNo ratings yet
- Bjectives: Chapter 1: Introduction To Control Systems ODocument41 pagesBjectives: Chapter 1: Introduction To Control Systems OabosheebaNo ratings yet
- Modeling An Oil Drilling Rig Total Productive ...Document10 pagesModeling An Oil Drilling Rig Total Productive ...cpmrNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control Techniques For CSTR Using MatlabDocument9 pagesModel Predictive Control Techniques For CSTR Using MatlabJeeva MJNo ratings yet
- Study of Model Predictive Control Using Ni LabviewDocument10 pagesStudy of Model Predictive Control Using Ni LabviewBrankko Jhonathan Torres SaavedraNo ratings yet
- MechatronicsDocument264 pagesMechatronicschandra shekharNo ratings yet
- Control EngineeringDocument5 pagesControl EngineeringAliceAlormenuNo ratings yet
- Bio Control SystemDocument87 pagesBio Control SystemRajeevSangamNo ratings yet
- Ec2255 - Control SystemDocument42 pagesEc2255 - Control SystemK.RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Modeling Simulation and Control of Large Scale CryDocument6 pagesModeling Simulation and Control of Large Scale CryPhilippe GayetNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dynamic System ModellingDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Dynamic System Modellingk_472894540No ratings yet
- Engineering: Systems The Glass IndustryDocument13 pagesEngineering: Systems The Glass IndustryAmer AlkalaifhNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Is Based On The Foundations of Feedback Theory and Linear System Analysis, and It GeneratesDocument38 pagesControl Engineering Is Based On The Foundations of Feedback Theory and Linear System Analysis, and It GeneratesRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
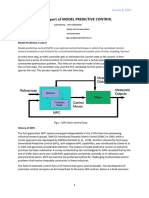
- Model Predictive ControlDocument6 pagesModel Predictive Controltigy vargheseNo ratings yet
- AR - Module-1 Q & A (SEE)Document8 pagesAR - Module-1 Q & A (SEE)Simply AkashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Control Systemsearnest normanNo ratings yet
- Control System Unit 1 (5 TH Sem.)Document61 pagesControl System Unit 1 (5 TH Sem.)kishan guptaNo ratings yet
- Logics and Distributed Control SystemDocument25 pagesLogics and Distributed Control SystemJoshNo ratings yet
- Bjectives: Chapter 1: Introduction To Control Systems ODocument41 pagesBjectives: Chapter 1: Introduction To Control Systems OYadana1No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Control SystemsDocument36 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Control SystemsBoon Keat Chung0% (1)
- Control System PresentationDocument10 pagesControl System PresentationVikneshwaran Keluan SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction: IME-365-Instrumentation and Control (Spring 2021)Document50 pagesCH 1 Introduction: IME-365-Instrumentation and Control (Spring 2021)Hammad AliNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Operations by Relation Extraction For Manufacturing Cell ControllersDocument16 pagesCoordination of Operations by Relation Extraction For Manufacturing Cell ControllersJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Articulo An Introduction To Event-Based Control For Networked Control SystemsDocument6 pagesArticulo An Introduction To Event-Based Control For Networked Control SystemsPaulina MarquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lecture 1 Introduction To Control SystemDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Lecture 1 Introduction To Control SystemOngNo ratings yet