Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lipids Presentation
Uploaded by
api-6665676240 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views13 pagesLipids serve three main purposes in the body: [1] They store energy in fatty tissue; [2] Fatty tissue provides insulation and protection; [3] Lipids are structural components of cell membranes. Lipids are found in fats, oils, waxes, hormones, and cell membranes. The hydrophobic tails of lipids face the interior of the cell membrane, while the hydrophilic head contains a negatively charged phosphate group. The nonpolar tails are insoluble in water, whereas the polar heads are soluble.
Original Description:
Original Title
lipids presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLipids serve three main purposes in the body: [1] They store energy in fatty tissue; [2] Fatty tissue provides insulation and protection; [3] Lipids are structural components of cell membranes. Lipids are found in fats, oils, waxes, hormones, and cell membranes. The hydrophobic tails of lipids face the interior of the cell membrane, while the hydrophilic head contains a negatively charged phosphate group. The nonpolar tails are insoluble in water, whereas the polar heads are soluble.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views13 pagesLipids Presentation
Uploaded by
api-666567624Lipids serve three main purposes in the body: [1] They store energy in fatty tissue; [2] Fatty tissue provides insulation and protection; [3] Lipids are structural components of cell membranes. Lipids are found in fats, oils, waxes, hormones, and cell membranes. The hydrophobic tails of lipids face the interior of the cell membrane, while the hydrophilic head contains a negatively charged phosphate group. The nonpolar tails are insoluble in water, whereas the polar heads are soluble.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
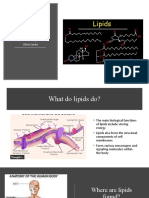
Lipids
Isabella Garcia, Jade Moreno, Isabella Ontiveros, Sam Quevedo
• Lipids store energy- Excess food and
energy into fatty tissue
• Insulation and protection- Fatty tissue
Purpose provides insulation
• Structural components of cell
membranes
Where are lipids
found?
Examples of lipids
• Fats
• Oils
• Waxes
• Hormones
• Cell membranes (not made of
protein)
Which part of the lipid is
hydrophobic? What
does that mean?
• The part of the lipid that is
hydrophobic are the tails
that face the interior of
the cell membrane
• (water fearing).
Which part of a lipid is hydrophilic?
What does that mean?
• Hydrophilic: Tendency to mix or
dissolve in water
• Lipids head is hydrophilic
• The head contains a negatively
charged phosphate group
• Insoluble: Substance incapable
of being dissolved
• Lipids in water are unable to be
dissolved
Which part of a • Water is a polar molecule and
Lipids
lipid is insoluble?
What does that
mean?
Which part of a lipid is non
polar? What does that mean?
• Non polar: Type of chemical bond
formed when electrons are shared
equally between two atoms
• Non polar lipids bind to
themselves which is why oils and
fats surface water
Which part of the lipid is
polar? What does that
mean?
-The heads (the phospho part) are polar while the tails
(the lipid part) are non-polar.
What are waxes?
• Waxes are a lot of chains of fatty acids that are
connected that create a hydrophobic surface
• This surface is sometimes seen on plants and some
animals like ducks and penguins
• Nonpolar chemical substance that is composed
What are oils? primarily of hydrocarbons
• Both hydrophobic and lipophilic
What are fats?
• Fats are a micronutrient found in
foods
• Composed of fatty acids
What is insulation?
• Insulation is the use of lipids in a
organism's body that helps
maintain the desirable temperature
on the inside of it's body
• For example: humans have a thin
layer of fat just beneath their skin
that helps regulate temperature
You might also like
- Lipids PowerpointDocument15 pagesLipids Powerpointapi-321789351100% (1)
- LIPIDS D PharmDocument65 pagesLIPIDS D PharmMadhuri poulkarNo ratings yet
- Lipids ReportDocument33 pagesLipids ReportCaryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- G10 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesG10 BiomoleculesMc AcebarNo ratings yet
- Lipids 1Document56 pagesLipids 1Arby Joy ManandegNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document13 pagesPresentation 4api-666782867No ratings yet
- Mlt-401 Biochemistry & Basic Hematology: By: Khushbu SoniDocument19 pagesMlt-401 Biochemistry & Basic Hematology: By: Khushbu Sonikhushbu rajanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Lipids: Laureno, Liza Marie B. G11-EpicurusDocument13 pagesBiomolecules: Lipids: Laureno, Liza Marie B. G11-EpicurusLizaNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument4 pagesLIPIDSJasper VillegasNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: What Molecules Keep Us Alive, and How Do They Do So?Document48 pagesBiomolecules: What Molecules Keep Us Alive, and How Do They Do So?Dummy AccountNo ratings yet
- BMS1011 Week3 L5Document25 pagesBMS1011 Week3 L5Arshaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Lipids in BiochemistryDocument19 pagesLipids in BiochemistryShaista AkbarNo ratings yet
- Final LipidsDocument17 pagesFinal Lipidssamantha garciaNo ratings yet
- Repot LipidsDocument36 pagesRepot LipidsAlyssa OngNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - LipidsDocument32 pagesWeek 3 - LipidsNICOLE KAYE MANALANGNo ratings yet
- Lipids in BiologyDocument17 pagesLipids in Biologyhaiderhacker2004No ratings yet
- MTChem2 Lab Module 3 Exp 5Document3 pagesMTChem2 Lab Module 3 Exp 511stem2.enriquemariajulianaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - TriglyceridesDocument28 pagesTopic 7 - TriglyceridestnotchwNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM LAB - Module 6Document4 pagesBIOCHEM LAB - Module 6TURARAY FRANCES MERLENENo ratings yet
- The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules الجزيئات الاربع الحيوية الاكبر في تركيب الكائناتDocument29 pagesThe FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules الجزيئات الاربع الحيوية الاكبر في تركيب الكائناتIraqiNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument30 pagesLipidsArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- BIO 111 Lecture LIPIDSDocument40 pagesBIO 111 Lecture LIPIDSChileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- 3 LipidsDocument24 pages3 LipidsJeswant T SNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument36 pagesThe Chemistry of LifeDeborah FisherNo ratings yet
- Classificiation of LipdisDocument33 pagesClassificiation of LipdisArslan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lipidss (Autosaved)Document21 pagesLipidss (Autosaved)ANo ratings yet
- Lipids: Unit 2: Part 1: Biological MoleculesDocument14 pagesLipids: Unit 2: Part 1: Biological MoleculesAtreyee De ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life 4th Form Life ScienceDocument42 pagesChemistry of Life 4th Form Life Sciencerileydebeer21No ratings yet
- AHS-Lipid Classiication & PropertiesDocument46 pagesAHS-Lipid Classiication & PropertiesManigandanNo ratings yet
- Hoy Ito Na Talaga Final LipidsDocument19 pagesHoy Ito Na Talaga Final LipidsJohn Daniel PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument53 pagesLipid ChemistryMayuri DhanushwarNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellDocument11 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The Cell陈康德No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biological Molecules: Santa Laurensia Senior High SchoolDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Biological Molecules: Santa Laurensia Senior High SchoolDeddy KismanaNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Long Term Energy Storage Concentrated EnergyDocument22 pagesLipids: Long Term Energy Storage Concentrated EnergyLoreta Avenido PertosNo ratings yet
- Basic Molecules of LifeDocument78 pagesBasic Molecules of LifeRavi ParkheNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument2 pagesLIPIDSAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument36 pagesLipidSina AgataNo ratings yet
- Lec 28. LipidsDocument14 pagesLec 28. LipidsJawher AliNo ratings yet
- Module On LipidsDocument15 pagesModule On LipidsBioclass BitesNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument6 pagesLIPIDSluzvi3110No ratings yet
- BioChem - LipidsDocument41 pagesBioChem - LipidsKYLE ANDREW SAWITNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document20 pagesWeek 4ML MLNo ratings yet
- Lipids - Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesLipids - Structure & FunctionPrashasti TiwariNo ratings yet
- L-1 Fatty Acids & LipidsDocument4 pagesL-1 Fatty Acids & LipidsLiyakath AliNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument44 pagesBIOMOLECULESSarah SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 LipidsDocument44 pagesLecture8 Lipidsfirst name last nameNo ratings yet
- Lipids (Stem G2)Document29 pagesLipids (Stem G2)Amielle LappayNo ratings yet
- Lipids by JastheneDocument11 pagesLipids by JastheneTin AngelesNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellDocument11 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellMohd IyadRaissa HijazNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Important Secondary Source of Energy in The BodyDocument4 pagesLipids: Important Secondary Source of Energy in The BodyAshley UmNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SHS 8.3 LipidsDocument17 pagesPhysical Science SHS 8.3 LipidsjouselleduayNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules of Cell: DR G V RamanaDocument24 pagesBiomolecules of Cell: DR G V RamanaSATYAJIT SAHUNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Document15 pagesChemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of CellDocument35 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of Cellgregory gumbangNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Essential For Vital Processes.: Series of Chemical ReactionsDocument75 pagesMetabolism Essential For Vital Processes.: Series of Chemical ReactionsValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 LipidsDocument4 pagesLesson 8 LipidsJanet Floreno VillasanaNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument4 pagesLipidAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Mls 311 Lecture Notes 4Document28 pagesMls 311 Lecture Notes 4CoffeeswanNo ratings yet
- Lipids and FatsDocument28 pagesLipids and FatsGericho UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet