Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cycle
Uploaded by
Xiasama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagescomplete cell cycle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcomplete cell cycle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCell Cycle
Uploaded by
Xiasamacomplete cell cycle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Cell Cycle
Wednesday, 12 April 2023
6:05 pm
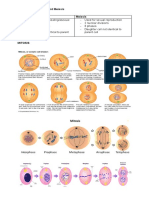
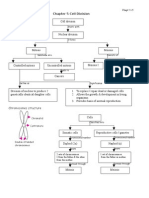
Mitosis
-the process by which a cell replicates its chromosomes and then segregates them, producing two
identical nuclei in preparation for cell division.
-Same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell.
-2 daughter cells
Meiosis
-a type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that reduces the number of chromosomes in
gametes
-1/2 the amount of chromosomes of the parent cell
-4 daughter cells
Phases:
Prophase
-the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into
two identical daughter cells.
Metaphase
-the point at which all of the chromosome pairs are fully condensed, attached to the mitotic spindle, and
aligned at the center.
-Spindle Fiber attaches to the centromere in the center of the cell.
Anaphase
- the stage in mitosis or meiosis following metaphase in which the daughter chromosomes move away
from each other to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase
-the final stage of cell division in which the spindle disappears and the nucleus forms around each set of
daughter chromosomes.
-This is where a furrow appears.
Cytokinesis
- the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter
cells.
Cell Cycle
-a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides.
Haploid
-One set of chromosomes (1/2 mother, 1/2 father)
Diploid
-the number of complete chromosome sets present in each cell of an organism
-diploid cells contain two complete sets
Homologous
-having the same relative position, value, or structure.
During 1st division, the exchange of genes is called "crossing over"
-Only in Meiosis
-they separate in 2nd division
Gamete
-a reproductive cell of an animal or plant.
Human
23 pairs of chromosomes (46)
Male - XY
Female - XX
When does Meiosis happen?
Male
At the start of puberty
Female
Before birth
You might also like
- Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiology Reviewerleleidy19emanoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis MeiosisJascha Isaac PangandianNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Key PointsDocument10 pagesCell Division - Key PointssivarajeshwarNo ratings yet
- 6 - The Cell Cycle, Meiosis, MitosisDocument13 pages6 - The Cell Cycle, Meiosis, MitosisHarold BrausteinNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument6 pagesMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument10 pagesMitosisSoulseekerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Document42 pagesChapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Nehjoy GerangueNo ratings yet
- Science ResearchDocument3 pagesScience ResearchShaira Jea ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 4 Notes (Grade 11)Document7 pagesBio Chapter 4 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (2)
- Chapter 5: Cellular ReproductionDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Cellular ReproductionDarwin Competente LagranNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDocument11 pagesCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyNo ratings yet
- Key Points (2 Copies)Document1 pageKey Points (2 Copies)Zendrix PauloNo ratings yet
- CH 15 NotesDocument5 pagesCH 15 NotesCJNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesMeiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Notes: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesNotes: Mitosis and MeiosisMazhar HaseebNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Anaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesDocument19 pagesAnaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesLucy AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- 4.2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument7 pages4.2 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument28 pagesMitosis and MeiosisPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division:-: Presented By:-Priyanjali Saini Nursing Tutor H.C.N.SDocument28 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division:-: Presented By:-Priyanjali Saini Nursing Tutor H.C.N.SPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Biology Semester 1 PST Modul 1 Kolej Matrikulasi Perak Chap 3 NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Semester 1 PST Modul 1 Kolej Matrikulasi Perak Chap 3 Notesrupertgrint200050% (2)
- Cell Division Personal Modified NotesDocument5 pagesCell Division Personal Modified NotesAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Personal Modified NotesDocument6 pagesCell Division Personal Modified NotesAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inDocument29 pagesMeiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inyamamaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - 2.structure of Chromosomes - 3.principles of GeneticsDocument148 pagesCell Division - 2.structure of Chromosomes - 3.principles of Geneticsankurbiology0% (1)
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocument11 pagesWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNo ratings yet
- Day 2 and 3 - Mitosis and MeiosisDocument63 pagesDay 2 and 3 - Mitosis and MeiosisDarlene Joyce ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Cell Division LessonDocument9 pagesCell Division LessonGerry100% (1)
- Biologists Traditionally Classify All Living Organisms Into Two Major GroupsDocument2 pagesBiologists Traditionally Classify All Living Organisms Into Two Major GroupsrahafNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisDocument27 pagesCell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisAngryBird_jinx100% (1)
- Biology 101 Module 4 Study GuideDocument18 pagesBiology 101 Module 4 Study GuideAdam GlassnerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Cell DivisionMaria Jose UribeNo ratings yet
- Cell Division (Edited)Document12 pagesCell Division (Edited)Ian Karlo NuñezNo ratings yet
- Mitosis NotesDocument15 pagesMitosis NotesAdam GlassnerNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Into Two Identical Daughter Cells (Cell Division)Document10 pagesMitosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Into Two Identical Daughter Cells (Cell Division)Holly Mc Kenzie Layson DalmanNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes Part 3Document13 pagesBotany Notes Part 3Rochenick MagoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle LectureDocument3 pagesCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesThe Cell CycleAngelooNo ratings yet
- Mitosis SsDocument21 pagesMitosis SsTamara RobertsNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Cell ReproductionDocument29 pagesChromosomes and Cell ReproductionTahreem BhattiNo ratings yet
- Module Three: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue LevelDocument35 pagesModule Three: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue LevelRoslyn TaylorNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle &division: Preexisting Cells Cell Division Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Some Tissues Must Be Repaired OftenDocument13 pagesCell Cycle &division: Preexisting Cells Cell Division Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Some Tissues Must Be Repaired OftenHafidzul A'limNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5Document5 pagesChapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5ctazimaNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-7 - Cell DivisionsDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-7 - Cell DivisionsMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NOTESDocument11 pagesMitosis Meiosis NOTESCaden DiazNo ratings yet
- 01 ReproductiveDocument58 pages01 Reproductiveglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument17 pagesBiologyMuskan ShreeNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument18 pagesMITOSISEdryan LambiquitNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument7 pagesCell DivisionJanella RedrinoNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis: All Sexual Life CyclesDocument23 pagesChromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis: All Sexual Life CyclesKevin KipkemboiNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle Activity 1Document5 pagesThe Cell Cycle Activity 1sugarxglossNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument79 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and Meiosismaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet