Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 02 MindMap
Chapter 02 MindMap
Uploaded by
songs 2019 MalikOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 02 MindMap
Chapter 02 MindMap
Uploaded by
songs 2019 MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
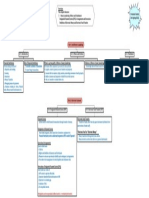
Overview:
CAF 04: Business Laws Offer and Acceptance are two most important elements of a Valid Contract.
Chapter 02: Introduction to Contract This chapter discusses:
Secret Sheet for Quick Revision Premium Content
Offer: Essentials, Communication, Revocation
(For students of Muhammad Asif, FCA) (For Spring 2022)
Acceptance: Essentials, Communication, Revocation
Contract: Essentials, Types
Part 1: Definitions and Basic Concepts
LO 1: Definitions LO2: Essentials of a Valid Contract LO 3: Types of Contracts
Offer/Proposal: 1. Offer and Acceptance Valid Contract: (Enforceable by Law) Void Agreement Vs. Void Contract:
One person shows his willingness: 2. Intention to create legal relationship Void Contract: (Not Enforceable by Void agreement: Void from start.
To do, or 3. Capacity/Competence of Parties Law) Void Contract: Valid from start but
Not to do something. 4. Free Consent Voidable Contract: (Enforceable at the became void subsequently.
5. Consideration option of aggrieved party)
Acceptance: 6. Legal Consideration/Object
When offeree communicates his consent to offeror. 7. Possibility of Performance
8. Certainty
Agreement: 9. Not expressely declared Void
Offer + Acceptance + Consideration = Agreement 10. Writing and Registered (Natural love and
affection, Time-barred debt, Arbitration)
Contract:
Agreement + Enforceability by Law = Contract. Part 3: Acceptance
Basic Concepts LO 7: Essentials of Acceptance LO 7: Communication of Acceptance LO 7: Revocation of Acceptance
Offer/Acceptance/Agreement can be either: Parties to the contract are called 1. Absolute and Unconditional. When: Before it comes to
Express (by words spoken or written), or "Promisor" and "Promisee". 2. Within stipulated or reasonable time. Against Offeror (when it is knowledge of Offeror
Implied (by conduct of parties) Other parties are called "Third 3. According to stipulated or reasonable mode/manner. sent by offeree)
Parties", or "Stranger to the contract". (If deviated, offeror may either accept or shall Against Offeree (when it
communicate non-acceptance) reaches offeror)
4. By person to whom it is made. (or his Agent)
5. Communicated to Offeror.
6. Not before offer.
7. Not implied from silence.
8. Rejected offer cannot be accepted.
9. Performance of condition, or acceptance of
consideration = Acceptance
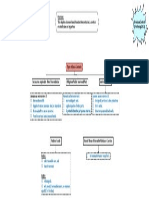
Part 2: Offer
LO 4: Types of Offer LO 5: Essentials of Offer LO 5: Communication of Offer LO 6: Revocation/Lapse of Offer
1. Specific (to specific person) 1. Two Persons. How: 1. By Offeror (before acceptance)
2. General (to general public) 2. Intention to create legal relationship. Express or Implied. 2. By Offeree (effective when it reaches offeror)
3. Counter (cancels original offer) 3. Certain and Definite. 3. Non-fulfilment of condition
4. Offer may be Conditional. (accept as it is) When: 4. Time passed.
5. Communicated to Offeree. When it comes to knowledge of Offeree. 5. Death or Insanity before Acceptance
6. Invitation to Offer, is not an Offer. Death of Offeree Important Concepts for Case Studies:
Death of Offeror 1. Revocation of Offer
6. Counter Offer 2. Communication and Revocation of Acceptance.
Examples of Invitation to Offer: 7. Subsequent illegality or destruction
Advertisement for Auction
Display of goods with price tags at store
Circulation of Information
Notice of Tender
You might also like
- Contracts OutlineDocument12 pagesContracts Outlineericachavez83% (18)
- Full Contracts OutlineDocument42 pagesFull Contracts OutlineDanielle Easton88% (8)
- Contract Law OutlineDocument8 pagesContract Law OutlineJ0221No ratings yet
- Law - Contract & AgencyDocument25 pagesLaw - Contract & AgencymontasirahmedNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Indian Contract Act - 1872 Question Bank Answer: 1. What Do You Understand by Breach of Contract'?Document8 pagesUNIT 1: Indian Contract Act - 1872 Question Bank Answer: 1. What Do You Understand by Breach of Contract'?ameyk8967% (3)
- Contract Law Crash CourseDocument9 pagesContract Law Crash CourseJane NgNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract Act 1872Document22 pagesThe Indian Contract Act 1872Varun SuriNo ratings yet
- Contracts Full OutlineDocument25 pagesContracts Full OutlineAnnie Weikel YiNo ratings yet
- Extract Law of ContractDocument38 pagesExtract Law of ContractRoné Scheepers100% (2)
- Contracts OutlineDocument44 pagesContracts OutlineCheyanne100% (1)
- Contracts Succinct OutlineDocument21 pagesContracts Succinct OutlineAmanda100% (1)
- Elements of ContractDocument6 pagesElements of ContractJerome ArañezNo ratings yet
- Quimbee - Contracts ClassDocument7 pagesQuimbee - Contracts ClassElsa Landeros100% (1)
- Chapter 2 CAF 03 MLaw PresentationDocument40 pagesChapter 2 CAF 03 MLaw Presentationkirankaurchahal.kkNo ratings yet
- Section 2h of The Indian Contract Act Defines Contract As "An Agreement Enforceable by Law Is A Contract"Document5 pagesSection 2h of The Indian Contract Act Defines Contract As "An Agreement Enforceable by Law Is A Contract"Riya PahujaNo ratings yet
- 02 - ContractsDocument15 pages02 - Contractsxara mizpahNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS - TondoDocument4 pagesCONTRACTS - TondoTondo JericaNo ratings yet
- EBCL Notes-218-231Document15 pagesEBCL Notes-218-231Shefali TailorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Contract Act, 1872: Business Legislation MBA (MDU) (3 Semester) Notes by Mr. Rahul SharmaDocument21 pagesUnit 1 The Contract Act, 1872: Business Legislation MBA (MDU) (3 Semester) Notes by Mr. Rahul SharmaRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument21 pagesLaw On ContractsHannah SyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PAM ContractDocument56 pagesIntroduction To PAM ContractLiana MNNo ratings yet
- RFBT.O 1602.law On Contracts WithanswersDocument42 pagesRFBT.O 1602.law On Contracts WithanswersDanielle Nicole Marquez0% (1)
- G1 Contract Act, 1872 - 22138 & 22139Document48 pagesG1 Contract Act, 1872 - 22138 & 22139chetan bariyaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ObliconDocument5 pagesReviewer ObliconDion AdalaNo ratings yet
- BRF Notes (2) finance and taxationDocument26 pagesBRF Notes (2) finance and taxationhisarahhh4No ratings yet
- Chapter 06 MindMapDocument1 pageChapter 06 MindMapsameedkhan123456789No ratings yet
- Contract Law 1 Short Notes by KalyanDocument56 pagesContract Law 1 Short Notes by KalyanIngith PrasanthNo ratings yet
- CH 12 (3) - Contracts and Sales - Introduction and FormationDocument8 pagesCH 12 (3) - Contracts and Sales - Introduction and FormationMaria ForkNo ratings yet
- Contracts: Legal FormsDocument88 pagesContracts: Legal Formsdaryl canozaNo ratings yet
- Contract Act Essentials of A Valid Contract Void Agreements Performance of Contracts BreachDocument21 pagesContract Act Essentials of A Valid Contract Void Agreements Performance of Contracts BreachakramNo ratings yet
- LAW OF CONTRACT COMPENDIUM 1Document13 pagesLAW OF CONTRACT COMPENDIUM 1ashleyquinnnyyyNo ratings yet
- NLM - ContractsDocument1 pageNLM - ContractsNa NaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Business Law and The Legal Environment 12th Edition Mann Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesEssentials of Business Law and The Legal Environment 12th Edition Mann Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFedithbellamyhd3a100% (11)
- Essentials of Business Law and The Legal Environment 12th Edition Mann Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesEssentials of Business Law and The Legal Environment 12th Edition Mann Solutions Manualdaineil2td100% (30)
- Contract Law Interview Questions - VskillsDocument1 pageContract Law Interview Questions - Vskillsaashna singhNo ratings yet
- L-2law On ContractsDocument9 pagesL-2law On ContractsDea Lyn BaculaNo ratings yet
- Bus. Law SummaryDocument8 pagesBus. Law SummaryJhonalyn MaraonNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of A Business NewDocument10 pagesLegal Aspects of A Business Newshantol wedderburnNo ratings yet
- Breach of Contract, FINALDocument16 pagesBreach of Contract, FINALRahat AliNo ratings yet
- Business Laws MaterialDocument42 pagesBusiness Laws MaterialVenugopalNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Law of Contract: Legal Term of The Day: ContDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Law of Contract: Legal Term of The Day: ContVERN JUN LEENo ratings yet
- CAFC Law RevisionDocument126 pagesCAFC Law Revisionzubair khanNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872Document18 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872ap GautamNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872Document14 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872Shweta BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- DisadvantagesDocument6 pagesDisadvantagesAlex MichaelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Law Notes Part 2Document32 pagesIntroduction To Law Notes Part 2isabel maunganidzeNo ratings yet
- Contract Act LDRs TCADocument31 pagesContract Act LDRs TCAKrishna SoniNo ratings yet
- Business Law, NotesDocument53 pagesBusiness Law, NotesMd.HasanNo ratings yet
- Pob Section 4- Legal Aspects of a BusinessDocument12 pagesPob Section 4- Legal Aspects of a Businessaaliyah675hNo ratings yet
- Business Law: Offer & Acceptance Competency of Parties ConsiderationDocument35 pagesBusiness Law: Offer & Acceptance Competency of Parties Considerationsyed moizNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument4 pagesLaw On ContractsRizza OlanoNo ratings yet
- Obligation and Contracts - CONSENTDocument8 pagesObligation and Contracts - CONSENTbrain lessNo ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument50 pagesContracts OutlineStephanie PrietoNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment: Karan KapoorDocument4 pagesLab Assignment: Karan KapoorkaranNo ratings yet
- Contracts Kang 2013Document22 pagesContracts Kang 2013tNo ratings yet
- Handouts For The Law On ContractsDocument5 pagesHandouts For The Law On ContractsHannah Jane UmbayNo ratings yet
- MGMT 260 CH 9 SLDocument11 pagesMGMT 260 CH 9 SLqhaweseithNo ratings yet
- Notes in ContractsDocument5 pagesNotes in ContractsSehyuk LimNo ratings yet
- Business & Commercial Law333333333312Document57 pagesBusiness & Commercial Law333333333312sajedulNo ratings yet
- Test 3 SolDocument2 pagesTest 3 Solsongs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27 PDFDocument1 pageLecture 27 PDFsongs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- ICAP Study Text Chap-4 (Solutions)Document3 pagesICAP Study Text Chap-4 (Solutions)songs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- ICAP Study Text Chap-4 (Questions)Document3 pagesICAP Study Text Chap-4 (Questions)songs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 MindMap PDFDocument2 pagesChapter 10 MindMap PDFsongs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 MindMapDocument1 pageChapter 12 MindMapsongs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 MindMapDocument1 pageChapter 09 MindMapsongs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 MindMap PDFDocument1 pageChapter 07 MindMap PDFsongs 2019 MalikNo ratings yet