Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RNA NOTES For SUMMATIVE TEST On BIOTECH 8
Uploaded by
Nadia Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesRibonucleic acid (RNA) is similar to DNA but contains ribose, uracil, and is usually single-stranded. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes for protein production, transfer RNA picks amino acids for proteins, and ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are synthesized. Protein synthesis requires two main steps - transcription of DNA to mRNA and translation of mRNA to proteins using ribosomes.
Original Description:
Biotech
Original Title
RNA NOTES for SUMMATIVE TEST on BIOTECH 8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRibonucleic acid (RNA) is similar to DNA but contains ribose, uracil, and is usually single-stranded. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes for protein production, transfer RNA picks amino acids for proteins, and ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are synthesized. Protein synthesis requires two main steps - transcription of DNA to mRNA and translation of mRNA to proteins using ribosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesRNA NOTES For SUMMATIVE TEST On BIOTECH 8
Uploaded by
Nadia KhanRibonucleic acid (RNA) is similar to DNA but contains ribose, uracil, and is usually single-stranded. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes for protein production, transfer RNA picks amino acids for proteins, and ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are synthesized. Protein synthesis requires two main steps - transcription of DNA to mRNA and translation of mRNA to proteins using ribosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
RNA NOTES for SUMMATIVE TEST on BIOTECH 8
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
- RNA is chemically similar to DNA except:
- it contains ribose instead of deoxyribose as its sugar;
- has the nitrogenous base uracil rather than thymine; and
- usually consists of a single strand rather than double strands.
A nucleic acid used is various body functions that uses Uracil instead of thymine to save
energy to manufacture.
Messenger (mRNA)
- molecules are long strands of RNA nucleotides that direct ribosomes to make
proteins.
- They travel from the nucleus to the ribosome.
Transfer (tRNA)
- Picks specific amino acid to the ribosomes and interpret the amino acid from the
mRna.
Ribosomal (rRNA)
- Molecules make up part of the ribosomes of the cell in the cytoplasm. Where
proteins are being synthesized based on the transcribes codes of mRNA.
Protein Synthesis
Getting from DNA to protein requires two major stages: transcription and translation.
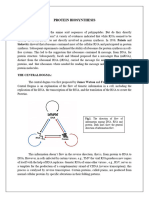
DNA RNA Protein Gene Expression
Translation and Transcription
(a) Bacterial cell- In a bacterial cell, which lacks a nucleus, mRNA produced by
transcription is immediately translated without additional processing.
(b) Eukaryotic cell- The nucleus provides a separate compartment for transcription.
The original RNA transcript, called pre-mRNA, is processed in various ways
before leaving the nucleus as mRNA.
Transcription
- The copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA.
- The synthesis of RNA suing information in the DNA.
- DNA strands provides a template for assembling a complementary sequence of RNA
nucleotides.
- For a protein-coding gene, the resulting RNA molecule is a faithful transcript of the
gene’s protein-building instructions.
- This type of RNA molecule is called messenger RNA (mRNA) because it carries a
genetic message from the DNA to the protein-synthesizing machinery of the cell.
The process of transcription is carried out by RNA polymerase (RNAP), which uses DNA
(black) as a template and produces RNA (blue).
RNAP- copies the template strand of the DNA.
During transcription, the gene determines the sequence of nucleotide bases along the
length of the RNA molecule that is being synthesized.
For each gene, only one of the two DNA strands is transcribed. This strand is called the
template strand because it provides the pattern, or template, for the sequence of
nucleotides in an RNA transcript.
Translation
- The synthesis of a polypeptide using the information in the mRNA.
- During this stage, there is a change in language: The cell must translate the
nucleotide sequence of an mRNA molecule into the amino acid sequence of a
polypeptide.
- The sites of translation are ribosomes, complex particles that facilitate the orderly
linking of amino acids into polypeptide chains.
Transcription and Translation
Occur in all organisms, both those that lack a membrane-bounded nucleus (bacteria
and archaea) and those that have one (eukaryotes).
The Base Pairing
The base-pairing rules for DNA synthesis also guide transcription, except that uracil
(U) takes the place of thymine (T) in RNA.
You might also like
- lecture_5.pptxDocument27 pageslecture_5.pptxAnimikh RayNo ratings yet
- CMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationDocument22 pagesCMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationTanalgo JPNo ratings yet
- 13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of RnaDocument13 pages13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of Rnawhether913No ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument24 pagesTranscription and TranslationGenesis FloresNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ExplainedDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis ExplainedHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- RNA PowerPointDocument20 pagesRNA PowerPointAnki0391100% (1)
- TranscriptionDocument25 pagesTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNo ratings yet
- RNA - Cell Physiology...Document13 pagesRNA - Cell Physiology...siddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument56 pagesDna and Rna StructureZeah RealNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument37 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingEarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsDocument12 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsAnne RussellNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)Document18 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA)Serap BayramNo ratings yet
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticDocument37 pagesIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Sci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationDocument7 pagesSci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationMel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- Heredity: 10 - AmaziahDocument33 pagesHeredity: 10 - AmaziahAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis423003157No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation Process & ComponentsDocument16 pagesDNA Translation Process & Components2C Lamsin, Estelle NerieNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis VocabularyDocument2 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis VocabularydherSZN ツNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA Review BIO 33Document32 pagesDNA RNA Review BIO 33Trixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- 1.central DogmaDocument2 pages1.central DogmaShantel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene Expressionaymnhssn2020No ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- Rna Protein Synthesis VocabDocument1 pageRna Protein Synthesis VocabChastity MiddlebrooksNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- Rotein Ynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesRotein Ynthesis: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesRna Protein Synthesisapi-545652980No ratings yet
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocument43 pagesTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument28 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument43 pagesTranscription and TranslationSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- CENTRAL DOGMA Translation Transcription Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesCENTRAL DOGMA Translation Transcription Protein SynthesisCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- M.I.T LessonsDocument12 pagesM.I.T LessonsChassy KammyNo ratings yet
- RNA Protein SynthesisDocument14 pagesRNA Protein SynthesisLAL BUKHSHNo ratings yet
- BIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinDocument47 pagesBIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinggttettanNo ratings yet
- Bio Keypoints ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Keypoints ReviewerFrancisNo ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument11 pagesMicrobial GeneticskimeehhNo ratings yet
- Reaya 3rd PeriodicalDocument16 pagesReaya 3rd PeriodicalRhenz San PedroNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of ProtiensDocument10 pagesSynthesis of ProtiensJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis With Video LinksDocument31 pagesProtein Synthesis With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument135 pagesProtein SynthesisCarlaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisArlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisArlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Protein Biosynthesis - 070214Document7 pagesProtein Biosynthesis - 070214LakshmipriyaNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgD_4-W690ZFeH2s_rHMUq8mWkwpq7AW9GvOxN7sF10Mwq5sZzGWrpp9CD2e740VEHQIRVJCro5aE8JvHS-YbjwJBpVt7rmU1krcsy8y4jTM4CLQoP4C9HA4yPQIutSMtGQyesNBytCtTek3Document2 pagesACFrOgD_4-W690ZFeH2s_rHMUq8mWkwpq7AW9GvOxN7sF10Mwq5sZzGWrpp9CD2e740VEHQIRVJCro5aE8JvHS-YbjwJBpVt7rmU1krcsy8y4jTM4CLQoP4C9HA4yPQIutSMtGQyesNBytCtTek3vuminhtut66No ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationDocument37 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationfangirltonNo ratings yet
- Page No: Prokaryotic Messenger RnaDocument17 pagesPage No: Prokaryotic Messenger Rnasplinterof2005No ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetJo JoNo ratings yet
- Gene to Protein: Transcription and Translation ExplainedDocument18 pagesGene to Protein: Transcription and Translation ExplainedMa. Joy JocosolNo ratings yet
- L18 Polypeptide SynthesisDocument18 pagesL18 Polypeptide Synthesisareejhussaini26No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document66 pagesLesson 9Irica Mae CiervoNo ratings yet