Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rna Protein Synthesis Vocab
Uploaded by
Chastity MiddlebrooksCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rna Protein Synthesis Vocab
Uploaded by
Chastity MiddlebrooksCopyright:
Available Formats
Vocabulary: RNA and Protein Synthesis
Vocabulary
Amino acid an organic molecule containing a carboxyl and an amino group
o Amino acids combine to form proteins.
Anticodon a region of a tRNA molecule that consists of three bases that are
complimentary to an mRNA codon.
Codon a set of three nucleotides that encodes an amino acid or signifies a start signal
or stop signal.
Gene a DNA sequence that codes for a specific protein.
o By coding for proteins, genes determine many traits of living things.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) a strand of RNA that encodes information to make a protein.
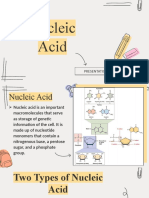
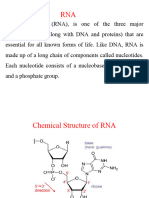
Nucleotide a subunit of a nucleic acid molecule that consists of a sugar, a phosphate,
and a nitrogenous base.
o In DNA, nucleotides have one of the following nitrogenous bases: adenine,
cytosine, guanine, or thymine.
o Nitrogenous bases in RNA may be adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil.
Ribosome a cell organelle that is the site of protein synthesis.
o Ribosomes are composed of RNA and protein.
RNA (ribonucleic acid) a nucleic acid that plays a role in protein synthesis.
o The three main types of RNA are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA
(tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
RNA polymerase an enzyme that enables the process of transcription by separating a
strand of DNA and forming a complimentary strand of mRNA.
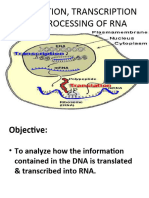
Transcription the process of forming a nucleic acid by using another molecule as a
template.
o Transcription starts the process of protein synthesis by using a strand of DNA to
form a complementary strand of mRNA.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) a strand of RNA that transfers amino acids to the growing end of
a protein molecule during translation.
Translation the process of using the codons in an mRNA molecule to specify the
sequence of amino acids in a protein molecule.
o Translation takes place in a ribosome.
You might also like
- RNA Methodologies: A Laboratory Guide for Isolation and CharacterizationFrom EverandRNA Methodologies: A Laboratory Guide for Isolation and CharacterizationNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis VocabularyDocument2 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis VocabularydherSZN ツNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ExplainedDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis ExplainedHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- lecture_5.pptxDocument27 pageslecture_5.pptxAnimikh RayNo ratings yet
- 13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of RnaDocument13 pages13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of Rnawhether913No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- Heredity: 10 - AmaziahDocument33 pagesHeredity: 10 - AmaziahAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument32 pagesProtein SynthesisJosefina JerezNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Biology Cheat Sheet For EllaDocument3 pagesBiology Cheat Sheet For EllaJay EdwardsNo ratings yet
- DNA-PROCESSESDocument28 pagesDNA-PROCESSESvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- (C) and Uracil (U) - The Five-Carbon (Pentose) Sugar in RNA Is RiboseDocument5 pages(C) and Uracil (U) - The Five-Carbon (Pentose) Sugar in RNA Is RiboseRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- RNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorDocument1 pageRNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldAndrew BurtsfieldNo ratings yet
- RNA NOTES For SUMMATIVE TEST On BIOTECH 8Document2 pagesRNA NOTES For SUMMATIVE TEST On BIOTECH 8Nadia KhanNo ratings yet
- RNA PowerPointDocument20 pagesRNA PowerPointAnki0391100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesProtein SynthesisRussel OtillaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsDocument12 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsAnne RussellNo ratings yet
- protien synth 11thDocument3 pagesprotien synth 11thtewoldeNo ratings yet
- genetic code, DNA, RNA, Protein synthesisDocument46 pagesgenetic code, DNA, RNA, Protein synthesisdeepakNo ratings yet
- Ms. Rima DessaiDocument46 pagesMs. Rima DessaiSanghaviNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgD_4-W690ZFeH2s_rHMUq8mWkwpq7AW9GvOxN7sF10Mwq5sZzGWrpp9CD2e740VEHQIRVJCro5aE8JvHS-YbjwJBpVt7rmU1krcsy8y4jTM4CLQoP4C9HA4yPQIutSMtGQyesNBytCtTek3Document2 pagesACFrOgD_4-W690ZFeH2s_rHMUq8mWkwpq7AW9GvOxN7sF10Mwq5sZzGWrpp9CD2e740VEHQIRVJCro5aE8JvHS-YbjwJBpVt7rmU1krcsy8y4jTM4CLQoP4C9HA4yPQIutSMtGQyesNBytCtTek3vuminhtut66No ratings yet
- RNA Protein SynthesisDocument14 pagesRNA Protein SynthesisLAL BUKHSHNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument15 pagesPhysical SciencelovelyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocument55 pagesNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Document2 pagesMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Jessa Mae IbalNo ratings yet
- Rotein Ynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesRotein Ynthesis: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)Document18 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA)Serap BayramNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument29 pagesGene ExpressionZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Meridian Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesMeridian Protein SynthesisjosewaltNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument46 pagesTranscription and TranslationEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument13 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationMohd JunaidNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument56 pagesDna and Rna StructureZeah RealNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) : Adnan BhanwadiaDocument24 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA) : Adnan BhanwadiaTeflon SlimNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation Process & ComponentsDocument16 pagesDNA Translation Process & Components2C Lamsin, Estelle NerieNo ratings yet
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDocument40 pages2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisDocument19 pagesDNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisAnonymous qMToncNo ratings yet
- Genetics Auto Saved)Document7 pagesGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis With Video LinksDocument31 pagesProtein Synthesis With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- The essential roles of RNA in protein synthesis and gene regulationDocument3 pagesThe essential roles of RNA in protein synthesis and gene regulationMira LutfianaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- RNA Types and Functions ExplainedDocument19 pagesRNA Types and Functions Explainedمحمد صالح ابراهيم محمدNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Protein - EnglishDocument11 pagesSintesis Protein - EnglishMarlina LinaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis ExplainedDocument33 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis ExplainedRaphael Ongodia100% (2)
- Bio 3Document11 pagesBio 3mtanveerhasan2001No ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- BIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinDocument47 pagesBIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinggttettanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument46 pagesNucleic AcidsM. MalonesNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument35 pagesCentral Dogmatariqul13017No ratings yet
- RNADocument21 pagesRNAManoj SigdelNo ratings yet
- Notes On DNADocument1 pageNotes On DNAChristina VlietNo ratings yet
- Chap 17 From Gene To Protein FixDocument30 pagesChap 17 From Gene To Protein FixRizaldi Al FauzanNo ratings yet