Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NUCMED Reviewer
NUCMED Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ryan Cuasay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pagesThe document discusses the history and components of the atom from ancient Greek models to modern quantum mechanics models. It describes the discoveries of key scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Goldstein, and Chadwick in developing understanding of the atom. It then discusses the structure of the atom including the nucleus, electrons, protons, and neutrons. It also summarizes the interaction of radiation with matter including different types of radiation and their properties.
Original Description:
Nuclear Medicine
Original Title
NUCMED reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the history and components of the atom from ancient Greek models to modern quantum mechanics models. It describes the discoveries of key scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Goldstein, and Chadwick in developing understanding of the atom. It then discusses the structure of the atom including the nucleus, electrons, protons, and neutrons. It also summarizes the interaction of radiation with matter including different types of radiation and their properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pagesNUCMED Reviewer
NUCMED Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ryan CuasayThe document discusses the history and components of the atom from ancient Greek models to modern quantum mechanics models. It describes the discoveries of key scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Goldstein, and Chadwick in developing understanding of the atom. It then discusses the structure of the atom including the nucleus, electrons, protons, and neutrons. It also summarizes the interaction of radiation with matter including different types of radiation and their properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
The Atom
Atom – The smallest part of an element that has all the properties of the elements
Centuries of Discoveries
1. Greek Atom
2. Dalton Atom – John Dalton (1808) Eye and Hook affair
3. Thompson atom – JJ Thompson Plum Pudding
4. Rutherford atom – Ernest Rutherford (1911) Nuclear Model
5. Bohr atom – Niels Bohr (1913) Miniature solar system
6. Quantum Mechanics
Electron –
Proton + (1 amu)
Neutron 0 (1 amu)
Proton – Eugene Goldstein
Neutron – James Chadwick (1932)
Electro – JJ Thompson (1897)
Nucleus – Ernest Rutherford (1911)
When an atom or molecule gain or loses an electron it becomes an ion.
A cation has lost an electron and therefore has a positive charge
An anion has gained an electron and therefore has a negative charge.
Structure of Atom
Nucleus – Center of Atom (P and N)
Electron “cloud” – Area surrounding nucleus (electrons)
Interaction of Radiation with Matter
Attenuation – intensity REDUCTION of X-ray as a pass-through matter
Five interactions of X-rays and Gamma Rays with Matter
Photoelectric effect – Very important in diagnostic radiology
Compton scatter – Very important in radiotherapy
Coherent scatter – Not important in diagnostic or therapeutic radiology
Pair production – important in diagnostic radiology
Photodisintegration – Neutron contamination of therapy beams
Alpha particles – Mass+=(4amu)2 N and 2 P (+2) short distance = 10 cm in air (paper or layer of
skin)
Beta particles –(Decay of Neutron into a P and E) small electric charge particles similar to
electrons (-1) (wood, aluminum foil)
Gamma-rays –(not particle) Electromagnetic photons or radiation (highly penetrating)
X-rays – Overlap with gamma-rays (highly penetrating)
Personal dosimeters – Provide a record of accumulated exposures
Alpha – Proportional or scintillation counters
Beta, gamma – Geiger-Mueller or Proportional counters
X-ray, gamma – Ionization chambers
Neutrons – Proportional counters
Transmutation – Changing one element into another through radioactive decay
Nuclear fission=Divide
Nuclear fusion=opposite of fission
PET – Positron Emission Tomography
-a 3D image of functional processes in the body
-Inject radioactive tracers (a simple sugar and a small amount of radioactive fluorine)
-Detects gamma rays emitted
-avoid unnecessary surgery
SPECT-Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
-Uses single photons
-Inject radionuclides
-scintillation cameras that acquire 2d planar projection images the projection data are
reconstructed into 3d images
-Produce 3d distribution of the gamma rays
-Technetium-99m (149keV) or iodine-123
-Physiological information
-looks like CT or MRI system
-A pulse Height Analyzer (PHA) decodes the energy of the emitted photon
SPECT images can be taken in 2 modes
-Continuous Acquisition – camera heads in motion
-Step and shoot – Camera stop and defined angles
180 = most common generally
360 = common in brain SPECT
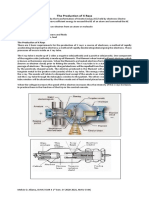
Gamma camera-a device that use gamma rays to carry out functional scans on patients
1. Collimator – limits the passage of gamma rays
2. Scintillator – made up of Sodium Iodide (Nal) crystal – Produces multi-photon flashes of
light when incoming gamma rays hit to the surface of the crystal
3. Photomultiplier tube (PMT) – convert the light signal into a useable current pulse
4. Computer – process current pulse into a useable image
5. Monitor – displayed the image
You might also like
- Radiopharmaceutics Presentation1Document52 pagesRadiopharmaceutics Presentation1alibinaminNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Nuclear Fission and FusionDocument12 pages4.6 Nuclear Fission and FusionRajat RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Pages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch10Document46 pagesPages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch10api-261034721No ratings yet
- English For Chemistry StudentsDocument3 pagesEnglish For Chemistry StudentsDaniela Tecucianu100% (1)
- AP Physics B - Atomic and Nuclear Physics PDFDocument33 pagesAP Physics B - Atomic and Nuclear Physics PDFjafarNo ratings yet
- Origin and Nature of Radiation (English)Document23 pagesOrigin and Nature of Radiation (English)laloooppNo ratings yet
- bm5602 Unit 1Document147 pagesbm5602 Unit 1sfssssNo ratings yet
- Edexcel p3 Revision Presentation 20min 18Document29 pagesEdexcel p3 Revision Presentation 20min 18api-255043845No ratings yet
- Rad PhysicsDocument5 pagesRad PhysicsSoleil SierraNo ratings yet
- Atomic & Nuclear PhysicsDocument9 pagesAtomic & Nuclear PhysicsPyay Lin ThantNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2217592035381457554Document142 pagesInbound 2217592035381457554Vincent PaulNo ratings yet
- Presented by Akhileshwar Rao 14311A0282Document19 pagesPresented by Akhileshwar Rao 14311A0282AkhileshwarNo ratings yet
- Pet Scan NotesDocument5 pagesPet Scan Notes111sparemailNo ratings yet
- Ai CP 01Document6 pagesAi CP 01Random gmailNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesModern Physics Revieweraaleah moscaNo ratings yet
- RadphysicsDocument143 pagesRadphysicspia toledoNo ratings yet
- Introduction, History & Basic PhysicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction, History & Basic PhysicsAbo QadeerNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 - CH 28-29-30 Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument31 pagesAP Physics 2 - CH 28-29-30 Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsLê Văn Hiệu Khoa KH Tự NhiênNo ratings yet
- Radiation & Radioactivity and Half LifeDocument27 pagesRadiation & Radioactivity and Half LifedwyphyNo ratings yet
- The ElectronDocument16 pagesThe ElectronAyan SantraNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy: Pranjal Verma Sem - 3 BSC Physics Honors A8955718005Document33 pagesPrinciples and Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy: Pranjal Verma Sem - 3 BSC Physics Honors A8955718005pranjalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nuclear RadiationDocument164 pagesChapter 3 Nuclear RadiationJoseph MabajenNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Radiology (Nuclear Medicine) - Radiological Anatomy of Thorax and Upper LimbDocument60 pagesFundamentals of Radiology (Nuclear Medicine) - Radiological Anatomy of Thorax and Upper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Radiology (Nuclear Medicine) - Radiological Anatomy of Thorax and Upper Limb CompressedDocument60 pagesFundamentals of Radiology (Nuclear Medicine) - Radiological Anatomy of Thorax and Upper Limb CompressedNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- Detection & Measurement of RadioactivityDocument7 pagesDetection & Measurement of RadioactivityChetan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document8 pagesLecture 2Vinayak KadamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationJohn Kenneth Palispis SecorNo ratings yet
- 8.1 - Nuclear RadiationDocument9 pages8.1 - Nuclear RadiationasNo ratings yet
- JotterPad - JotterPadDocument21 pagesJotterPad - JotterPadOlajide HeritageNo ratings yet
- X Ray LithographyDocument59 pagesX Ray LithographyMohammad RameezNo ratings yet
- Nats 1570 Chapter 18Document5 pagesNats 1570 Chapter 18studentNo ratings yet
- Exam 1Document17 pagesExam 1CraigNo ratings yet
- 2 CH 28 Nuclear Chemistry (Def Radioactivity)Document58 pages2 CH 28 Nuclear Chemistry (Def Radioactivity)Fatin IziantiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Part II: Signor Rinno D. MontalesDocument42 pagesAtomic Structure - Part II: Signor Rinno D. MontalesChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Notebook 3 FinalDocument6 pagesNotebook 3 Finalapi-339050167No ratings yet
- Presented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearDocument52 pagesPresented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearSandeep VermaNo ratings yet
- Radiology Equipment Final Test TipsDocument9 pagesRadiology Equipment Final Test TipsAbdullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging and X-Ray FormationDocument9 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging and X-Ray FormationElah TapangNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Medicine Definition of Terms 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNuclear Medicine Definition of Terms 1 PDFpia toledoNo ratings yet
- Ionizing RadiationDocument5 pagesIonizing RadiationCristinaNo ratings yet
- 5 X RAyDocument5 pages5 X RAyJonorie Bag-oyenNo ratings yet
- Lec28 MatterDocument21 pagesLec28 MatterChandralal SharmendraNo ratings yet
- Radiation Cueto NajitoDocument89 pagesRadiation Cueto NajitoCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- X-Ray ProductionDocument109 pagesX-Ray ProductionGarry LasagaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - 2Document121 pagesNuclear Physics - 2Rose MusariraNo ratings yet
- Bone LandmarkDocument3 pagesBone LandmarkDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- RADIOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL LatestDocument52 pagesRADIOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL LatestManish SinghNo ratings yet
- Thompson ScatteringDocument181 pagesThompson ScatteringAnas Abdel RihemNo ratings yet
- Afs Ojhar: Project Submitted By: Sumit Anand Class: XII-ADocument17 pagesAfs Ojhar: Project Submitted By: Sumit Anand Class: XII-ASumit AnandNo ratings yet
- Greg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduDocument132 pagesGreg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduSpoiled BratNo ratings yet
- CH. 4 Radiation 2015Document54 pagesCH. 4 Radiation 2015MaxxaM8888No ratings yet
- Training On RT - ASNT Level IIDocument72 pagesTraining On RT - ASNT Level IIAguara OghenevwedeNo ratings yet
- Block 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityDocument70 pagesBlock 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Radiation & Radioactivity: Department of Medical Biophysics and Informatics 3rd Medical Faculty of Charles UniversityDocument34 pagesRadiation & Radioactivity: Department of Medical Biophysics and Informatics 3rd Medical Faculty of Charles UniversityahkiaenaaaaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Discovery of ElectronDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure: Discovery of ElectronHarsh GargNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument11 pagesProjectMehak Parvez HamdaniNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument20 pagesPhysicsMelanie De SousaNo ratings yet
- Physics - The Physics of The AtomDocument8 pagesPhysics - The Physics of The AtomNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpectrosDocument27 pagesIntroduction To SpectrosSheila Shamuganathan100% (2)
- Radio PharmaceuticsDocument52 pagesRadio PharmaceuticsDrGaurav TiwariNo ratings yet
- 05 Compton ScatteringDocument36 pages05 Compton ScatteringrevnaldNo ratings yet
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- TH-5 Activity No.1Document2 pagesTH-5 Activity No.1Ryan CuasayNo ratings yet
- Social Teachings of The Church (Concept)Document2 pagesSocial Teachings of The Church (Concept)Ryan CuasayNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 TH6 BSRT 3 PrelimsDocument4 pagesActivity 3 TH6 BSRT 3 PrelimsRyan CuasayNo ratings yet
- Topic V. Abdomen and Pelvis (Reviewer)Document6 pagesTopic V. Abdomen and Pelvis (Reviewer)Ryan CuasayNo ratings yet
- NihoniumDocument6 pagesNihoniumKevinNo ratings yet
- h2 Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesh2 Physics DefinitionsJerald LimNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 LESSON 13 Periodic Relationships Among ElementsDocument22 pagesCHEM1 LESSON 13 Periodic Relationships Among ElementsLoraine CastroNo ratings yet
- The Deuteron: Structure and Form FactorsDocument81 pagesThe Deuteron: Structure and Form FactorsSapna ShaNdilNo ratings yet
- M SC - Physics-SemesterDocument43 pagesM SC - Physics-SemesterMokibul IslamNo ratings yet
- Particle Molecule AtomDocument3 pagesParticle Molecule AtomGermaeGonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chem12 C0402 SWBSDocument4 pagesChem12 C0402 SWBSWildboy 2008No ratings yet
- NMRDocument35 pagesNMRnikhila11reddyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Term Two - Solution Class 12thDocument30 pagesImportant Questions Term Two - Solution Class 12thGargi MishraNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Form 5: Unit 5: RadioactivityDocument27 pagesPHYSICS Form 5: Unit 5: RadioactivityDahliza KamatNo ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument3 pagesAtoms Molecules and Ionsapi-304350501No ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions:: Fission & FusionDocument40 pagesNuclear Reactions:: Fission & FusionAman TiwariNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsShreya SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2019 Mock Test1 QPDocument24 pagesJEE Main 2019 Mock Test1 QPgauravNo ratings yet
- Q3 Physical Science: Day 1 What Is The Periodic Table?Document6 pagesQ3 Physical Science: Day 1 What Is The Periodic Table?Kinect Nueva EcijaNo ratings yet
- Ciencia y Tecnologia 2do Secundaria - 2023Document72 pagesCiencia y Tecnologia 2do Secundaria - 2023Lucero Cabrera AguinagaNo ratings yet
- OCR A Chemitry Transition Student SheetDocument14 pagesOCR A Chemitry Transition Student SheetDrew SetionoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry SpecDocument74 pagesGCSE Chemistry SpecAli Hasan MaherNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument64 pagesForceAashka GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1Imperial PlayzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Modules 4 9Document10 pagesChemistry Modules 4 9JasminNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets As 1001 Atomic StructureDocument1 pageChemsheets As 1001 Atomic StructurejnfjngsdjNo ratings yet
- 0625 s18 QP 12 PDFDocument16 pages0625 s18 QP 12 PDFalishaluthfiyaNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Into Life 15th Edition Mader Test BankDocument25 pagesInquiry Into Life 15th Edition Mader Test BankGregoryVasqueztkbn100% (54)
- CBI1 Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument4 pagesCBI1 Fundamentals of ChemistryRianna NNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22JelloNo ratings yet
- 7 1 Classifying MatterDocument15 pages7 1 Classifying Matterapi-275233798No ratings yet