Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology ANS Drugs
Uploaded by
Charissa Ng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pagePharmacology ANS Drugs
Uploaded by
Charissa NgCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
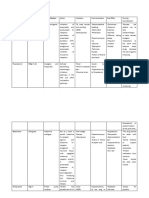
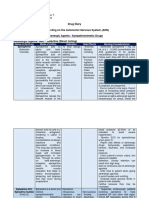
Muscarinic Agonist AchE Inhibitor Muscarinic Antagonist
- Pilocarpine Reversible: - Atropine
- Methancholine - Physostigmine - Scopolamine
- Bethanochol - Neostigmine - Glycopyrronium Bromide
- Carbachol - Edrophonium - Ipratopium Bromide
- Pyridostigmine - Cyclopentalate
- Tropicamide
Pilocarpine and Carbachol topical application to eyes Physostigmine, Neostigmine, and Atropine used to increase HR during surgery,
to induce miosis (pupil constriction) Edrophonium treat myasthenia gravis pre-medicate for salivation, dilation of eye for eye
exam.
Use AchEI to reserve NMJ block NMJ
blocking drugs will block Ach from binding to Atropine also used to reverse AchEI PNS
the Nm (somatic nicotinic) receptors at the effects that may occur when using AchEI to
NMJ. Use AchEI to increase the duration of reverse NMJ block
Ach at the site to overcome the Nm antagonist
(blocking) drug. Careful, because AchEI can
also increase Ach at muscarinic receptor in
PNS and induce more PNS effects
(bradycardia)
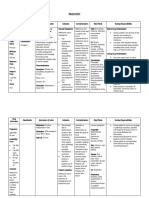
Alpha-1 Agonist - Phenylpropanolamine (propalin) - Phenylpropanolamine: used to treat
- Phenylephrine urinary incontinence in the bitch.
Increases tone of urinary sphincter. Can
induce hyper-excitability or aggression
b/c it causes NE release
- Phenylephrine: causes vasoconstriction
and increase in BP. Used when BP is so
low that there is no other choice. Also
causes mydriasis (pupil dilation)
Alpha-1 Antagonist - Prazosin - Prazosin: Causes vasodilation, relaxes
- Phenoxybenzamine the sphincter and contract the detrusor
muscle. Used to treat some UTIs,
urinary retention, helps with blocked
cats.
- Phenoxybenzamine: irreversible drug.
Risk of hypotension. Has been used in
the treatment of laminitis as well as
urinary retention.
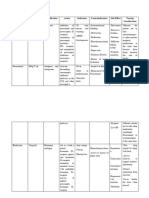
Alpha-2 Agonist - Clonidine - In general these drugs are used
- Sedatives (see Anaesthesia 5) primarily in anaesthesia for central
sedative effects
- Clonidine: used to diagnosis growth
hormone deficiency
Alpha-2 Antagonist - Antisedan (see Anaesthesia 5) - Used to reverse sedation
Beta-1 Agonist - Dobutamine - Beta-1 agonists have primarily cardiac
effects increase HR and force of
contraction
- Dobutamine: Used frequently in equine
anaesthesia, helps maintain HR
Beta-1 Antagonist - Propranolol (non-selective beta
antagonist), esmolol, atenolol,
metoprolol, timolol
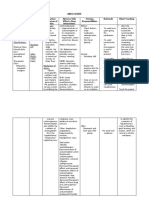
Beta-2 Agonist - Clenbuterol - Beta-2 agonists have primarily
- Salbuterol bronchodilation effect
- Terbutaline - Clenbuterol: can treat COPD in horses
- Isoxuprine - Isoxuprine: can treat navicular disease
vasodilation of vascular bed
Beta-2 Antagonist - Propranolol (non-selective beta
antagonist)
You might also like
- Effector OrganDocument2 pagesEffector OrganCamille De JesusNo ratings yet
- Medications TackledDocument3 pagesMedications TackledAl-Khan HadjailNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic - Antagonists TableDocument3 pagesAdrenergic - Antagonists Tablehovico3936No ratings yet
- Cholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableDocument2 pagesCholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableFNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument14 pagesPharmacology SummaryteddyjolinNo ratings yet
- If These Are Stimulated It Produces An Array of Effects in The BodyDocument4 pagesIf These Are Stimulated It Produces An Array of Effects in The BodyAnne Giselle PatocNo ratings yet
- DrugssDocument7 pagesDrugssgoguaroyceNo ratings yet
- Propranolol: Body Tissue/organ Sympathetic (Norepinephrine) Parasympathetic (Acetylcholine)Document4 pagesPropranolol: Body Tissue/organ Sympathetic (Norepinephrine) Parasympathetic (Acetylcholine)chn pastranaNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Zalameda CNS-PNSDocument43 pagesZalameda CNS-PNSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetics and SympatholyticsDocument3 pagesSympathomimetics and Sympatholyticsbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Analgesics: Opioid Medication Class Drug PK PD CU ToxicityDocument2 pagesAnalgesics: Opioid Medication Class Drug PK PD CU ToxicityDabrat JullzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EpinephrineDocument2 pagesDrug Study EpinephrinePearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Neuropharmacology ANSDocument47 pagesNeuropharmacology ANSnezifzenu2023No ratings yet
- Piri Pharm Tables Pharmacology Therapeutics SpringDocument110 pagesPiri Pharm Tables Pharmacology Therapeutics SpringNormala Macabuntal SaripadaNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument4 pagesPharma NotesMayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyJB RSNJNNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsDocument7 pagesNorepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsJohn denver FloresNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Veterinary CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesVeterinary CNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyDocument10 pagesSympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyHaroon JavedNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System DrugsDocument7 pagesAutonomic Nervous System DrugsLucañas PringelNo ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDocument1 pageDRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Respratory Drugs I-IIDocument10 pagesRespratory Drugs I-IITyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AgonistsDocument1 pageCholinergic AgonistsAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument5 pagesDruggoguaroyceNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AsDocument3 pagesDrug Study Askev mondaNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- Ventolin DrugstudyDocument1 pageVentolin DrugstudyMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezNo ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument4 pagesAutonomic DrugsSabrinaNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyJamesBond123098No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IIDocument12 pagesPharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IIPrincess Mara DuranNo ratings yet
- Ans NursingDocument15 pagesAns Nursingwww.nikhilbabu123No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AcetamenophinDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY - AcetamenophinChenime AñanaNo ratings yet
- Margo-7 New - VersionDocument27 pagesMargo-7 New - VersionKhushman KaurNo ratings yet
- Respi Drugs 1Document10 pagesRespi Drugs 1TpdNo ratings yet
- Kuliah SSO2Document11 pagesKuliah SSO2Kuaci SmurfNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IntroductionDocument2 pagesPharmacology Introductionad-adNo ratings yet
- Drug Study inDocument3 pagesDrug Study inaycee0316No ratings yet
- Antiseizure DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiseizure DrugsMaika DoronelaNo ratings yet
- Logic ChartDocument1 pageLogic ChartAya AmerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Module For FinalsDocument11 pagesPharmacology Module For FinalsCarlo GaradoNo ratings yet
- Case 8-13Document24 pagesCase 8-13Trizian ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPauline BelbisNo ratings yet
- Barcelon Antihypertensive-AgentsDocument12 pagesBarcelon Antihypertensive-AgentsFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Othmani111n Easy Pharma - 220401 - 163518Document7 pagesOthmani111n Easy Pharma - 220401 - 163518Hassan HekmatNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Antibiotics - ViosDocument8 pagesAssignment On Antibiotics - ViosIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- 12 Muscle Relaxants 2 4Document5 pages12 Muscle Relaxants 2 4dfdxgfcvhbNo ratings yet
- Zalameda ANSDocument32 pagesZalameda ANSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723No ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Parasympathomimetics - Direct "-Chol", Indirect "-Stigmine" or "Stigmime"Document3 pagesParasympathomimetics - Direct "-Chol", Indirect "-Stigmine" or "Stigmime"mclNo ratings yet
- Detect Pharmaceutical Health Hazards and ActDocument81 pagesDetect Pharmaceutical Health Hazards and Acttemesgen dinsaNo ratings yet
- Perkutan Kateter Vena Sentral Dibandingkan Perifer Kanula Untuk Pengiriman Nutrisi Parenteral Ada NeonatusDocument3 pagesPerkutan Kateter Vena Sentral Dibandingkan Perifer Kanula Untuk Pengiriman Nutrisi Parenteral Ada NeonatusmuslihudinNo ratings yet
- Occupational HealthDocument8 pagesOccupational HealthFemale calm0% (1)
- 4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 : Division of Forensic SciencesDocument7 pages4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 : Division of Forensic SciencesAttila KissNo ratings yet
- Encouraging TeenagersDocument17 pagesEncouraging TeenagersTahNo ratings yet
- PANCE Prep Pearls Cardio Questions PDFDocument9 pagesPANCE Prep Pearls Cardio Questions PDFkat100% (3)
- The Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsJame SmithNo ratings yet
- What Is The DASH Eating Plan - (Printer-Friendly)Document5 pagesWhat Is The DASH Eating Plan - (Printer-Friendly)Are-nim Hanim100% (1)
- AminoglycosidesDocument20 pagesAminoglycosidesHassan.shehri100% (5)
- MedicalerrorDocument38 pagesMedicalerrorchanda jabeenNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument2 pagesReferensiYuanita RosalinaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy and DkaDocument6 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy and Dkajames garciaNo ratings yet
- Community Radio Script - Why We Have COVID Vaccines NowDocument2 pagesCommunity Radio Script - Why We Have COVID Vaccines NowBenBuilds PHNo ratings yet
- De So 3Document6 pagesDe So 3To Minh PhuongNo ratings yet
- Nu 712 Health DisparitiesDocument5 pagesNu 712 Health Disparitiesapi-555218722No ratings yet
- Adams4e Tif Ch47Document19 pagesAdams4e Tif Ch47fbernis1480_11022046100% (1)
- Adoption Foster ApplicationDocument4 pagesAdoption Foster Applicationlb8757No ratings yet
- Alcohol Research Paper OutlineDocument6 pagesAlcohol Research Paper Outlineafmctmvem100% (1)
- Full Download Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhy PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhy PDF Full Chapteradrianblackiadxetkrqm100% (15)
- Fidelis Drug List 2018Document80 pagesFidelis Drug List 2018Annie AnnaNo ratings yet
- MCHHDocument2 pagesMCHHEDENNo ratings yet
- Proceedings GRANADA 1Document70 pagesProceedings GRANADA 1wingsskyNo ratings yet
- HPP Neuro Paper GraserDocument12 pagesHPP Neuro Paper GraserCaro ErazoNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant (Rahul Sharma) ChambaDocument17 pagesMedicinal Plant (Rahul Sharma) ChambaRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bile Esculine TestDocument2 pagesBile Esculine TestVincent OngNo ratings yet
- Palmer Et Al v. Amazon - Com Inc Et AlDocument41 pagesPalmer Et Al v. Amazon - Com Inc Et AlGeekWireNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAdor AbuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing ShortageDocument16 pagesNursing Shortageapi-240927368No ratings yet
- Unit 4 ReadingDocument4 pagesUnit 4 ReadingElvantNo ratings yet
- Left Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDocument9 pagesLeft Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDominic BristolNo ratings yet