Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6184ae6ba2c63 NCP For Pcap
Uploaded by
Melrhean Grace0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesIneffective airway clearance r/t retained secretions due to pediatric community acquired pneumonia high risk. The patient exhibited increased work of breathing with the use of accessory muscles and crackles heard on the left lung field. Nursing interventions included assessing respiratory patterns, monitoring vital signs, auscultating lung sounds, back rubbing, encouraging increased fluid intake and milk to help liquefy secretions.
Original Description:
notes
Original Title
20211105040915_6184ae6ba2c63_ncp_for_pcap
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIneffective airway clearance r/t retained secretions due to pediatric community acquired pneumonia high risk. The patient exhibited increased work of breathing with the use of accessory muscles and crackles heard on the left lung field. Nursing interventions included assessing respiratory patterns, monitoring vital signs, auscultating lung sounds, back rubbing, encouraging increased fluid intake and milk to help liquefy secretions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pages6184ae6ba2c63 NCP For Pcap
Uploaded by
Melrhean GraceIneffective airway clearance r/t retained secretions due to pediatric community acquired pneumonia high risk. The patient exhibited increased work of breathing with the use of accessory muscles and crackles heard on the left lung field. Nursing interventions included assessing respiratory patterns, monitoring vital signs, auscultating lung sounds, back rubbing, encouraging increased fluid intake and milk to help liquefy secretions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Notre Dame University
College of Health Sciences
Cotabato City
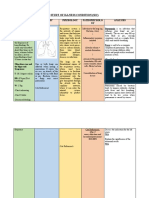
Name of Patient: Tipanero,Leil Name of Student: Michaella Olivia P. Awal
Human Nursing Cues Pathophysiological Nursing Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Response Diagnosis Basis Outcome Interventions
Pattern
E Ineffective S-“May ubo Germs called Within the -Assessed -Use of accessory
X airway sya,dati bacteria or viruses shift the respiratory muscles to breathe
C clearance naadmit nay an usually patient will movements and the indicates an abnormal
H r/t retained sya kasi may cause pneumonia. Pn be able to use of accessory increase in work of
A secretions pneumonia,nga eumonia usually maintain a muscles. breathing.
N yon High risk starts when you normal RR
G na daw ang breathe the germs -Monitor vital signs -To check for any
I pneumonia into your lungs. You especially the RR. unusualities with the
N nya” as may be more likely VS.
G verbalized by to get the disease
mother after having a cold -Auscultate the -Crackles are heard
O-Crackles or the flu. lung sounds when fluid is present.
heard at Left Pneumonia is an There would be
lung field upon infection that possible adventitious
auscultation inflames the air sacs breath sounds that
-prolonged in one or both lungs. needs to be assessed.
expiration The air sacs may fill -Back rubbing done -Back rubbing
phase with fluid or pus
-Productive (purulent material), comforts the patient.
cough noted causing cough with
phlegm or pus, fever, -Encouraged to
chills, and difficulty -Hydration can help
increase milk liquefy viscous
breathing. intake phlegm.
Diagnosis: Pediatric Community Acqured Pneumonia High Risk Name of CI: Prof. Joybelle O.Rpdriguez RN
Room/Ward: Blessed Imelda Ward Date: February 6,2018
You might also like
- Respiratory Disorders & TB in Children (Part I and Ii) - Dr. MendozaDocument17 pagesRespiratory Disorders & TB in Children (Part I and Ii) - Dr. MendozaRea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- VSIM Nursing Clinical Rotation WorksheetDocument13 pagesVSIM Nursing Clinical Rotation WorksheetVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MSN 1Document14 pagesLesson Plan MSN 1SHREE SWAMINARAYAN NURSING COLLEGE CHIKHLINo ratings yet
- Torax1d Cofre 09Document6 pagesTorax1d Cofre 09Pamela Susana Rivera GómezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: Basco, Kimberly BSN-2Document5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: Basco, Kimberly BSN-2Cxazandra Kaith CasasNo ratings yet
- Client in Context Present State Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Patient History: Subjective Cues: IndependentDocument3 pagesClient in Context Present State Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Patient History: Subjective Cues: IndependentMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaFaith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- NCP, Drug StudyDocument9 pagesNCP, Drug StudyTresha CaliboNo ratings yet
- SIC (Carpio, Kurt Andrew)Document5 pagesSIC (Carpio, Kurt Andrew)Kurt Andrew CarpioNo ratings yet
- Study of Illness Condition (Sic) : Assessment Anatomy Physiology Pathophysiolo GY AnalysisDocument5 pagesStudy of Illness Condition (Sic) : Assessment Anatomy Physiology Pathophysiolo GY AnalysisKurt Andrew CarpioNo ratings yet
- MS Notes MidtermsDocument13 pagesMS Notes MidtermsWelfe DupitNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaChiro Rouy Malaluan100% (2)
- Pedia Rotation CroupDocument2 pagesPedia Rotation CroupKaren ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananNo ratings yet
- CPCgr3 Case03 FinishDocument27 pagesCPCgr3 Case03 FinishPingky khingthongNo ratings yet
- KAYLA H. LOPEZ OPST Template 2Document3 pagesKAYLA H. LOPEZ OPST Template 2Raynard MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsDocument9 pagesRespiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration R/T Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Absent Soft Palate IDocument4 pagesRisk For Aspiration R/T Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Absent Soft Palate Imonike07No ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianeDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- CARE PLAN For BRONCHIECTASISDocument8 pagesCARE PLAN For BRONCHIECTASISCecil MonteroNo ratings yet
- NCP - Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesNCP - Respiratory DistressDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing: Proposed By: Mrs. Sharry Mae G. Awayan, RN, MANDocument4 pagesSaint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing: Proposed By: Mrs. Sharry Mae G. Awayan, RN, MANKyle PoticarNo ratings yet
- Medication and Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesMedication and Nursing Care PlanRubina MasihNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Ovarian New Growth (Mucinous Cystadenomacarcinoma)Document20 pagesA Case Study Ovarian New Growth (Mucinous Cystadenomacarcinoma)HappieSayonara Sardoma Minaves100% (1)
- The Health Sciences CenterDocument5 pagesThe Health Sciences CenterStef ReyesNo ratings yet
- Papers: Community Study Ofviral Infections Exacerbations Ofasthma in Old ChildrenDocument5 pagesPapers: Community Study Ofviral Infections Exacerbations Ofasthma in Old ChildrendianNo ratings yet
- Medical and Nursing Management Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesMedical and Nursing Management Nursing Care PlanPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: SecretionsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: SecretionsMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Case - Study (PCAP)Document27 pagesCase - Study (PCAP)Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Flash CardDocument2 pagesFlash CardRoy CabuenasNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument15 pagesAsthmaDiana HuañecNo ratings yet
- IPPA SampleDocument28 pagesIPPA Samplekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- University of Perpetual Help - Dr. Jose G. Tamayo Medical University Sto. Niño, Biñan, LagunaDocument13 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help - Dr. Jose G. Tamayo Medical University Sto. Niño, Biñan, LagunaMarivic Grazielle MarianoNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesCase AnalysisDarlyn Amplayo100% (1)
- Sample NCPDocument3 pagesSample NCPchenri1318No ratings yet
- 316 RevalidaDocument14 pages316 RevalidaPAOLA LUZ CRUZNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer HA LECTURE Assignments CompilationDocument5 pagesReviewer HA LECTURE Assignments CompilationAmbot sa ImoNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument33 pagesPNEUMONIAgabrielle panganNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Ovarian New Growth (Mucinous Cystadenomacarcinoma)Document21 pagesA Case Study Ovarian New Growth (Mucinous Cystadenomacarcinoma)HappieSayonara Sardoma MinavesNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: Case ReportDocument6 pagesRecurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: Case ReportPradhana FwNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7Document7 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7jomariNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat: Navigating The Differential DiagnosisDocument7 pagesSore Throat: Navigating The Differential DiagnosisCaity YoungNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Asthma Handout V23Document3 pagesPediatrics - Asthma Handout V23Pamela AlleyNo ratings yet
- NCP of Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesNCP of Respiratory DistressDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Noninvasive Ventilation: Cathy HautDocument7 pagesPediatric Noninvasive Ventilation: Cathy HautsiputamaliaputriNo ratings yet
- SEM OutputDocument8 pagesSEM OutputJireh Vien AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan SampleDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Sampleyeye22100% (39)
- Opd) Ba) CSDocument7 pagesOpd) Ba) CSFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Examinations: Allen's Test Normal Finding: Hand Quickly BecomesDocument9 pagesLaboratory Examinations: Allen's Test Normal Finding: Hand Quickly BecomesShane GumaponNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN PneumoniaDocument38 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN PneumoniaLuna JadeNo ratings yet
- 02 Acute Airway ObstructionDocument3 pages02 Acute Airway Obstructioncharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument3 pagesPoliomyelitisDiana Fadhilah SariNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF THE EAR, NOSE, MOUTH AND THROAT (Chapter 12)Document4 pagesASSESSMENT OF THE EAR, NOSE, MOUTH AND THROAT (Chapter 12)Christianne CapuaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsDocument7 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Apis Mellifica; or, The Poison of the Honey-Bee, Considered as a Therapeutic AgentFrom EverandApis Mellifica; or, The Poison of the Honey-Bee, Considered as a Therapeutic AgentNo ratings yet
- Secondhand Smoking ScriptDocument2 pagesSecondhand Smoking ScriptMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Activity 1-Globalization Application: Remarks ScoreDocument2 pagesActivity 1-Globalization Application: Remarks ScoreMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument2 pagesMalariaMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Secondhand SmokingDocument2 pagesSecondhand SmokingMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- RPH Early Practices of Early Filipinos TacataalejonDocument6 pagesRPH Early Practices of Early Filipinos TacataalejonMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Maridhel Rañon BSN 1 ADocument1 pageMaridhel Rañon BSN 1 AMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- PCOMDocument2 pagesPCOMMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Words Are So StrongDocument1 pageWords Are So StrongMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- DENGA-EY, Activity 1 and 2Document3 pagesDENGA-EY, Activity 1 and 2Melrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Advantages of GlobalizationDocument4 pagesAdvantages of GlobalizationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- SpeachDocument4 pagesSpeachMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Lorenz M. Rafael - P.E 102 - Fitness ExercisesDocument6 pagesLorenz M. Rafael - P.E 102 - Fitness ExercisesMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- My ExampleDocument1 pageMy ExampleMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- BOTSDocument4 pagesBOTSMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Misa RobotDocument1 pageMisa RobotMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- My Sisters KeeperDocument3 pagesMy Sisters KeeperMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- MR and Miss Intramurals 2022Document1 pageMR and Miss Intramurals 2022Melrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Act. 1Document2 pagesNursing Informatics Act. 1Melrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument20 pagesPleural EffusionMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Humanitarian Crisis in Yemen 1Document5 pagesHumanitarian Crisis in Yemen 1Melrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- DENGA EY. StereotypeDocument2 pagesDENGA EY. StereotypeMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver ScriptDocument2 pagesLeopold's Maneuver ScriptMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Name and Classification of DrugDocument7 pagesName and Classification of DrugMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- DIARYDocument2 pagesDIARYMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- History of Brgy. TiaganDocument1 pageHistory of Brgy. TiaganMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Visual ArtsDocument3 pagesVisual ArtsMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Dont JudgeDocument1 pageDont JudgeMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet