Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 37
Uploaded by
Abdul MajidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 37
Uploaded by
Abdul MajidCopyright:
Available Formats
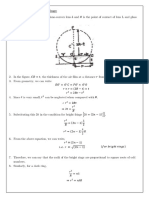
5-37
(a)
To finding eigen values of 𝐿⃗̂2 and 𝐿⃗̂ 𝑧 we act them on given states
𝐿⃗̂2 𝑌21 (𝜃, 𝜑) = 2(2 + 1)ℏ2 𝑌21 (𝜃, 𝜑) = 6ℏ2 𝑌21 (𝜃, 𝜑)
𝐿⃗̂ 𝑧 𝑌21 (𝜃, 𝜑) = 1ℏ𝑌21 (𝜃, 𝜑) = ℏ𝑌21 (𝜃, 𝜑)
(b)
For this state eigen value for 𝐿⃗̂2 is 12ℏ2 and for 𝐿⃗̂ 𝑧 is −2ℏ.
(c)
1 1 ̂2 1 ̂2
𝐿⃗̂2 (𝑌33 (𝜃, 𝜑) + 𝑌3,−3 (𝜃, 𝜑)) = 𝐿⃗ 𝑌33 (𝜃, 𝜑) + 𝐿⃗ 𝑌3,−3 (𝜃, 𝜑)
√2 √2 √2
1 1
= 12ℏ2 ( 𝑌33 (𝜃, 𝜑) + 𝑌3,−3 (𝜃, 𝜑))
√2 √2
1 1 1
𝐿⃗̂ 𝑧 (𝑌33 (𝜃, 𝜑) + 𝑌3,−3 (𝜃, 𝜑)) = 3ℏ ( 𝑌33 (𝜃, 𝜑) − 𝑌3,−3 (𝜃, 𝜑))
√2 √2 √2
So, this state is eigen state of 𝐿⃗̂2 with eigen value 12ℏ2 but not eigen state of 𝐿⃗̂ 𝑧
(d)
For this state eigen value for 𝐿⃗̂2 is 20ℏ2 and for 𝐿⃗̂ 𝑧 is 0.
Mohammad Behtaj & Adel Sepehri
Translated by:
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan L J Bain Bab 8Document34 pagesPembahasan L J Bain Bab 8fira100% (3)
- Soal Chapter 4, Sec.7 No. 7Document3 pagesSoal Chapter 4, Sec.7 No. 7D'ferti AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Sequence & SeriesDocument6 pagesSequence & SeriesBOKA CHODANo ratings yet
- Formulae and Tables For Final ExamDocument1 pageFormulae and Tables For Final ExamMuhammad Shayan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Question BankDocument9 pagesMathematics - Question BankFaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Test 3 - Elevate Classes - 11628509 - 2022 - 12!25!19 - 54Document7 pagesModern Physics Test 3 - Elevate Classes - 11628509 - 2022 - 12!25!19 - 54dixitratan68No ratings yet
- The Generalised Form of Liouville Dirichlet Integrals (In N-Dimensional SpacesDocument4 pagesThe Generalised Form of Liouville Dirichlet Integrals (In N-Dimensional SpacesInije EjiroNo ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanics GuideDocument28 pagesOrbital Mechanics GuidePrakruthi K PNo ratings yet
- Formulario AlmacenesDocument1 pageFormulario AlmacenesMelodyNo ratings yet
- HR and SR from EOSDocument5 pagesHR and SR from EOSanonymoussionNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledYulexi Yajaira Pesantes ApoloNo ratings yet
- Limit and Continuity: Complex VariableDocument7 pagesLimit and Continuity: Complex VariableRokibul HasanNo ratings yet
- CH162 HW2 Partial Molar QuantitiesDocument4 pagesCH162 HW2 Partial Molar QuantitiesStudent 1No ratings yet
- 2020 Nov PPR 2 Suggested Marking Guide by TrockersDocument29 pages2020 Nov PPR 2 Suggested Marking Guide by TrockersPriscaNo ratings yet
- Ch:2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions:-: FormulasDocument2 pagesCh:2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions:-: FormulasPATEL AUM S.No ratings yet
- Solution To Extra Problem Set 4Document12 pagesSolution To Extra Problem Set 4物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Statistical Formulae GuideDocument2 pagesStatistical Formulae GuideB BhavyaNo ratings yet
- Sección 1.3 y 1.4Document5 pagesSección 1.3 y 1.4juancho 507No ratings yet
- S Announcement 16727 PDFDocument1 pageS Announcement 16727 PDFSagi NesiNo ratings yet
- TI#1Document3 pagesTI#1yuslihatindwiyantiNo ratings yet
- ImaginariosDocument9 pagesImaginariosJoShUa PrONo ratings yet
- General 2 Order System Response DerivationDocument5 pagesGeneral 2 Order System Response DerivationMuhammad Zahid Muhammad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Scholar Paper 13 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesScholar Paper 13 Answer KeyAashika DhareNo ratings yet
- Eda FormulasDocument2 pagesEda FormulasLee Angus SantosNo ratings yet
- Formulari 2023-24Document2 pagesFormulari 2023-24agraciabalaguerNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 optimization and root-finding techniquesDocument6 pagesAssignment #2 optimization and root-finding techniquesMalek Al-AsaliNo ratings yet
- TERM 1 TEST MATHS GRADE 12 MEMODocument6 pagesTERM 1 TEST MATHS GRADE 12 MEMOtrevlynnaidoo08No ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics (part-II)Document30 pagesStatistical Mechanics (part-II)Shadow GamingNo ratings yet
- MATH 1022 Discrete Structure Second AssignmentDocument7 pagesMATH 1022 Discrete Structure Second AssignmentAchyut NeupaneNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Vector FieldsDocument7 pages3.1 Vector FieldsSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
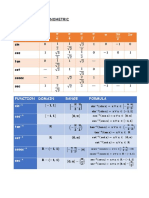
- Fórmulas y Funciones TrigonométricasDocument5 pagesFórmulas y Funciones TrigonométricasMohammed BenabdelkaderNo ratings yet
- HW02 - Ly Thierno Mouhamadou Samassa - D2021738Document4 pagesHW02 - Ly Thierno Mouhamadou Samassa - D2021738Thierno Samassa LyNo ratings yet
- Finite Difference Methods for Two-Point Boundary Value ProblemsDocument3 pagesFinite Difference Methods for Two-Point Boundary Value ProblemsasasdNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Pre-MidDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Pre-MidUzair KhanNo ratings yet
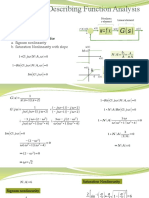
- NCS21 - 03 - Describing Function Analysis - 04Document8 pagesNCS21 - 03 - Describing Function Analysis - 04zain khuramNo ratings yet
- HW 3 Mechanics of Materials 2 (1-4)Document6 pagesHW 3 Mechanics of Materials 2 (1-4)AdzimNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 EE 472 For UNLVDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 EE 472 For UNLVistraight1No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledJitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- On Radio D-Distance in Harmonic Mean Labelling of Some GraphsDocument6 pagesOn Radio D-Distance in Harmonic Mean Labelling of Some GraphsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 5.Z - Transforms Notes1Document17 pages5.Z - Transforms Notes1312820110033 SRI PRABHU RNo ratings yet
- Newton's RingsDocument2 pagesNewton's RingsJagan KagithalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Modeling in The Frequency Domain Partial Fraction-Expansion Case 1 Ex. 2.3Document4 pagesChapter 2 Modeling in The Frequency Domain Partial Fraction-Expansion Case 1 Ex. 2.3Joy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic force equations of aircraft motionDocument4 pagesAerodynamic force equations of aircraft motionMilena Rocío LamonegaNo ratings yet
- Final 20 21iDocument9 pagesFinal 20 21ialikhalidd23No ratings yet
- Solution 4Document2 pagesSolution 4chandraadityaofflNo ratings yet
- RadiofrecuenciaDocument9 pagesRadiofrecuenciaSilviTaPinOsNo ratings yet
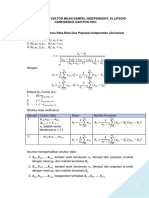
- Uji Mean Ellipsoid Pos Hoc IndependentDocument37 pagesUji Mean Ellipsoid Pos Hoc IndependentEdi Susanto edisusanto.2022No ratings yet
- Week 7Document7 pagesWeek 7Hasnain DanishNo ratings yet
- Explanation To Iteration of STDocument1 pageExplanation To Iteration of SToptimisteveNo ratings yet
- Formulario Parcial 2Document1 pageFormulario Parcial 2Viviana RamírezNo ratings yet
- Equation sheetDocument10 pagesEquation sheetNorris wongNo ratings yet
- Trigonometic FormulasDocument2 pagesTrigonometic FormulasLoreloom JoharNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Formula Sheet: Tss SDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Formula Sheet: Tss SFgfdesdgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Notes - Advanced Arch Dams Part 2Document10 pagesLecture 6 Notes - Advanced Arch Dams Part 2Chalang AkramNo ratings yet
- 4 7Document4 pages4 7趙睿中No ratings yet
- MIdterm SolDocument3 pagesMIdterm Sol백승헌No ratings yet
- 5 38Document1 page5 38Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis Quick Review Akhtar Abbas PDFDocument24 pagesComplex Analysis Quick Review Akhtar Abbas PDFAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-04-11 13.18.35Document50 pagesNew Doc 2019-04-11 13.18.35Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument11 pagesModern PhysicsAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Key Book To Programming Exercises of OOP C (FreeBooks - PK) PDFDocument137 pagesKey Book To Programming Exercises of OOP C (FreeBooks - PK) PDFAbdul MajidNo ratings yet