Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terminology Tables
Uploaded by
Panagiota Dima0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Terminology-Tables
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesTerminology Tables
Uploaded by
Panagiota DimaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Position Relationship Terminology Description
Superior Above, closer to the head
Inferior Below, closer to the feet
Medial Closer to the midline
Lateral Further away from the midline
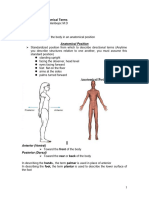
Anterior Closer to the front of the body
Posterior Closer to the back of the body
Ventral Closer to the front or the belly of the body, a
term used more frequently in embryology and
zoology where ventral and anterior can differ
Dorsal Closer to the back of the body, a term used
more frequently in embryology and zoology
where dorsal and posterior can differ
Superficial Closer to the surface
Intermediate Between a superficial structure and a deep
structure
Deep Further away from the surface
Proximal Closer to the point of origin, or the centre of
body
Distal Further away from the point of origin or centre
of body
Rostral Closer to the front of the face, i.e. nose and
mouth, term used more frequently in
embryology
Cranial Closer to the head of the body, a term used
more frequently in embryology where
superior and cranial can differ
Caudal Closer to the tail end of the body, a term used
more frequently in embryology where inferior
and caudal can differ
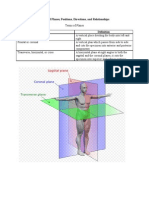
Anatomical Plane Terminology Description
Coronal Plane (AKA Frontal) Equal or unequal section that divides the
body anteriorly and posteriorly
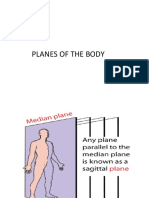
Sagittal Plane Unequal section that divides the body into left
and right parts
Medial Plane (AKA Mid-sagittal) Equal section that divides the body into left
and right halves
Transverse Plane (AKA Axial, Horizontal) Equal or unequal section that divides the
body superiorly and inferiorly
Oblique Plane Equal or unequal section that divides the
body at an angle not parallel to the horizontal
or vertical axes
Muscle Movement Terminology Description
Flexion Decreasing the angle of the joint
Extension Increasing the angle of the joint
Hyperextension Extension beyond the normal limit of
movement of a joint
Abduction Movement away from the midline
Adduction Movement towards the midline
Circumduction Combination of flexion, extension, abduction
and adduction
Medial Rotation Rotational movement towards the midline
Lateral Rotation Rotational movement away from the midline
Dorsiflexion Movement of the ankle joint resulting in the
toes pointing up
Plantar flexion Movement of the ankle joint resulting in toes
pointing down
Inversion Movement of the foot in which the bottom of
the foot is tilted to face the midline
Eversion Movement of the foot in which the bottom of
the foot is tilted to face away from the midline
Opposition Movement of the thumb bringing it and the
little finger together
Reposition Movement of the thumb away from the little
finger
Pronation Rotation of the forearm resulting in the palm
facing posteriorly in relation to anatomical
position. The radius bone crosses over the
ulna bone to perform this action.
Supination Rotation of the forearm resulting in the palm
facing anteriorly in relation to anatomical
position
Protraction Movement of a part of the body anteriorly,
drawing it forwards
Retraction Movement of a part of the body posteriorly,
drawing it backwards
Elevation Movement of a part of the body superiorly
Depression Movement of a part of the body inferiorly
You might also like
- Part 2 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesPart 2 Anatomy and Physiologyzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionDocument7 pagesAnatomical PositionJeffrey SyliongcoNo ratings yet
- REHA2171 - Osteopathy Theory and Practice 1: Anatomical PlanesDocument3 pagesREHA2171 - Osteopathy Theory and Practice 1: Anatomical PlanesHammad -ullahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Anatomical TerminologyDocument3 pagesGlossary of Anatomical TerminologypoggerNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Position and Movement TerminologyDocument23 pagesLec 1 Position and Movement TerminologyFareeha KausarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Midterm PathfitDocument2 pagesReviewer Midterm PathfitMelendez, Abegail T.No ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument7 pagesAnatomical TermsKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Yoga Teacher Training Anatomy of Movement For Yoga TeachersDocument22 pagesYoga Teacher Training Anatomy of Movement For Yoga TeachersMarkusNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Terms, Tissues and Medical ImagingDocument17 pagesWeek 1 - Terms, Tissues and Medical Imagingatgriffo100% (1)
- OT 211 - Notes - IntroductionDocument21 pagesOT 211 - Notes - Introductionno nameNo ratings yet
- PE-READING-MATERIALS-AND-ACTIVITY-SHEET-FINALDocument14 pagesPE-READING-MATERIALS-AND-ACTIVITY-SHEET-FINALMARY JOY MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- Terminology: Jose Roilo D. Mula, PTRPDocument33 pagesTerminology: Jose Roilo D. Mula, PTRPGesal GageloniaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Handbook-CodeworksDocument171 pagesAnatomy Handbook-CodeworksBe GameNo ratings yet
- Pe1-Anatomical Reference Postion & Directional TermsDocument11 pagesPe1-Anatomical Reference Postion & Directional TermsJinky JunioNo ratings yet
- 3 Branches: 1. Macroscopic (Gross)Document41 pages3 Branches: 1. Macroscopic (Gross)Susan ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Body CavitiesDocument11 pagesBody Cavitiesapi-421877616No ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument2 pagesAnatomical TermsTeryy HerreraNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical Terminology GuideDocument3 pagesBasic Anatomical Terminology GuideJennifer PaltiyanNo ratings yet
- 1.an Overview of AnatomyDocument23 pages1.an Overview of AnatomyAmrith LordNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologyDocument41 pagesChapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologymintsaoraNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy notesDocument2 pagesHuman Anatomy notesSamantha LiberatoNo ratings yet
- Kin2222 - Anatomical Terms, Planes - Movements 2 2Document2,607 pagesKin2222 - Anatomical Terms, Planes - Movements 2 2AmreenNo ratings yet
- The Language of Anatomy 1Document1 pageThe Language of Anatomy 1michelleannantiqueNo ratings yet
- Muscle Types, Actions, and AnatomyDocument48 pagesMuscle Types, Actions, and AnatomyBianca ParasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Fundamentals ExplainedDocument36 pagesAnatomy Fundamentals ExplainedJustineNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Intro To AnatomyDocument5 pagesCh1 Intro To AnatomyztolmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter I IntroductionDocument58 pagesChapter I Introductionnot meNo ratings yet
- ANPH111 PRELIMS [LAB]Document20 pagesANPH111 PRELIMS [LAB]Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument31 pagesAnatomical PositionsShravani NajanNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology PDFDocument22 pagesAnatomical Terminology PDFProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- Kinesiology: MahboobullahDocument22 pagesKinesiology: MahboobullahZuhaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Language of AnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Language of Anatomyjava_biscocho122950% (2)
- Planes of The BodyDocument16 pagesPlanes of The BodyHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Anatomical TerminologyDocument105 pagesExercise 1 Anatomical TerminologyRicardo Robinson100% (1)
- Anatomy IntroDocument21 pagesAnatomy IntroMHKNo ratings yet
- General ZoologyDocument64 pagesGeneral ZoologyCarmelle ZanoriaNo ratings yet
- Anatomcial PositonDocument18 pagesAnatomcial PositonAicelle GayapNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument32 pagesAnatomical PositionsPearl Lee MetiamNo ratings yet
- Anatomical-Positions-Directional-Terms PE 2 ACTIVITY - FLORES, RENNETH READocument9 pagesAnatomical-Positions-Directional-Terms PE 2 ACTIVITY - FLORES, RENNETH REARenneth Rea FloresNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument38 pagesAnatomical Termsrajni singhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy Lec1Document38 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy Lec1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology 2022Document24 pagesAnatomical Terminology 2022Arm UdomratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Human BodyDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Human BodyClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body MovementsDocument23 pagesAdvanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body Movementseyob yirsaw basaznewNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Best Short Notes and Flow ChartDocument5 pagesAnatomy Best Short Notes and Flow ChartNikhilNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Anatomical Termsoluebuben02No ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionDocument16 pagesAnatomical Positionmaclaineheart.migNo ratings yet
- IC SocketDocument307 pagesIC SocketChandan Mahapatra100% (1)
- Anatomy Terminology PDFDocument2 pagesAnatomy Terminology PDFRachelle Anne LuisNo ratings yet
- Anatomicial PositonDocument19 pagesAnatomicial PositonMariel GuzonNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument8 pagesAnatomical TermsDAGUMAN, FIONA DEI L.No ratings yet
- Terms of Planes Positions Directions and RelationshipsDocument4 pagesTerms of Planes Positions Directions and RelationshipsWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- 1.introdution To Human Anatomy 1Document51 pages1.introdution To Human Anatomy 1ruwanganiNo ratings yet
- Rad. Positioning 2Document553 pagesRad. Positioning 2Lalaine De JesusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology OrientationDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OrientationBeatriz Nidea83% (6)
- Mcmillan, 1987) - in A Normal Walk The Toes Are: Key Facts About The Anatomical Terminology Anatomical PositionDocument2 pagesMcmillan, 1987) - in A Normal Walk The Toes Are: Key Facts About The Anatomical Terminology Anatomical PositionCarla NatividadNo ratings yet
- ANATOMICAL POSITION Amen AmenDocument12 pagesANATOMICAL POSITION Amen AmenJyross MacapogasNo ratings yet



























![ANPH111 PRELIMS [LAB]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719863137/149x198/c165ee1737/1712198106?v=1)