Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 - 02 Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
Uploaded by
amr AboelnagaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 - 02 Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
Uploaded by
amr AboelnagaCopyright:
Available Formats
National Project, O&M Management
Organization (Mashroat)
Mashroat Projects White Book
Volume 11, Chapter 4
Project Control of Hazardous Materials
Procedure
Document No. EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 1 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
Document Revisions History:
Revision: Date: Reason For Issue
000 20/09/2017 For Use
001 03/12/2017 For Use
002 19/11/2018 For Use
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 2 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
THIS NOTICE MUST ACCOMPANY EVERY COPY OF THIS DOCUMENT
IMPORTANT NOTICE
This document, (“Document”) is the exclusive property of the National Project, Operation and Maintenance
Management Organization (“Mashroat”).
This Document should be read in its entirety including the terms of this Important Notice. The government entities may
disclose this Document or extracts of this Document to their respective consultants and/or contractors, provided that
such disclosure includes this Important Notice.
Any use or reliance on this Document, or extracts thereof, by any party, including government entities and their
respective consultants and/or contractors, is at that third party’s sole risk and responsibility. Mashroat, to the maximum
extent permitted by law, disclaim all liability (including for losses or damages of whatsoever nature claimed on
whatsoever basis including negligence or otherwise) to any third party howsoever arising with respect to or in
connection with the use of this Document including any liability caused by negligent acts or omissions.
This Document and its contents are valid only for the conditions reported in it and as of the date of this Document .
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 3 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
Table of Contents
1.0 PURPOSE ...................................................................................................................................... 5
2.0 SCOPE ........................................................................................................................................... 5
3.0 DEFINITIONS ................................................................................................................................. 5
4.0 REFERENCES................................................................................................................................ 5
5.0 RESPONSIBILITIES ....................................................................................................................... 5
5.1 Project Manager .............................................................................................................................. 5
5.2 Construction Manager, Site Manager or Designee .......................................................................... 6
5.3 HSE Representative or Designee .................................................................................................... 6
5.4 Supervisors ..................................................................................................................................... 6
5.5 Employees ...................................................................................................................................... 6
5.6 Waste Manager ............................................................................................................................... 6
6.0 RISK ASSESSMENT ...................................................................................................................... 6
7.0 PROCESS ...................................................................................................................................... 7
7.1 Hazardous Material Control and Communication ............................................................................ 7
7.2 Chemical Registers ......................................................................................................................... 7
7.3 Hazard Communication Program .................................................................................................... 9
7.4 Storage of Hazardous Material ........................................................................................................ 9
7.5 Safety Data Sheets (SDS) ............................................................................................................... 9
7.5.1 Communication Standard of Safety Data Sheets (SDS) ................................................. 10
7.6 Labelling........................................................................................................................................ 11
7.7 Placarding ..................................................................................................................................... 11
7.8 Signage ......................................................................................................................................... 11
7.9 Disposal of Waste Products .......................................................................................................... 11
8.0 RECORDS .................................................................................................................................... 12
9.0 ATTACHMENTS ........................................................................................................................... 12
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 4 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
1.0 PURPOSE
The purpose of this procedure is to describe the primary elements of a hazard communication program that
will allow for the adequate protection of workers from the potential dangers associated with hazardous
materials in the workplace and provide guidelines for administering an onsite hazardous materials control
program.
2.0 SCOPE
The scope of this procedure applies to all works performed under all Government Construction Contracts
executed throughout the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
3.0 DEFINITIONS
Definitions Description
Hazardous Material Materials harmful to human health and/or the environment that is
solid, semi-solid, liquid, or gas and may include hazardous wastes.
Hazardous Material Inventory A log of hazardous materials stored and in use onsite, including type,
quantity, location, and safety data sheet (SDS) documentation.
IBC Intermediate Bulk Container
OSHA Occupational Health and Safety Administration
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) A document that states the material’s hazardous constituents,
chemical and physical properties, health hazards, permissible
exposure levels, first-aid procedures, emergency procedures, and the
recommended handling and use requirements. The manufacturer
must provide an SDS for all hazardous materials.
Entity Entity - includes Government Ministry, EPMO, Engineering
Management Company or any other agency authorized by the
Government Ministry to work on its behalf.
4.0 REFERENCES
OSHA 29CFR 1910 Subpart H Hazardous Materials.
OSHA 29CFR 1910 Subpart I Personal Protective Equipment.
OSHA 29CFR 1910 Subpart J General Environmental Controls.
OSHA 29CFR 1910 Subpart Z Toxic and Hazardous Substances.
OSHA 29CFR 1910.1200 Hazard Communication
EPM-KSS-PR-000003 - Project Personal Protective Equipment Procedure
EPM-KSS-PR-000004 - Project Fire Protection and Prevention Procedure.
EPM-KSS-PR-000006 - Project Barricades and Signs Procedure
EPM-KSE-PR-000001 - Project Pollution Control Procedure
EPM-KSE-PR-000002 - Project Waste Management Procedure
EPM-KSH-PR-000004 - Project Respiratory Protective Equipment Procedure.
5.0 RESPONSIBILITIES
Each Project shall define responsibilities through its governing policies, plans, procedures and the
organization structure respectively. The following proposed responsibilities demonstrate expectations
based on the industry’s standard practices:
5.1 Project Manager
The Project Manager is responsible for ensuring the resources and arrangements are available for the
implementation and management of this procedure.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 5 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
5.2 Construction Manager, Site Manager or Designee
Responsible for the overall program.
Responsible for chemicals and hazardous materials brought on or into the project/facility including
those brought on/in by lower tier contractors under their supervision.
Ensures that the number of chemicals stored are kept to a minimum.
Ensures that necessary approvals are processed prior to allowing chemicals to be brought on site,
consult with his environmental/waste management department to authorize purchase and disposal
of chemical substances.
5.3 HSE Representative or Designee
Maintain a chemical inventory list on their respective sites.
Maintain records of Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for the chemicals in the inventory list.
Assist and advise the Construction Manager on hazardous material control standards and
regulations.
Ensure that the necessary emergency kits are available and in a good condition.
5.4 Supervisors
Ensures that all hazardous chemicals are properly labelled, stored, and disposed of in accordance
with the SDS.
Ensure that his employees are trained in the safe use of hazardous chemicals for routine and non-
routine tasks.
5.5 Employees
Expected to handle chemicals and chemical substances in the proper manner at all times.
Report any problems/issues/concerns regarding chemicals and/or chemical substances to their
supervisor.
Participate in their employer’s hazardous material training program and sign on the training log
indicating they have received the required training.
5.6 Waste Manager
Advises Construction Manager or designee on approving chemical substances for purchase.
Provides technical assistance on disposal of chemicals in accordance with the Saudi National
Regulations.
6.0 RISK ASSESSMENT
An integral aspect of the work planning process is the performance of a proper risk assessment. Risk
Assessments must be conducted at the Planning Stage to identify the hazard risks and determine control
measures.
The Risk Assessments that shall be conducted at the Planning Stage are as follows:
Project Risk Assessment.
Work Method Statements (WMS)
Job Hazard Analysis (JHA).
Safety Task Analysis and Risk Reduction Talk (STARRT).
Responsible Contractors shall conduct a health risk assessment for their specific chemicals aligned with
their scope of work, and the information developed in the assessment shall be included in Job Hazard
Analyses for their work.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 6 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
The purpose of the assessment is to enable decisions to be made about appropriate chemical selection,
control measures, induction and training, monitoring and health surveillance as may be required by the
local regulations requirements. Risk assessments and mitigations shall be completed prior to any personnel
exposure.
Responsible contractors must complete a suitable and sufficient assessment of any work involving potential
exposure to any hazardous substance. Assessments must also include an environmental component that
includes but is not limited to:
Hazardous substances when working on or near water.
Restricting or substitution of hazardous substances to reduce environmental impact.
The chemical assessment process includes:
Substitution with a non-hazardous or less hazardous chemicals when available.
Identification of hazardous substances.
Review of information about chemicals.
Identification of physical and health risks from potential exposure to chemical substances.
Communication of hazards and mitigations to protect Project personnel will be accomplished using SDSs,
labels, JHA, and STARRT processes Hazardous substance risk assessments will be conducted by the
Responsible HSE personnel, supported by their employees who will be using the product. Responsible
Contractors will keep risk assessments up-to-date and readily available for audit purposes. Responsible
Contractors will indicate on Hazardous Substances Chemical Register (see Table in Section 7.2 for
example) Assessment status and applicability.
7.0 PROCESS
7.1 Hazardous Material Control and Communication
Projects must develop specific plans that include a Hazardous Material Control and Communication
procedure based on this requirement. The procedure shall describe project/facility-specific actions to be
undertaken to manage hazardous materials properly, prevent incidents, and reduce waste generation
onsite.
A standard Hazardous Material Control and Communication procedure shall cover the following elements:
Materials selection.
Procurement.
Transportation.
Storage and dispensing process to users.
Training and handling.
Disposal.
Record keeping.
Audits and assessment.
7.2 Chemical Registers
Responsible Contractors must develop and maintain a register (inventory) listing all Chemicals which are
used, stored, or are under their control in the workplace utilising an electronic system. The Contractor will
prescribe the format in which the register is to be maintained. The register and associated SDSs will be
initially submitted to Contractor prior to mobilization for review and approval and kept up -to-date monthly.
The register will be updated as new chemicals are introduced to the workplace and the use or production
of existing chemical is discontinued, and be readily available for audit by Contractor. Responsible personnel
will use their respective registers as a source of information and as a tool to manage substances used on
the Project.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 7 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
All chemical registers shall be compiled within a Project Chemical Register that the Contractor HSE
Supervisor or designee shall maintain. The intent of this document is to have one up-to-date register for all
chemicals on-site and shall be updated on a periodic basis, as needed, or when chemicals are either
received or removed from site.
The minimum information which will be included in the register is a list of all chemicals used at the workplace
and the SDS for all chemicals as required by the Local regulations/standards.
Personnel with potential for exposure to chemicals, employee representatives, Contractor, emergency
services and relevant public authorities will have ready access to the register. The register can either be
centrally located or kept in the workplace to which it pertains. The location of the chemical register will be
communicated to Contractor and Project personnel.
The Chemical Register will be comprised of the following.
A list of all the chemicals used (including storage location)
The SDSs for all those chemicals
Notation against each chemical as to whether a risk assessment has been completed (all
chemicals determined as hazardous or dangerous must have a risk assessment completed).
Chemicals are determined as hazardous or dangerous as indicated on the SDS sheets.
Hazardous Substance Chemical Register (Example)
Hazardous Substance Chemical Register
Company: ABC Project Date: 01-July-2017
Worksite: Riyadh Contact: J. Chem
Issue Date: Company:
(Date and record of assessment outcome and assessor is required where risk is not significant OR reference to
assessment report where risk is significant. Assessment is optional for substances not classified as hazardous.)
Name of Date of
Supplier Hazardous Assessment
Substance Determination
Bright Wash Hunter Supplies N 7/2008 Not required
Ethylene oxide BDH Chemicals Y 9/2006 Assessed 01-Oct-2007, Risk significant but
controlled, see report RA1.
Super Clean AAA Chemicals Y 1/2006 Assessed 06-Nov-2008, Risk not significant
whiteboard due to small quantities held and used and
cleaner method of application minimizing skin
contact – assessed by J. Chem.
Sulphuric acid BDH Chemicals Y 12/2007 Assessed 15-Nov-2007, Risk significant
98% and actions taken, see report RA2.
Morning Fresh Woolworths N 2/2008 Not required
Sodium BDH Chemicals N 6/2007 Not required
bicarbonate
Xylene Merck Y 1/2009 Assessed 15-Jan-2009, Risk not significant
due to small quantities used and controls in
place (fume hood, fume hood maintenance
program, PPE, PPE maintenance and
replacement program, staff training) –
assessed by J. Chem.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 8 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
The Contractor HSE Supervisor or designee will audit the Responsible Entity’s annual physical inventory
of all chemicals on-site. Substances no longer stored or used on-site will be moved from the register to a
redundant file.
7.3 Hazard Communication Program
Workplaces where employees might be exposed to hazardous materials must have a written plan that cover
the following:
Implemented methods to communicate to the employees the hazards they might be exposed to
during the course of executing their work.
How to identify a hazardous material.
Understanding the hazards associated with each material.
Knowing the locations of hazardous material on the work site.
Emergency Response.
Personal Protective Equipment Requirements.
7.4 Storage of Hazardous Material
Hazardous materials must be stored in a manner that adequately protects both human health and the
environment from unintended exposure to the primary hazards associated with the materials. These
primary hazards may include explosion, fire, reactivity, toxicity or any combination of these hazards.
Criteria for the location of suitable storage areas include but not limited to:
Located away from high traffic areas on site and reasonably protected from the potential for
vehicle/equipment damage by guardrails, fences, or other structural controls.
Provided with a means to control access to the materials so that only authorized (e.g., trained)
personnel may remove and use the materials.
Located away from fence line locations immediately adjacent to environmentally sensitive
resources (e.g., wetlands, streams, archaeological sites)
Provided with adequate secondary containment in the form of an impermeable surface surround
by curbing or equivalent means to minimize the release of accidentally spilled product to the
environment.
Provided with a means of segregating combustible and flammable materials form oxidizing
agents and other sources of ignition.
7.5 Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The purpose of SDS is to provide the information needed to allow the safe handling of chemicals used at
work. The SDS for a chemical substance describes its identity, relevant health hazard information,
precautions for use and safe handling information.
Manufacturers/suppliers and importers shall produce SDS for all chemicals that they supply.
Assigned Sub-contractor and other delegates shall provide to Contractor, prior to mobilization, a Chemical
Register and an SDS for each chemical listed on the register utilizing the Contractor electronic system.
Contractor shall review and approve the use of each chemical. Materials and substances that are not
approved will not be allowed on-site. When new chemicals are to be brought to site, Responsible Entity
shall submit the SDS for approval prior to having the chemical sent to the site.
Contractor will keep copies of SDS on-site for all chemicals that have been approved.
Contractor and Responsible sub-tiers, shall make sure that all employees have ready access to SDS.
Employers will require employees to read SDS for those chemicals to which they may be exposed during
their work, be trained in its use and participate in its risk assessment.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 9 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
Hard copies of SDS will be maintained in the areas or warehouse where chemicals are stored, and
individual SDS shall be available in the work areas where the specific products are used.
Access to SDS may be provided in several ways including:
Centrally located paper copy collections of SDS
Computerized SDS databases
Regardless of the method for SDS storage, Contractor will verify:
Current SDS are available
Any storage or retrieval equipment is kept in good working order
Personnel are trained on how to access the information
Where information is displayed electronically, there shall be means of obtaining a paper copy of
that information.
Copies of the SDSs will be reviewed during JHA or STARRT Card reviews as applicable.
7.5.1 Communication Standard of Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
It is important that all personnel who are using hazardous chemicals have access to relevant information
that can assist them in the Risk Management Process. Having access to SDSs helps in that process.
The Hazard Communication Standard OSHA 29CFR 1910.1200 requires that the chemical manufacturer,
distributor, or importer provide SDSs for each hazardous chemical to downstream users to communicate
information on these hazards. The information contained in the SDS is largely required to be presented in
a consistent user-friendly, 16-section format. This provides guidance to help workers who handle hazardous
chemicals to become familiar with the format and understand the contents of the SDSs.
The SDS includes information such as the properties of each chemical; the physical, health, and
environmental health hazards; protective measures; and safety precautions for handling, storing, and
transporting the chemical. The information contained in the SDS must be in English (although it may be in
other languages as well).
Sections 1 through 8 contain general information about the chemical, identification, hazards, composition,
safe handling practices, and emergency control measures (e.g., firefighting). This information should be
helpful to those that need to get the information quickly. Sections 9 through 11 and 16 contain other
technical and scientific information, such as physical and chemical properties, stability and reactivity
information, toxicological information, exposure control information, and other information including the date
of preparation or last revision. The SDS must also state that no applicable information was found when the
preparer does not find relevant information for any required element.
The SDS must also contain Sections 12 through 15, to be consistent with the UN Globally Harmonized
System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS).
A description of all 16 sections of the SDS, along with their contents, is presented below:
Section 1 – Identification.
Section 2 – Hazard(s) Identification.
Section 3 – Composition/Information on Ingredients.
Section 4 – First Aid Measures.
Section 5 – Fire-Fighting Measures.
Section 6 – Accidental Release Measures.
Section 7 – Handling and Storage.
Section 8 – Exposure Controls/Personal Protection.
Section 9 – Physical and Chemical Properties.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 10 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
Section 10 – Stability and Reactivity.
Section 11 – Toxicological Information.
Section 12 – Ecological Information. (non-mandatory)
Section 13 – Disposal Considerations. (non-mandatory)
Section 14 – Transport Information. (non-mandatory)
Section 15 – Regulatory Information. (non-mandatory)
Section 16 – Other Information.
7.6 Labelling
All containers of chemicals supplied to, used in or handled in the workplace shall be appropriately labelled
to allow the chemical to be used safely.
Where a chemical is decanted at work, the container into which the chemical is decanted will be labelled
with the product name and the risk and safety phrases.
Where labelling is required but the container into which the chemical is decanted is very small, the label
may be attached to supporting apparatus. Alternatively, a tag may be used to enable the required
information to be provided.
If Contractor or Responsible Entity finds a container that does not have a label or is improperly labelled,
action will be taken to correctly label the container
If the contents of the container are not known, this will be clearly marked on the container, for example,
“Caution: Do Not Use: Unknown Substance.” Such a container will be stored in isolation until its contents
can be identified and, if hazardous, the container is appropriately labelled. If the contents cannot be
identified, they should be disposed of in an acceptable manner.
7.7 Placarding
Placarding is required on every bulk dangerous goods storage container, at the entrance to any building in
which the dangerous goods are stored in bulk and on or adjacent to every place outside a building where
the dangerous goods are stored in bulk but not in a container.
Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs) containing dangerous goods are termed placardable units since they
are a receptacle with a capacity greater than 500kg (L) and therefore need to be placarded with emergency
information panels. Once an IBC has been emptied of all dangerous goods and cleaned per
manufacturer/supplier’s recommendations, placarding can be removed.
7.8 Signage
Signs are to be placed in appropriate locations to provide information to those entering the area or who use
the substances and for emergency response.
7.9 Disposal of Waste Products
More information for disposal of waste products can be found in EPM-KSE-PR-000002 Project Waste
Management Procedure. In summary, disposal should be done through licensed subcontractor, records of
receipts should be maintained.
Disposal forms should cover the following elements:
The quantity to be disposed.
The type of container the product is currently in.
Conditions of the product.
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 11 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
Project Control of Hazardous Materials Procedure
8.0 RECORDS
The following records are to be retained on-site for the duration of the project. The following records shall
be kept on file by the Contractor (unless noted) and made available for audit and inspection:
Applicable training records (Contractor and Responsible Entity as applicable)
Chemical requests (Forms and electronic record)
SDSs (Contractor and Responsible Entity)
Chemical Register (Contractor and Responsible Entity as applicable)
Risk Assessments (Contractor and Responsible Entity)
Personnel or area monitoring results (Contractor and Responsible Entity as applicable)
The results of health surveillance programs, if medical confidentiality is maintained (Contractor
and Responsible Entity as applicable).
9.0 ATTACHMENTS
N/A
EPM-KSH-PR-000007 Rev 002 Level - 3-E - External Page 12 of 12
Electronic documents once printed, are uncontrolled and may become out-dated. Refer to ECMS for current revision.
This Document is the exclusive property of Mashroat and is subject to the restrictions set out in the Important Notice contained in this Document.
You might also like
- EPM-KSS-PR-000029 - 02 Project Roofing Work ProcedureDocument13 pagesEPM-KSS-PR-000029 - 02 Project Roofing Work Procedureamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- EPM-KSH-PR-000010 - 02 Project Hearing Conservation ProgramDocument16 pagesEPM-KSH-PR-000010 - 02 Project Hearing Conservation Programamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- EPM-KSS-PR-000008 - 02 Project Elevated Work Platform ProcedureDocument12 pagesEPM-KSS-PR-000008 - 02 Project Elevated Work Platform Proceduremuhammad.younisNo ratings yet
- CH2-001-Project Construction General Procedure-EPM-KCC-PR-000001ENDocument13 pagesCH2-001-Project Construction General Procedure-EPM-KCC-PR-000001ENZohr CAMSNo ratings yet
- EPM-KSS-PR-000004 - 02 Project Fire Prevention and Protection ProcedureDocument16 pagesEPM-KSS-PR-000004 - 02 Project Fire Prevention and Protection Proceduremuhammad.younisNo ratings yet
- EPM-KSH-PR-000009 - 02 Project Asbestos Management ProcedureDocument33 pagesEPM-KSH-PR-000009 - 02 Project Asbestos Management Procedureamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- Inspection-Record-AHUDocument2 pagesInspection-Record-AHUSchwihdi ZakNo ratings yet
- Guide M Chapter 15 Appendix Legislation Summary TableDocument6 pagesGuide M Chapter 15 Appendix Legislation Summary TableHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Statutory Maintenance and Inspection RequirementsDocument20 pagesStatutory Maintenance and Inspection RequirementsSama88823No ratings yet
- 00-Site InstructionDocument7 pages00-Site InstructionSyed Munawar AliNo ratings yet
- EHS Hazardous Energy Control ProcedureDocument20 pagesEHS Hazardous Energy Control ProcedureRam Kumar BarathanNo ratings yet
- Copbdapr 2011Document50 pagesCopbdapr 2011Wai Khuin LumNo ratings yet
- MS of Tower Facade - 2016-05-30Document126 pagesMS of Tower Facade - 2016-05-30Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Construction Block PavingDocument11 pagesMethod Statement For Construction Block PavingMunaku TafadzwaNo ratings yet
- QAC 8131 REC4 Mockup Inspection ReportDocument1 pageQAC 8131 REC4 Mockup Inspection ReporttinzarmoeNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTOR SAFETY MEASURES FOR STONE WORKSDocument5 pagesCONTRACTOR SAFETY MEASURES FOR STONE WORKSyahiya0% (1)
- MST For Below Ground UPVC Drainage PipesDocument17 pagesMST For Below Ground UPVC Drainage Pipesمقاول تكييف كهرباء وصحيNo ratings yet
- Split Unit InstallationDocument33 pagesSplit Unit Installationsree100% (1)
- WHS Report FormDocument2 pagesWHS Report FormRamanaMurthy KotiNo ratings yet
- Permit To Work - Mechanical ContractorDocument2 pagesPermit To Work - Mechanical ContractorSamsudin AhmadNo ratings yet
- ARM Who We Are 2017Document30 pagesARM Who We Are 2017OladeleIfeoluwaOlayodeNo ratings yet
- Ten Tips On Managing RFIs For Your Construction Projects PDFDocument3 pagesTen Tips On Managing RFIs For Your Construction Projects PDFYoke ShuNo ratings yet
- Evr J0100 Msra CL 02Document10 pagesEvr J0100 Msra CL 02Marwan NizarNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Installation of Steam RoomDocument10 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Steam RoomSanto E0% (1)
- RA - 18 - For Concrete Topping On Hollow Core SlabDocument14 pagesRA - 18 - For Concrete Topping On Hollow Core SlabIbrahim EsmatNo ratings yet
- OJEU Process Chart: Click The First Arrow of Each Procedure To Link To A More Detailed FlowchartDocument5 pagesOJEU Process Chart: Click The First Arrow of Each Procedure To Link To A More Detailed FlowchartMiDuNo ratings yet
- Method For Installation of Protection Panels, Control Cable Pulling & Termination - GOSP 10Document6 pagesMethod For Installation of Protection Panels, Control Cable Pulling & Termination - GOSP 10Subhash Chekka SEC 115KV ProjectNo ratings yet
- Gate Pass ItemsDocument1 pageGate Pass Itemsronelyn llameraNo ratings yet
- Safety Awareness Print OutsDocument35 pagesSafety Awareness Print OutsStan MacapiliNo ratings yet
- 007 - WMS of K2 PasteDocument6 pages007 - WMS of K2 Pastealla malikNo ratings yet
- 37 Material StorageDocument5 pages37 Material StorageCaron KarlosNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Marble Stone InstallationDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For Marble Stone Installationchinna_p_123No ratings yet
- Suppliers H&S Pre Qualification QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesSuppliers H&S Pre Qualification QuestionnaireJoe GrantNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: Perform The WeldDocument4 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Perform The WeldSachin Raj0% (1)
- Construction Workflow GuideDocument25 pagesConstruction Workflow GuidetekeNo ratings yet
- Install HVAC Duct SystemDocument16 pagesInstall HVAC Duct SystemLouis ClarkNo ratings yet
- Annual building checklist for safety and maintenanceDocument9 pagesAnnual building checklist for safety and maintenanceNur MajNo ratings yet
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding SafetyDocument4 pagesOxy-Acetylene Welding SafetyBajaj NitinNo ratings yet
- Contractor To Check and Verify All Dimensions Before Execution of The WorkDocument3 pagesContractor To Check and Verify All Dimensions Before Execution of The Worksarathirv6No ratings yet
- Incident Investigation ReportDocument2 pagesIncident Investigation ReportRaajha MunibathiranNo ratings yet
- Qcs 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions For Electrical InstallaDocument15 pagesQcs 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions For Electrical Installabryanpastor106100% (1)
- Tiling Works Course GuideDocument9 pagesTiling Works Course GuideWan AnisNo ratings yet
- RA Termite PDFDocument1 pageRA Termite PDFMohammad Arif RasheedNo ratings yet
- STH-Helipad Operational Procedure (Controlled Document)Document45 pagesSTH-Helipad Operational Procedure (Controlled Document)aeroridhNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Project DeliverablesDocument28 pagesFertilizer Project DeliverablesClément50% (2)
- Method Statement For Installation of DBsDocument11 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of DBstristan guarinoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Procedure PDFDocument6 pagesWaste Management Procedure PDFASHIQ KOYITH VEETILNo ratings yet
- 6th Term - Utilities & Facilities ManagementDocument110 pages6th Term - Utilities & Facilities ManagementShreedhar100% (2)
- Guide To Alterations and Works London Underground Tenanted PremisesDocument34 pagesGuide To Alterations and Works London Underground Tenanted PremisesTan ChingNo ratings yet
- Plant and Equipment ManagementDocument7 pagesPlant and Equipment ManagementKhan MohhammadNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management (Control of Hazardous Substances) RegulationsDocument78 pagesEnvironmental Management (Control of Hazardous Substances) RegulationsMoleki NgendaNo ratings yet
- Safety ManualDocument126 pagesSafety ManualMuhammad Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Submittal Sheet: From: CCDocument2 pagesSubmittal Sheet: From: CCCaberte JohnnyNo ratings yet
- 13 Emergency Response: Project Employer Engineer ContractorDocument9 pages13 Emergency Response: Project Employer Engineer ContractorcenkunalNo ratings yet
- 15need of SOP in Building Construction Managemenmanagementt PDFDocument4 pages15need of SOP in Building Construction Managemenmanagementt PDFJannatul FirdousNo ratings yet
- HOT WORK PERMITDocument3 pagesHOT WORK PERMITJohn Ralph VegaNo ratings yet
- NOVEC System - Commissioning and TestingDocument5 pagesNOVEC System - Commissioning and TestingSalim Bakhsh100% (1)
- Condition SurveyDocument24 pagesCondition Surveypankajsingh fosrocNo ratings yet
- Tiling WorksDocument21 pagesTiling WorksGhayas JawedNo ratings yet
- EPM-KSH-PR-000008 - 02 Project Heat Stress Management ProcedureDocument13 pagesEPM-KSH-PR-000008 - 02 Project Heat Stress Management Procedureamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- EPM-KSH-PR-000009 - 02 Project Asbestos Management ProcedureDocument33 pagesEPM-KSH-PR-000009 - 02 Project Asbestos Management Procedureamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- Project Managemer Handbook GuidlineDocument72 pagesProject Managemer Handbook Guidlineamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- ACP - AutoCADDocument6 pagesACP - AutoCADamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- ACP - Civil 3DDocument6 pagesACP - Civil 3Damr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- معادلة رسم البروفيل من خلال الاوتوكادDocument441 pagesمعادلة رسم البروفيل من خلال الاوتوكادamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- معادلة حساب الكميات التقديرية للطرق من خلال البروفيل و الاكسيلDocument1,007 pagesمعادلة حساب الكميات التقديرية للطرق من خلال البروفيل و الاكسيلamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- نقل البيانات من الاكسيل الى الاوتوكاد الاصدار الجديدDocument1,292 pagesنقل البيانات من الاكسيل الى الاوتوكاد الاصدار الجديدamr AboelnagaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument86 pagesProjectrajuNo ratings yet
- Decembermagazine 2009Document20 pagesDecembermagazine 2009maria_diyah4312No ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesMultivariate Analysis Homework Questions歐怡君No ratings yet
- Ringkasan LaguDocument4 pagesRingkasan LaguJoe PyNo ratings yet
- The Unbounded MindDocument190 pagesThe Unbounded MindXtof ErNo ratings yet
- Environmental Threats Differentiated Reading Comprehension Ver 1Document20 pagesEnvironmental Threats Differentiated Reading Comprehension Ver 1Camila DiasNo ratings yet
- Openness To Experience: Intellect & Openness: Lecture Notes 8Document8 pagesOpenness To Experience: Intellect & Openness: Lecture Notes 8Danilo Pesic100% (1)
- ChromosomesDocument24 pagesChromosomesapi-249102379No ratings yet
- Cyber Security 2017Document8 pagesCyber Security 2017Anonymous i1ClcyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Maths PlaneDocument62 pagesYear 10 Maths Planehal wangNo ratings yet
- NSX 100-630 User ManualDocument152 pagesNSX 100-630 User Manualagra04100% (1)
- Organic Chem Diels-Alder Reaction LabDocument9 pagesOrganic Chem Diels-Alder Reaction LabPryanka BalleyNo ratings yet
- A ULTIMA ReleaseNotesAxiomV PDFDocument38 pagesA ULTIMA ReleaseNotesAxiomV PDFIVANALTAMARNo ratings yet
- Komatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646Document26 pagesKomatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646juan santa cruzNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2-Week 2-Module 4-Evidence of EvolutionDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology 2-Week 2-Module 4-Evidence of EvolutionFEMALE Dawal LaizaNo ratings yet
- Ek Pardesi Mera Dil Le Gaya Lyrics English Translation - Lyrics GemDocument1 pageEk Pardesi Mera Dil Le Gaya Lyrics English Translation - Lyrics Gemmahsa.molaiepanahNo ratings yet
- SeparatorDocument2 pagesSeparatormmk111No ratings yet
- 266 009-336Document327 pages266 009-336AlinaE.BarbuNo ratings yet
- 2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION IN P. E 2019-2020Document3 pages2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION IN P. E 2019-2020Lyzl Mahinay Ejercito MontealtoNo ratings yet
- PropensityModels PDFDocument4 pagesPropensityModels PDFSarbarup BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- State of Education in Tibet 2003Document112 pagesState of Education in Tibet 2003Tibetan Centre for Human Rights and DemocracyNo ratings yet
- European Business in China Position Paper 2017 2018 (English Version)Document408 pagesEuropean Business in China Position Paper 2017 2018 (English Version)Prasanth RajuNo ratings yet
- Class 7thDocument24 pagesClass 7thPriyaNo ratings yet
- Virtio-Fs - A Shared File System For Virtual MachinesDocument21 pagesVirtio-Fs - A Shared File System For Virtual MachinesLeseldelaterreNo ratings yet
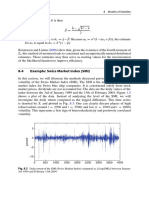
- 8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityDocument3 pages8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityNickesh ShahNo ratings yet
- The Interview: P F T IDocument14 pagesThe Interview: P F T IkkkkccccNo ratings yet
- Political Engineering and Party Politics in Conflict-Prone SocietiesDocument18 pagesPolitical Engineering and Party Politics in Conflict-Prone SocietiesNashiba Dida-AgunNo ratings yet
- 99th Indian Science Congress (Bhubaneshwar)Document95 pages99th Indian Science Congress (Bhubaneshwar)Aadarsh DasNo ratings yet
- TILE FIXING GUIDEDocument1 pageTILE FIXING GUIDEStavros ApostolidisNo ratings yet
- College of Physical Therapy Produces Skilled ProfessionalsDocument6 pagesCollege of Physical Therapy Produces Skilled ProfessionalsRia Mae Abellar SalvadorNo ratings yet