Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SDGFH 987 GHNSFG 871 SF 8 GH
Uploaded by
Alya Barrot0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesgfhm,j
Original Title
sdgfh987ghnsfg871sf8gh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentgfhm,j
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesSDGFH 987 GHNSFG 871 SF 8 GH
Uploaded by
Alya Barrotgfhm,j
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
DOWNER
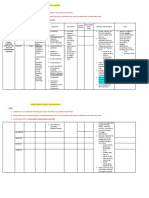
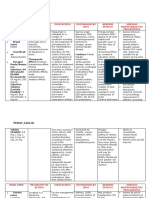
ALCOHOL ABUSE DEFINITIONS
Rapidly absorbed in bloodstream DETOXIFICATION – removing toxic substance
10mL alcohol in 1L blood = alcoholism WITHDRAWAL – surge of adrenaline once abrupt
LEVELS EFFECTS OVERDOSE stop using
0.1-0.2 Slow coordination Altered LOC INTOXICATION – physical/mental control decreases
Slurred speech INTOXICATION WITHDRAWAL
0.2-0.3 Tremors Breathing low + STIMULANTS
Irritability vomiting (Drugs)
Violence DEPRESSANTS
0.3 up Unconscious Coma (Alcohol,
Death Narcotics,
EFFECTS Opiates)
Aggression Impaired attention
Blackouts No concentration EFFECTS OS SUBSTANCE ABUSE
Coordination problem Impaired memory NO friends
Unsteady gait Lack judgment NO leisure activities
Polyuria NO spiritual values
NO moral standards
WERNICKE – KORSAKOFF’s SYNDROME abNOrmal physical functions
Amnesia COMMON BEHAVIORS
Increased family tension
Clouding of consciousness Denial Increased mental deterioration
Confabulation Dependency Sexual problems
Peripheral neuropathy Demanding Occupational problems
ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL Destructive
SYND. Domineering
STAG EFFECTS
E TREATMENT OPIOIDS – desensitizes physiologic & psycho pain
1 6-8 hrs after intake Detoxification with medical Ex.
supervision OPIOID INTOXICATION
Anxiety and anorexia Morphine
Insomnia and Pinpoint pupils
Opium
DRUGS Apathy
tremors Meperidine (Demerol)
Benzodiazepines (S/S) Respiratory depression
N/V and Codeine
1.Lorazepam (Ativan) Lethargy & restless
hyperactivity Hydrocodone Attention & memory
2.Diazepam (Valium)
HR and BP up Methadone – detoxification impairment
Depression Uncoordinated
Alcohol antagonist DRUGS
2 8-12 hrs after intake movements
Disulfiram (Antabuse) Naloxone
Confusion Slurred speech
Give after atleast 12hrs Opioid antagonist
Gross tremors Immediately improves
Inhibits acetaldehyde into
Nervousness Respiration & consciousness S/S
a. dehydrogenase
Disorientation Craving
Severe adverse effects
Auditory and visual WITHDRAWAL Restlessmess &
Arrhythmias
hal. Drug intake ceases rhinorrhea
MI Markedly decreased
Illusions Anxiety w/ aching
Cardiac failure Precipitated by Naloxone backs and legs
Nightmares
Seizures Nausea Vomiting
3 12-48 hrs after intake
Coma Dysphoria & diarrhea
Severe hal.
Death Sweating
Seizures GIVE
AVOID ANY ALCOHOL Fever
DILANTIN
ONCE TAKEN THIS MEDS Lacrimation
4 3-5 days after intake
Moderate effects
Confusion and
Sweating, flushing, N/V
delirium
HR up, BP down, RR up
Clouding of
Throbbing headache
consciousn.
Disorientation Tremors
Visual and tactile hal. Weakness
Fever and BP up X PERFUMES, SHAVING WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS
Tremors and HR up CREAMS W/ ALCOHOL Occurs 6-8 hrs after intake
S/S
EMERGENCY PR, RR, BP, Temp up Nausea
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME (FAS) – 1ST trimester Hand Tremors Insomnia
Microcephaly Anxiety Psychomotor agitation
Severe mental retardation
Stillbirth DRUGS DRUGS
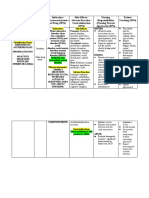
SEDATIVES, HYPNOTICS, ANXIOLYTICS – depressants
Lack of coordination Benzodiazepines – anxiolytics Barbituates & hypnotics
Slurred speech & stupor Unsteady gait Lethargic & confusion Phenobarbital
Impaired communication Labile mood Valium CAN BE LETHAL ONCE 2-10g
Coma Impaired attention Xanax S/S Respi arrest, cardiac
RARELY FATAL ONCE P.O. failure, coma, death
TAPER TO DETOXIFY
UPPER
STIMULANTS – Limited indications = high potential for abuse INHALANTS – causes PNS damage and liver disease
Anesthetics
INHALANT ABUSE IN BRAIN
Amphetamines (Onamine) – to lose weight Nitrates Oxygen deprivation
Cocaine and ectasy – no use, immediate feeling of euphoria Organic solvents
Neurotoxicity
Gasoline
INTOXICATION develops: PHYSIOLOGIC changes: Seizures
Glue
Super active, talkative HR BP up Brain shrinkage
Paint thinner
Impaired judgment Dilated pupils Cognitive impairment
Spray paint
Weight loss Diaphoresis and chills Behavioral changes
Unhappiness or anger Nausea
Anorexia Chest pain and confusion TREATMENT
Anxiety Cardiac arrhythmias Stop using inhalants
Hallucinations & illusions Seek medical attention
euphoria Provide supportive care
Detoxification – addressing the effects to the body
Cocaine – “bugs” beneath skin / FORMICATION and foul smells Rehabilitation
- Nasal septum perforation
COCAINE WITHDRAWAL
Hours to days
Depressive symptoms
o Marked dysphoria
o Agitation
o Nightmares
o Appetite increases
o Psychosis
o Suicidal ideations increases
Cannabis (Marijuana) – Delta-2 Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Found in flowering tops and stems of the plant
- Hashish – dried resinous exudates from female plants
THERAPEUTIC uses: INTOXICATION develops:
Lowers IOP Less than 1 min
Relieves N/V associated Peak levels: 20-30 mins
with chemotherapy Lasts atleast 2-3 hours
(dronabinol, nabilone) HR up, BP down
Eye redness
TREATMENT Psychotic symptoms
Symptomatic and Abnormal motor
overdose doesn’t occur coordination
Withdrawal symptoms Short-term memory loss
not present when Inappropriate laughter
sudden cessation Social withdrawal
Increases appetite
Disorientation
Delirium
Dysphoria
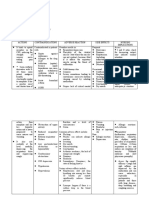
Hallucinogens / Psychedelics
NATURAL SYNTHETIC
Mescaline LSD – lysergic acid diethylamide
Psilocybin STP – dimethoxy-4
methylamphetamine
Cannabis PCP – Pencyclidine (most potent)
DMT – dimethyl tryptamine
DMA – methylene dioxyam
phetamine
INTOXICATION develops: TOXIC REACTIONS
Behavioral and Except PCP
psychological changes Primarily psychological
Hallucinations Overdose doesn’t occur
Anxiety
Paranoid ideation TREATMENT
Depression Isolation
Dangerous behaviors Physical restraints LAST
Ideas of reference RESORT
ABUSE
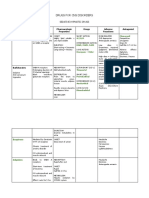
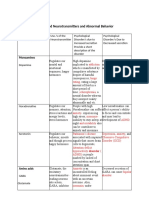
S/S VIOLENT FAMILY CHARACTERISTIC PARTNER ABUSE CHILD ABUSE
Upset Social isolation Maltreatment of another in Maltreatment of child
Agitation Abuse of power and control an intimate relationship
Withdrawn Alcohol and drug abuse TYPES
Aloof Intergeneration transmission process TYPES o Physical
Psychological abuse o Emotional
ABUSER CHARACTERISTIC Emotional abuse – hard o Neglect
Inadequacy Low self-esteem to cope o Sexual
Immature Jealous and possessive Physical abuse
Poor problem solving Act is rewarding o Choking CHARACTERISTICS OF PARENTS
o Fractures 1. Lack of parenting skills
o Homicide 2. Lack of understanding in
NURSING INTERVENTIONS children’s needs
Sexual abuse
Ensure the child’s safety and well-being. 3. Lack of money
o Pulling hair 4. Lack of education
Thorough psychiatric evaluation.
o Biting nipples 5. With history of child abuse
Establish trust to help child deal with trauma of abuse.
Use play therapy to express his feelings.
WARNING SIGNS
Refer to social works. Absence of trauma
Bruised genitalia
Unusual injuries
Switching child history
Evidence of old injuries
Delay in seeking treatment
You might also like
- AddictionDocument35 pagesAddictionOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: A Sedative Can Become A Hypnotic If It Is Given in Large Enough DosesDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System: A Sedative Can Become A Hypnotic If It Is Given in Large Enough Doseschubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- BuspironeDocument2 pagesBuspironeFatima Diane S. MondejarNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic DrugsDocument4 pagesAntipsychotic DrugsDrSamia El WakilNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument10 pagesDrug Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationMaria Fatima MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Substance Abuse TableDocument6 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuse TablespamNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy Biomedical Techniques PresentationDocument92 pagesPsychotherapy Biomedical Techniques PresentationRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System MedicationsDocument27 pagesCentral Nervous System MedicationsminhuaNo ratings yet
- Selectively: Inhibitors Inhibit Serotonin Reuptake and Elicit An Antidepressan T ResponseDocument2 pagesSelectively: Inhibitors Inhibit Serotonin Reuptake and Elicit An Antidepressan T ResponseDanii LuvNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Anesthesia)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Anesthesia)Jane Arian Berzabal100% (4)
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Sunstance AbuseDocument1 pageSunstance AbusecoolluckNo ratings yet
- Drug Overdose: Withdrawal ChartDocument4 pagesDrug Overdose: Withdrawal ChartRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Intro To PsychopharmacologyDocument8 pagesIntro To Psychopharmacologyprettykiran7No ratings yet
- DTR (2nd Set)Document7 pagesDTR (2nd Set)Fionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersDocument4 pagesPharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersJireh MejinoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive Drugs and Their EffectsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive Drugs and Their Effects85784703No ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 pagesPsychotherapeutic AgentsjustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Types of Psychoactive Substances: Class of Substance Name Common Main Effects Examples Trade/StreetDocument3 pagesTypes of Psychoactive Substances: Class of Substance Name Common Main Effects Examples Trade/StreetJor Lu ChamocasNo ratings yet
- SchizoDocument4 pagesSchizoR-Jeane ZubiagaNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury - TBI Medication ChartDocument5 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury - TBI Medication ChartPNo ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOLDocument1 pageHALOPERIDOLAlyxen Pelingen75% (4)
- Module 5: Chemotherapies Unit 2: Anti-Anxiety Drugs (Anxiolytics)Document8 pagesModule 5: Chemotherapies Unit 2: Anti-Anxiety Drugs (Anxiolytics)Luz TanNo ratings yet
- CONSUMO PsicoactivasDocument36 pagesCONSUMO PsicoactivasYulieth Paola Gutierrez MercadoNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism: Alcohol WithdrawalDocument2 pagesAlcoholism: Alcohol Withdrawaldarla ryanNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument5 pagesPsychiatryJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument3 pagesDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoNo ratings yet
- Substances Use: Neural Zone What Smokers Want To Achieve Abstinence WDDocument4 pagesSubstances Use: Neural Zone What Smokers Want To Achieve Abstinence WDKristy BonoNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Substance Abuse Table Assignment-3Document10 pagesDrugs and Substance Abuse Table Assignment-3saliha.haji16No ratings yet
- Substance AbuseDocument5 pagesSubstance AbuseMary Belle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- SchizoDocument4 pagesSchizoR-Jeane ZubiagaNo ratings yet
- Description: Tags: 86pg14-15Document2 pagesDescription: Tags: 86pg14-15anon-701575No ratings yet
- Drug Study01Document6 pagesDrug Study01JrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicDocument2 pagesValproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics - AMBOSS PDFDocument7 pagesAntipsychotics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Bahaya Narkoba (Maulana)Document12 pagesBahaya Narkoba (Maulana)Kang SomayNo ratings yet
- Dug Study PsycheDocument33 pagesDug Study PsycheAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants - SSRIs and SNRIs - Nursing Pharmacology - OsmosisDocument2 pagesAntidepressants - SSRIs and SNRIs - Nursing Pharmacology - Osmosisprettykiran7No ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument26 pagesPsychiatric EmergenciesKai Zi (凯)No ratings yet
- Depressive-Disorders SheetDocument2 pagesDepressive-Disorders SheetCrystal MarloweNo ratings yet
- Drowsiness, Sedation, LightDocument2 pagesDrowsiness, Sedation, LightGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Drug of ChoiceDocument43 pagesDrug of ChoiceJanna mae PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorDocument3 pagesImbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorInah100% (1)
- Antipsychotic MedicationDocument3 pagesAntipsychotic MedicationMichelle Angela CerezoNo ratings yet
- PHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument15 pagesPHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- Drug Tabulation orDocument23 pagesDrug Tabulation orChin Villanueva UlamNo ratings yet
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- Psychi BulletDocument4 pagesPsychi BulletHEALTH TIPSNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Abuse & DependenceDocument3 pagesDrug Abuse & DependenceJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Some Drugs in PsycheDocument19 pagesSome Drugs in PsycheGrace Ann RoxasNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology Article StyleDocument9 pagesPsychopharmacology Article StyleLizethNo ratings yet
- TRIAZOLAMDocument4 pagesTRIAZOLAMEzequiel RosalesNo ratings yet
- NCA2 Almo Neuro Part 2Document6 pagesNCA2 Almo Neuro Part 2Pebbles PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Second PartDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Second Partibrahim AbdiNo ratings yet
- SFDGSFDGHDocument1 pageSFDGSFDGHAlya BarrotNo ratings yet
- Deed of Undertaking & Liability Release WaiverDocument2 pagesDeed of Undertaking & Liability Release WaiverAlya BarrotNo ratings yet
- Deed of Undertaking & Liability Release WaiverDocument2 pagesDeed of Undertaking & Liability Release WaiverAlya BarrotNo ratings yet
- Deed of Undertaking & Liability Release WaiverDocument2 pagesDeed of Undertaking & Liability Release WaiverAlya BarrotNo ratings yet
- 11102022119226070042Document8 pages11102022119226070042Alya BarrotNo ratings yet
- 11092022119226070042Document9 pages11092022119226070042Alya BarrotNo ratings yet
- Date & Time of Placental Expulsion: AM / PM Type of Placental DeliveryDocument1 pageDate & Time of Placental Expulsion: AM / PM Type of Placental DeliveryAlya BarrotNo ratings yet
- W1 CEFR Based English 051 Course GuideDocument5 pagesW1 CEFR Based English 051 Course GuideAlya BarrotNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 and 2 Ucm - 488417Document49 pagesCase Study 1 and 2 Ucm - 488417Monna Jane ObiedoNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson SyndromeDocument4 pagesStevens-Johnson SyndromeBelleNo ratings yet
- Lampi DragerDocument68 pagesLampi DragerAlin Mircea PatrascuNo ratings yet
- 2019 Dent4060Document10 pages2019 Dent4060Jason JNo ratings yet
- MenopauseDocument19 pagesMenopauseMuhammad AsmiNo ratings yet
- 4 Ophthalmologists Cullman, AL: We Found NearDocument2 pages4 Ophthalmologists Cullman, AL: We Found NearSantosh Sharma VaranasiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFDocument26 pages01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFawinsyNo ratings yet
- Determinants of HealthDocument29 pagesDeterminants of HealthMayom Mabuong92% (12)
- Medoroga& Its ManagementDocument6 pagesMedoroga& Its ManagementChintamani VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment MarketDocument3 pagesGlobal Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment MarketiHealthcareAnalyst, Inc.No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Pediatrics PDFDocument208 pagesThe Little Book of Pediatrics PDFPaulo GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Animal Care QP U1Document12 pagesAnimal Care QP U1boho14No ratings yet
- Nonoperative Management of Femoroacetabular ImpingementDocument8 pagesNonoperative Management of Femoroacetabular ImpingementRodrigo SantosNo ratings yet
- Treatment MGRDocument12 pagesTreatment MGRMod AntbugNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Surgical & Electrosurgical System: All in One Pla Orm, All With Superior PerformanceDocument2 pagesUltrasonic Surgical & Electrosurgical System: All in One Pla Orm, All With Superior PerformanceDiego DulcamareNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000: Key Indexing TermsDocument4 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000: Key Indexing TermsRandom PersonNo ratings yet
- Fees and Charges - Summary From 1 July 2020 Version 1.0, June 2020Document51 pagesFees and Charges - Summary From 1 July 2020 Version 1.0, June 2020QualityMattersNo ratings yet
- Devoir de Synthèse N°2 2011 2012 (Lycée Ali Bourguiba Bembla)Document4 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°2 2011 2012 (Lycée Ali Bourguiba Bembla)ferchichi halimaNo ratings yet
- Tetagam P: Human Tetanus Immunoglobulin IM 250 IUDocument25 pagesTetagam P: Human Tetanus Immunoglobulin IM 250 IUhamilton lowisNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument31 pagesGastric CancerHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- 83 Nutripuncture OverviewDocument12 pages83 Nutripuncture OverviewTimoteo Pereira TfmpNo ratings yet
- Four Big Pollution Diseases of Japan - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument6 pagesFour Big Pollution Diseases of Japan - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFudayngNo ratings yet
- Nicaragua Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesNicaragua Reflection Paperapi-487254609No ratings yet
- Pre Op NCPDocument1 pagePre Op NCPJoshua Kelly0% (2)
- Perineal Urethrostomy PUDocument2 pagesPerineal Urethrostomy PUclara FNo ratings yet
- The Following Resources Related To This Article Are Available Online atDocument8 pagesThe Following Resources Related To This Article Are Available Online atFerdina NidyasariNo ratings yet
- MHC PDFDocument2 pagesMHC PDFYuvarani AruchamyNo ratings yet
- DosulepinDocument4 pagesDosulepinbrickettNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Mangosteen (Garcinia Mangostana) Rind in The Blood Glucose Levels of Adult Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Mangosteen (Garcinia Mangostana) Rind in The Blood Glucose Levels of Adult Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusFiqoh Puteri FauziNo ratings yet
- 811 2Document16 pages811 2almightyx10No ratings yet