0% found this document useful (0 votes)
224 views26 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance: Submitted By-Sakshi Singh Jayant Kumar
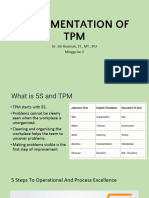
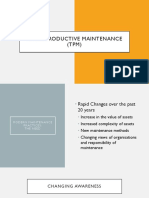
The document discusses Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). TPM is a maintenance strategy that improves equipment performance through integrating production and maintenance activities. It aims to enhance equipment efficiency and effectiveness, provide personnel education and training, and develop equipment to facilitate maintenance prevention. TPM implementation focuses on eliminating losses like breakdowns, set-ups, idling, defects and rework. The eight pillars of TPM are 5S, autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, quality maintenance, focused improvement, training and education, safety and office TPM. Benefits of TPM include increased equipment availability, cost reductions, employee development and motivation, improved quality control and decreased accidents.
Uploaded by
Sakshi SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
224 views26 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance: Submitted By-Sakshi Singh Jayant Kumar
The document discusses Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). TPM is a maintenance strategy that improves equipment performance through integrating production and maintenance activities. It aims to enhance equipment efficiency and effectiveness, provide personnel education and training, and develop equipment to facilitate maintenance prevention. TPM implementation focuses on eliminating losses like breakdowns, set-ups, idling, defects and rework. The eight pillars of TPM are 5S, autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, quality maintenance, focused improvement, training and education, safety and office TPM. Benefits of TPM include increased equipment availability, cost reductions, employee development and motivation, improved quality control and decreased accidents.
Uploaded by
Sakshi SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd