Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KEY 8.1 Carbon Cycle
Uploaded by
Angela Cui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesKEY 8.1 Carbon Cycle
Uploaded by
Angela CuiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Carbon Cycle Topic List
Answer all questions in RED!
1. Insert an image of the Carbon Cycle. In your own words, explain the overall
process of the carbon cycle.
2. What are organic molecules?
Organic molecules are molecules that contain carbon. Organic molecules are
usually found in living systems.
CO2 and CO are inorganic!
3. Where do plants, animals, and organisms deep in the oceans get their energy
from?
Organisms deep in the ocean get their energy from chemosynthesis. Hydrogen
sulfide molecules are released from hydrothermal vents (at divergent
boundaries) and organisms use these molecules for energy.
4. What happens when wood is burned (to the molecules, energy)?
When wood is burned, it is turned into ash and gas (CO2 and vapor).
Molecules are broken down and turn into new molecules but atoms are
conserved.
Heat and light (energy) are produced.
5. What are biological ways for inorganic carbon to be returned to the
atmosphere? What are abiotic ways?
Abiotic = not from living organisms
Biotic/biological = from living organisms
Inorganic carbon enters our atmosphere abiotically via fossil fuel burning/wood
Burning.
Inorganic carbon enters our atmosphere biotically via animal and plant
respiration.
6. Waste product(s) of consuming food
Waste products of consuming food (specifically glucose) are water and carbon
dioxide.
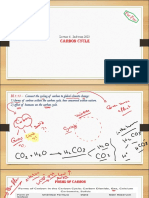
7. Write the balanced equations for the following:
a. Photosynthesis
6H2O + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2
b. Cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2
8. What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration (also known as cellular respiration) is the process in which
all organisms use glucose and oxygen for energy and create carbon dioxide and
water as waste products
9. Discuss the “slow” carbon cycle and the role of the ocean in this cycle?
The slow carbon cycle initiates when atmospheric carbon combines with water
to form carbonic acid (H2CO3). This acid falls (as rain) on rocks and it dissolves
them. When the rocks dissolve they form ions such as calcium and these ions
flow into the rivers, which lead to the ocean. In the ocean, the calcium ions
react with carbonate and produce calcium carbonate, which makes the shells of
different organisms. When these organisms die, they sink to the bottom of the
ocean where layers of sediment are buried and carbon is stored in limestone.
10.What is released during the decomposition of bacteria and fungi in
decomposing animal/plant waste?
Decomposition of bacteria and fungi in decomposing animal/plant waste
releases carbon dioxide.
11.How do animals help recycle carbon atoms in the carbon cycle?
Animals eat plants that produce glucose (takes them in) then release carbon
dioxide as a waste product returning the carbon back to the atmosphere.
12.How do humans negatively affect the carbon cycle?
The burning of fossil fuels is adding more carbon into the atmosphere than
there should be which is then overloading the amount of carbon, which plants
cannot compensate for.
13.What is one of the largest carbon reservoirs? Smallest?
The lithosphere (rocks) is the largest carbon reservoir.
The atmosphere is the smallest carbon reservoir.
14.What effect does deforestation have on this cycle?
Deforestation is the process of cutting down trees. Trees take in the carbon
dioxide that is in the atmosphere and turn it into oxygen for animals to breathe.
If there are fewer trees, there is less oxygen being produced and more carbon
dioxide staying in the atmosphere.
15. What is the natural residence time of carbon in the atmosphere? The hydrosphere? The
geosphere? The biosphere?
Atmosphere: 100s of years; Hydrosphere: 1000s of years; Biosphere: days-years;
geosphere: 1,000,000’s of years
You might also like
- Self Esteem and The Real Body ImageDocument12 pagesSelf Esteem and The Real Body ImageChy Alcarde50% (2)
- Nutrient Cycles Pogil Manuel TzulDocument7 pagesNutrient Cycles Pogil Manuel Tzulapi-323831182No ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon CycleRyan NegadNo ratings yet
- 7Document40 pages7Felipe RichardiosNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Perkins 4012 46TAG1A 46TAG2ADocument18 pagesCatalogue Perkins 4012 46TAG1A 46TAG2AAbdoul-aziz Ben Ousmanou100% (1)
- The Carbon Cycle UpdatedDocument15 pagesThe Carbon Cycle UpdatedFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument31 pagesBiogeochemical Cyclesd gNo ratings yet
- Ole Cycling of Matter Lesson KiserDocument4 pagesOle Cycling of Matter Lesson Kiserapi-306414523100% (1)
- Carbon Cycle by Isabella GobelDocument16 pagesCarbon Cycle by Isabella Gobelapi-311703865100% (2)
- Oxygen Cycle: PlantsDocument3 pagesOxygen Cycle: PlantsApam BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Fire Flow CalculationsDocument37 pagesFire Flow CalculationsAmy CurryNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument14 pagesThe Carbon CycleJennifer Bernas-Dooma100% (1)
- Factors, Impact, Symptoms of NPADocument7 pagesFactors, Impact, Symptoms of NPAMahesh ChandankarNo ratings yet
- Carbon Oxygen CycleDocument3 pagesCarbon Oxygen CycleRommel Villaroman EstevesNo ratings yet
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Five Brothers and Their Mother's LoveDocument4 pagesFive Brothers and Their Mother's Lovevelo67% (3)
- The Carbon CycleDocument14 pagesThe Carbon CycleJennifer Bernas-Dooma100% (1)
- L - Ch3.4 Cycles of Matter Guided ReadingDocument5 pagesL - Ch3.4 Cycles of Matter Guided ReadingHexagon LyricsNo ratings yet
- The Water Carbon CycleDocument9 pagesThe Water Carbon Cyclebrittany peckNo ratings yet
- Term 1 2023 ExamDocument6 pagesTerm 1 2023 Examtofoo234No ratings yet
- How Nutrients Are Recycled Through Ecosystems (Nutrient CyclesDocument4 pagesHow Nutrients Are Recycled Through Ecosystems (Nutrient CyclesAnna Marie LaganzonNo ratings yet
- Arthur Carbon Cycle Project WorkDocument7 pagesArthur Carbon Cycle Project WorkJoshuaNo ratings yet
- c6 ClimatechangeDocument35 pagesc6 ClimatechangeJohn Michael SomorostroNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle: Name Date PeriodDocument5 pagesWater Cycle: Name Date PeriodMrfatasianNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument5 pagesCarbon CycleJOHN VINCENT CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Carbon Oxygen CycleDocument28 pagesCarbon Oxygen CycleGeorgette MatinNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Phtysics 37rDocument5 pagesAtomic and Molecular Phtysics 37raslam janNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle-File Grade 6Document4 pagesCarbon Cycle-File Grade 6Rasha GhabbounNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen Cycle and The Carbon Dioxide CycleDocument3 pagesThe Oxygen Cycle and The Carbon Dioxide Cyclevincent gavinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and The Carbon Cycle HA&S 220a: C H O + 6O - 6CO 6H ODocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis and The Carbon Cycle HA&S 220a: C H O + 6O - 6CO 6H OSpecsy GuyNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument8 pagesCarbon CycleLenovoNo ratings yet
- Add A Heading 1Document60 pagesAdd A Heading 1athenatr1207No ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument4 pagesOxygen CyclePradnya GoreNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument5 pagesCarbon Cycleapi-283804229No ratings yet
- carboncycleDocument4 pagescarboncycleDylan DidiNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle ExplainedDocument10 pagesThe Carbon Cycle ExplainedFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: Submitted By, Jeeva Raj Joseph 1 M.Sc. M.B. MsrcascDocument24 pagesCarbon Cycle: Submitted By, Jeeva Raj Joseph 1 M.Sc. M.B. MsrcascSikhya PradhanNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle: CO2 Exchange Between Land, Sea & AirDocument2 pagesThe Carbon Cycle: CO2 Exchange Between Land, Sea & Airschoolworks IrishNo ratings yet
- In The Carbon Cycle, Animals Can Release Carbon Back Into The Cycle Through - or Through - Respiration - . - DecompositionDocument3 pagesIn The Carbon Cycle, Animals Can Release Carbon Back Into The Cycle Through - or Through - Respiration - . - DecompositionRyan Jhes TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument14 pagesCarbon CycleRosano SelgaNo ratings yet
- Biogeological CyclesDocument16 pagesBiogeological CyclesMark Vincent Salcedo CardinalNo ratings yet
- Oxygen N Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesOxygen N Carbon CycleScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Terjemah Karya Tulis RIKADocument17 pagesTerjemah Karya Tulis RIKAKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Big Picture: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Describe The Paths in Which Carbon Move Throughout The EnvironmentDocument17 pagesBig Picture: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Describe The Paths in Which Carbon Move Throughout The Environmentjapheth louie m. gofredoNo ratings yet
- Uses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleDocument7 pagesUses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleSyed Sulman SheraziNo ratings yet
- ES Lecture 6Document15 pagesES Lecture 6Erico TambanganNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles - "Energy Flows and Matter Cycles" ANSWER KEYDocument2 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles - "Energy Flows and Matter Cycles" ANSWER KEYJay Astillo NicanorNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon CycleRochelle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: Lecture 6.. 2nd Term 2023Document33 pagesCarbon Cycle: Lecture 6.. 2nd Term 2023Adam Saeed FNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument12 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesFazilaNo ratings yet
- Ecology NotesDocument5 pagesEcology NotesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument15 pagesCarbon CycleVaishnavi Kalantri100% (1)
- A Report On The Carbon CycleDocument4 pagesA Report On The Carbon CycleJL V. AdrianoNo ratings yet
- carbon cycle2Document2 pagescarbon cycle2The King studioNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-AND-THE-ANTHROSPHEREDocument22 pagesCHEMISTRY-AND-THE-ANTHROSPHEREMichelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 7Document6 pagesMaharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 7drushti luteNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Natural CyclesDocument13 pagesUnit-1 Natural CyclesAkshit KansalNo ratings yet
- CARBON CYCLEDocument9 pagesCARBON CYCLEsoneera.07No ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesCarbon Cycleznw9mn9j9cNo ratings yet
- Cycling WebQuest Spring 2009 ANSWERS - 2Document5 pagesCycling WebQuest Spring 2009 ANSWERS - 2Anggi Putra PermanaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Carbon Cycle?: Element Oceans Air Rocks Living ThingsDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Carbon Cycle?: Element Oceans Air Rocks Living ThingsMohammed IqbalNo ratings yet
- 07 Carbon CycleDocument14 pages07 Carbon CycleMERIDIAN SEESNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Environmental ScienceDocument18 pagesWeek 4 Environmental ScienceJosh AndradeNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document7 pagesGroup 4David ValentonNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Definition & StepsDocument10 pagesWater Cycle Definition & StepsJE-ANN LUGPITNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide CycleDocument15 pagesThe Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide CycleRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Admin, 085 - 799 - Ivan Master Worung - GalleyDocument5 pagesAdmin, 085 - 799 - Ivan Master Worung - GalleyM Ali AdrianNo ratings yet
- Dezurik Balancing Valves Flow Curve 12quot 300mm 12-30-1jDocument1 pageDezurik Balancing Valves Flow Curve 12quot 300mm 12-30-1jgm_revankar3942No ratings yet
- SPE/IADC-189336-MS Pioneering The First Hydraulic Fracturing in Iraq's Complex ReservoirDocument12 pagesSPE/IADC-189336-MS Pioneering The First Hydraulic Fracturing in Iraq's Complex ReservoirKarar AliNo ratings yet
- Using Roger's Diffusion of Innovation Theory To Implement The Healthy Schools National AccreditationDocument6 pagesUsing Roger's Diffusion of Innovation Theory To Implement The Healthy Schools National AccreditationputriNo ratings yet
- What Is Communication: What Is Communication MEANING OF COMMUNICATION: It Is Very Difficult To Define The TermDocument12 pagesWhat Is Communication: What Is Communication MEANING OF COMMUNICATION: It Is Very Difficult To Define The Termmanik ghoshNo ratings yet
- Wo PRJ #304Document2 pagesWo PRJ #304Gigin PlusNo ratings yet
- CaraKumpul - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kls 12Document7 pagesCaraKumpul - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kls 12akusayanklenaNo ratings yet
- HPLC Determination of Caffeine in Coffee BeverageDocument7 pagesHPLC Determination of Caffeine in Coffee Beveragemuhammad ihklasulNo ratings yet
- English Form 2 Mod23042022001Document10 pagesEnglish Form 2 Mod23042022001Qiash JontezNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Surface Protection and Paint CoatingsDocument2 pagesAircraft Surface Protection and Paint CoatingsSarah SNo ratings yet
- Plasma MachiningDocument14 pagesPlasma MachiningMayankNo ratings yet
- ResiboDocument1 pageResiboAlex RespicioNo ratings yet
- Optimized Die Steel Reference GuideDocument16 pagesOptimized Die Steel Reference GuideKeattikhun ChaichanaNo ratings yet
- Serving TechniquesDocument4 pagesServing TechniquesSindy FadyaNo ratings yet
- A300-600 Ammfx1 29 24 00 03 0Document5 pagesA300-600 Ammfx1 29 24 00 03 0Fahimeh HayatinasabNo ratings yet
- Nichita Stanescu - The Poet of Loneliness and LossDocument28 pagesNichita Stanescu - The Poet of Loneliness and LossEmanuelaCiocanNo ratings yet
- University of Groningen MagazineDocument14 pagesUniversity of Groningen MagazineKhanh Phuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Brachytherapy GYN Applicator CatalogDocument64 pagesBrachytherapy GYN Applicator CatalogJuan Lombardero100% (1)
- Midterm MMMDocument2 pagesMidterm MMMasdfghjkl zxcvbnmNo ratings yet
- Standardized Recipes - Doc2Document130 pagesStandardized Recipes - Doc2epic failNo ratings yet
- PT. Citilink Indonesia N P W P: 0 2 - 8 2 7 - 5 9 7 - 2 - 0 9 3 - 0 0 0 Jl. Raya Juanda Sawotratap Gedangan SidoarjoDocument2 pagesPT. Citilink Indonesia N P W P: 0 2 - 8 2 7 - 5 9 7 - 2 - 0 9 3 - 0 0 0 Jl. Raya Juanda Sawotratap Gedangan SidoarjoZemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Zhane CruzNo ratings yet
- Exe Summ RajatCement Eng PDFDocument12 pagesExe Summ RajatCement Eng PDFflytorahulNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy 6Document12 pagesWind Energy 6Shanthi RameshNo ratings yet