0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views4 pagesControl System Analysis and Design Guide
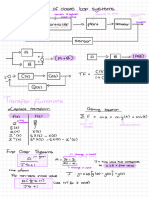
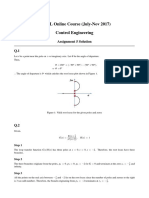
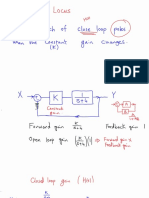
This document provides information about analyzing linear time-invariant (LTI) systems using Laplace transforms and stability criteria. It contains formulas, theorems, and steps for: 1) taking the Laplace transform to analyze a system in the frequency domain, 2) using the final value theorem to determine the steady state output, and 3) applying the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion to test if a system is stable.
Uploaded by
Ian PichoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views4 pagesControl System Analysis and Design Guide
This document provides information about analyzing linear time-invariant (LTI) systems using Laplace transforms and stability criteria. It contains formulas, theorems, and steps for: 1) taking the Laplace transform to analyze a system in the frequency domain, 2) using the final value theorem to determine the steady state output, and 3) applying the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion to test if a system is stable.
Uploaded by
Ian PichoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd