0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views1 pageVaccine Injection Guide for Adults
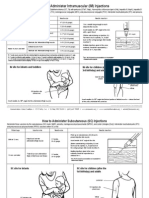
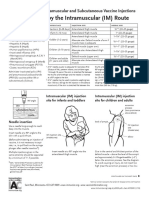
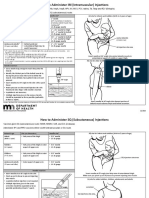
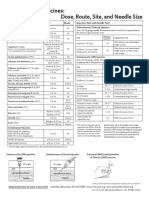
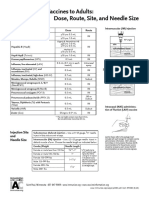
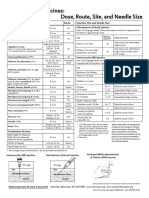
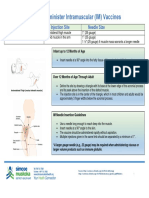
This document provides guidance on intramuscular injection for vaccines in adults 19 years and older. It lists which vaccines should be administered via intramuscular injection, including influenza, hepatitis A & B, HPV, meningococcal and pneumococcal vaccines. It describes proper injection technique, including using a new needle and syringe for each injection, following aseptic technique, and hand hygiene. It identifies the deltoid muscle as the recommended injection site and provides guidance on needle size selection and insertion based on patient weight and gender. Proper administration in the middle of the muscle at a 90 degree angle is emphasized.
Uploaded by
Daniel TurkeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views1 pageVaccine Injection Guide for Adults
This document provides guidance on intramuscular injection for vaccines in adults 19 years and older. It lists which vaccines should be administered via intramuscular injection, including influenza, hepatitis A & B, HPV, meningococcal and pneumococcal vaccines. It describes proper injection technique, including using a new needle and syringe for each injection, following aseptic technique, and hand hygiene. It identifies the deltoid muscle as the recommended injection site and provides guidance on needle size selection and insertion based on patient weight and gender. Proper administration in the middle of the muscle at a 90 degree angle is emphasized.
Uploaded by
Daniel TurkeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd