Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scaffolding Safety Report
Uploaded by
Ram RamirezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scaffolding Safety Report
Uploaded by
Ram RamirezCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction
Scaffolding safety is a combination of practices and safety procedures that enforces
proper and safe use of scaffoldings. It involves a set of preemptive actions in building,
inspecting, and using scaffolds. Standard rules and requirements for working on scaffoldings can
minimize or remove workers’ exposure to hazards such as falls, electrocutions, and falling
objects.
Scaffolding safety is important because it can help prevent workplace incidents from
recurring. With baseline scaffold requirements to keep workers safe such as better inspections,
training, and controls, frontline teams can ensure scaffolding safety and be proactive about
building a safety culture from the ground up.
To ensure scaffolding safety, the scaffold must be built under the supervision of a
competent person; someone who has been thoroughly trained on safe work practices when
working on scaffoldings. And workers must be trained by a qualified person before they use the
scaffold. The scaffold and its components should also be checked by a competent person and
properly tagged before the start of the shift to ensure its integrity and safety.
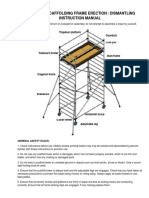
Specifications of Scaffolds at Site
H – Frame Set (1.20m x 1.70m)
Platform – (1.20m x 500mm)
GI Pipe (1 ½” x 6m, 3m, 1m)
Swivel Clamp (1 ½”)
Base Jack (30mm x 600mm)
PPE Required for Installation for Scaffolding
The PPEs required when working on a scaffolding typically include of hard hats, safety
harnesses, safety shoes or heavy-duty boots, gloves, eye and face protection, and high-visibility
vests or clothing. Note, however, that these PPE requirements still vary depending on several
factors so it is important that employers set specific PPE guidelines to ensure the safety of
workers.
Scaffolding Safety Dos:
1. Inspect the scaffold using a checklist before the work shift and ensure it is safe and in proper
working order.
2. Provide proper training.
3. Have a toolbox talk before beginning work.
4. Wear appropriate PPE.
5. Know the weight capacity of the scaffold.
6. Have a handhold above the scaffold platform.
7. Level the scaffold after each move. Do not extend adjusting leg screws more than 12 inches.
8. Use your safety belts and lanyards when working on scaffolding at a height of 10 feet or more
above ground level. Attach the lanyard to a secure member of the scaffold.
9. Safely use the ladder when climbing the cross braces for access to the scaffold.
10. Keep both feet on the decking.
11. Stay off the scaffold during loading or unloading.
12. Ensure planking is overlapping or secured from movement.
13. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions when erecting the scaffold, under the direct supervision
of a competent person.
14. Be mindful of coworkers working above and below you at all times, as well as others working on
the scaffold.
Scaffolding Safety Don’ts:
1. Leave anything on the scaffold at the end of your shift.
2. Overload the scaffold.
3. Use unstable objects such as barrels, boxes, loose brick or concrete blocks to support scaffolds,
increase your work height or planks.
4. Work on platforms or scaffolds unless they are fully planked.
5. Use a scaffold unless guardrails and all flooring are in place.
6. Stand on ties, guardrails, or extensions.
7. Use the scaffold if it appears damaged in any way, has been tampered with, or if there are
components missing such as planking, guardrails, toeboards, debris nets or protective canopies.
8. Walk on scaffold planking covered in ice, snow or mud.
9. Avoid using a scaffold during adverse weather such as heavy rain, sleet, ice snow or strong
winds.
10. Climb on any portion of the scaffold frame not intended for climbing.
11. Never climb with any materials or tools in your hand, they should be hoisted up to the scaffold
separately.
12. Jump from, to, or between scaffolding.
13. Lean out or overreach outside the guardrails.
14. Rock the scaffold.
15. Throw anything “overboard” unless a spotter is available.
16. Move a mobile scaffold if anyone is on it.
How to Use Scaffolding Properly
1. Secure the scaffolding area and put signage indicating an ongoing scaffolding structure.
2. Validate the correct number of parts by comparing them with existing documentation.
3. Find the corner point and align the scaffolding with the building.
4. Assemble the parts of the first lift to set up positions for soleplates then ensure that they form a
firm foundation for the scaffolding.
5. Adjust the baseplates to accommodate uneven floors and grounds.
6. Erect the first bay by starting at the highest point.
7. Use a spirit level to align the bay then alter the baseplates through baseplate adjustments.
8. Check if the distance of the bay from the building is correct then move it if required—use a lever
to safely move the bay.
9. Measure the diagonal dimensions of the bay or align the plates to make sure that they are
squared.
10. Create a working platform by arranging planks in a lift—this makes it easier to add the
succeeding upper ledgers and transoms.
11. Build an access bay on the non-operating area of the structure using stairs to provide easy access
to the scaffold.
12. Add transverse braces to the scaffold to strengthen the structure and prevent it from swaying.
13. Construct scaffold returns similar to how the other bays were structured.
14. Connect the main scaffold to the return by tying them together using scaffold tubes and right-
angled couplers.
15. Add longitudinal braces to every fourth bay then form the next temporary platform by
transferring the planks from the base working platform on the next lift.
16. Install the standards for the next level then set up transoms and ledgers to function as temporary
guard rails.
17. Set up the working platform by arranging all the transoms and ledgers for the next lift.
18. Continue to build the scaffold until the desired number and height of lifts are established.
19. Arrange a working platform between the scaffold and the building.
20. Inspect the scaffold to ensure safety before authorizing its use.
Scaffolding Safety Checklist
Inspect Scaffolding Integrity
Inspect Scaffolding Platforms
Inspect Scaffolding Access
Inspect Scaffolding Working Conditions
Evaluate Fall Protection Measures
Evaluate Personnel Training
You might also like
- Auditing Case 3Document12 pagesAuditing Case 3Kenny Mulvenna100% (6)
- CasesDocument8 pagesCasesLinh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Training 2023Document98 pagesScaffold Training 2023HILAL ALSAMA100% (1)
- Scaffolding ProcedureDocument3 pagesScaffolding Proceduremd ruman100% (2)
- SOP Scaffold AustralianDocument3 pagesSOP Scaffold Australiantemter100% (2)
- Scaffolding WORK PRCEDUREDocument2 pagesScaffolding WORK PRCEDUREeng_hma100% (3)
- Ultimate Guide: Barns, Sheds & Outbuildings, Updated 4th Edition: Step-by-Step Building and Design Instructions Plus Plans to Build More Than 100 OutbuildingsFrom EverandUltimate Guide: Barns, Sheds & Outbuildings, Updated 4th Edition: Step-by-Step Building and Design Instructions Plus Plans to Build More Than 100 OutbuildingsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Ce161p A88 q1 MakeupDocument1 pageCe161p A88 q1 MakeupRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Rsa Netwitness Endpoint: Detect Unknown Threats. Reduce Dwell Time. Accelerate ResponseDocument8 pagesRsa Netwitness Endpoint: Detect Unknown Threats. Reduce Dwell Time. Accelerate ResponseRaghavNo ratings yet
- BROC Mackam Dab en v1.0Document2 pagesBROC Mackam Dab en v1.0jangri1098No ratings yet
- Osha CFR 1910Document16 pagesOsha CFR 1910CI Amilcar100% (3)
- SDSU PhD Research on Soil HealthDocument2 pagesSDSU PhD Research on Soil HealthTiruneh GA25% (4)
- Scaffolding SafetyDocument20 pagesScaffolding SafetyKate Ann Baja IINo ratings yet
- Scaffolding-Fixed and MobileDocument1 pageScaffolding-Fixed and MobileAsyraf ZainiNo ratings yet
- Tower Scaffolds: What You Need To DoDocument3 pagesTower Scaffolds: What You Need To DoEdwin Maglapid RamosNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety TrainingDocument25 pagesScaffolding Safety Trainingmt_powers100% (1)
- HSE SWP 033 Ladders Scaffold SafetyDocument4 pagesHSE SWP 033 Ladders Scaffold SafetyGia Minh Tieu TuNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument2 pagesScaffoldingroland magoNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating ProceduresDocument1 pageScaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating Proceduresmohammed muzammilNo ratings yet
- SWP1127 Mobile Scaffold 3Document4 pagesSWP1127 Mobile Scaffold 3kannanNo ratings yet
- Cis 49Document2 pagesCis 49tiagoulbraNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Management Training Pack Part 2Document41 pagesConstruction Site Management Training Pack Part 2Jaka Sembung GolokNo ratings yet
- SOPDocument8 pagesSOPAilyn MercadoNo ratings yet
- 04.scaffold ManualDocument6 pages04.scaffold ManualJOSE LUISNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding 1Document2 pagesScaffolding 1Anica Pollyn Bumanglag VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Written ReportDocument21 pagesScaffolding Written ReportJenie Marie Nitoral100% (1)
- Safety While Working at HeightsDocument57 pagesSafety While Working at HeightsRísês Ãfröz100% (2)
- Tower Scaffolds: What You Need To DoDocument3 pagesTower Scaffolds: What You Need To DoMario Marasigan100% (1)
- Cuplock Scuffolding SOPDocument3 pagesCuplock Scuffolding SOPElangoNo ratings yet
- Section 8 - Scaffold Appreciation and Working at Height No. 18 ScaffoldingDocument1 pageSection 8 - Scaffold Appreciation and Working at Height No. 18 ScaffoldingMunawar Sher MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Vcsu Safe Operating Procedures: Scaffolding SafetyDocument3 pagesVcsu Safe Operating Procedures: Scaffolding SafetyUmair RafiNo ratings yet
- Employee RULES & Safety ManualDocument9 pagesEmployee RULES & Safety ManualwallyNo ratings yet
- What Should You Check Before Using Scaffold?Document2 pagesWhat Should You Check Before Using Scaffold?Ange JuanNo ratings yet
- Walking Work SurfacesDocument8 pagesWalking Work SurfacesSb TeoNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding AO 2024 - Final SafetyDocument3 pagesScaffolding AO 2024 - Final SafetyWarrenNo ratings yet
- NASAC - Dos and Donts On ScaffoldsDocument1 pageNASAC - Dos and Donts On ScaffoldsHs supervisorsNo ratings yet
- Vale ScaffoldsSafetyAwarenessDocument36 pagesVale ScaffoldsSafetyAwarenessGoldwin Ricky AritonangNo ratings yet
- Safety Policy 2007-10Document2 pagesSafety Policy 2007-10Bob SilvaNo ratings yet
- Guide Scaffold Inspection MaintenanceDocument7 pagesGuide Scaffold Inspection MaintenanceMalahati HashinaNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument46 pagesScaffoldingsho baryNo ratings yet
- Safe scaffold workDocument3 pagesSafe scaffold workmd sarfaraz khanNo ratings yet
- Construction Site PremisesDocument52 pagesConstruction Site PremisesAya AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Method StatementDocument4 pagesMethod StatementRichmond SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Safety Standards ScaffoldDocument9 pagesSafety Standards ScaffoldhassanNo ratings yet
- SG4 Is A Safe System of Work Design To Prevent You From Falling From A Scaffolds During All Stages of ErectingDocument3 pagesSG4 Is A Safe System of Work Design To Prevent You From Falling From A Scaffolds During All Stages of ErectingEden Rafael100% (1)
- Scaffolding Work ProcedureDocument6 pagesScaffolding Work ProcedureMuhammad Shiraz KhalidNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Work HandoutDocument2 pagesScaffold Work HandoutRija Hossain100% (1)
- TBT - 037 Scissor LiftsDocument4 pagesTBT - 037 Scissor LiftsRich PellettNo ratings yet
- Ladder SafetyDocument3 pagesLadder SafetyJomy JohnyNo ratings yet
- HGT Safe Systems of Work For ForkliftsDocument7 pagesHGT Safe Systems of Work For ForkliftsVeeramuthu SundararajuNo ratings yet
- 28 - Scaffolding ProceduresDocument17 pages28 - Scaffolding ProceduresLalit Tomar100% (1)
- WAH Final PresentationDocument72 pagesWAH Final PresentationS RNo ratings yet
- Worker HandBook ENG FinalDocument17 pagesWorker HandBook ENG FinalhazopmanNo ratings yet
- MOS Dismantling Aluminium Strips Ceiling and Aluminium Composits PanelDocument5 pagesMOS Dismantling Aluminium Strips Ceiling and Aluminium Composits PanelAhmad Fauzi Bin OmarNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety On Construction Sites: Safe Operation of LiftsDocument9 pagesHealth and Safety On Construction Sites: Safe Operation of Liftsmichael.cotugnoNo ratings yet
- Drew Ladder Safety Program Policy SOP 0412Document6 pagesDrew Ladder Safety Program Policy SOP 0412MechanicalNo ratings yet
- IUPUI Scaffold Safety ProgramDocument8 pagesIUPUI Scaffold Safety ProgramSb TeoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Grade 11 Carpentry NC Ii I.: Week 3/480 MinutesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Grade 11 Carpentry NC Ii I.: Week 3/480 MinutesArnold Asio100% (2)
- Ladder Training ProgramDocument31 pagesLadder Training ProgramAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Scaffold SafetyDocument4 pagesScaffold SafetyMahadevan Somasundaram100% (1)
- Scaffolds ConstructionDocument34 pagesScaffolds Constructionharshal patilNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety GuidelinesDocument6 pagesScaffolding Safety GuidelinesCaron KarlosNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety EssentialsDocument12 pagesScaffolding Safety EssentialsSyed Mustafa Hussain100% (1)
- GL 21 Safe Use of LaddersDocument1 pageGL 21 Safe Use of Ladderstp101267No ratings yet
- Ladder SafetyDocument3 pagesLadder SafetyTXsafetymasters12No ratings yet
- Aeroplane Flight Training: Lesson Plans for Students & Instructors With Questions - Plus a Lot MoreFrom EverandAeroplane Flight Training: Lesson Plans for Students & Instructors With Questions - Plus a Lot MoreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Work Inspection Checklists (11!06!2019)Document53 pagesWork Inspection Checklists (11!06!2019)Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Puppy Bottle Feeding and Stomach Capacity Chart PDFDocument1 pagePuppy Bottle Feeding and Stomach Capacity Chart PDFJohn Rowel S. CañonNo ratings yet
- Used Sack To Be Used As The Sleeve Material in The Horizontal Bar Lap Splice Instead of Felt PaperDocument8 pagesUsed Sack To Be Used As The Sleeve Material in The Horizontal Bar Lap Splice Instead of Felt PaperRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- RMExtractionDocument21 pagesRMExtractionRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Academic Advising FormDocument1 pageAcademic Advising FormRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Correl - AlgebraDocument12 pagesCorrel - AlgebraRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- RMExtractionDocument21 pagesRMExtractionRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Course Expectation AlbaDocument1 pageCourse Expectation AlbaRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: School of Civil, Environmental and Geological EngineeringDocument1 pageMapúa Institute of Technology: School of Civil, Environmental and Geological EngineeringJJ Sean CruzNo ratings yet
- Final Assesment: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. December 9, 2015 CE121/B2 Engr. BalmorisDocument3 pagesFinal Assesment: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. December 9, 2015 CE121/B2 Engr. BalmorisRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Mapua Construction Materials ProblemsDocument5 pagesMapua Construction Materials ProblemsRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Exp 8 10 ConmatDocument3 pagesExp 8 10 ConmatRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Workout#2 Ramirez, Charles Jon N.Document32 pagesWorkout#2 Ramirez, Charles Jon N.Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- FW1Document18 pagesFW1Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Name: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. MEC 32-1 A2 July 28, 2015 S#: 2013150342 SNDocument2 pagesName: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. MEC 32-1 A2 July 28, 2015 S#: 2013150342 SNRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Course Expectation: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. October 7, 2015 CE-3 / 2013150342 Engr. BalmorisDocument1 pageCourse Expectation: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. October 7, 2015 CE-3 / 2013150342 Engr. BalmorisRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Phy13 E401 Conclusion QuestionsDocument1 pagePhy13 E401 Conclusion QuestionsRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Palon Fieldwork2Document12 pagesPalon Fieldwork2Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- PeerDocument1 pagePeerRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Palon Fieldwork2Document12 pagesPalon Fieldwork2Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds ApparatusDocument20 pagesLAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds Apparatusmizizasbonkure9055% (11)
- Apply for Scholarship FormDocument3 pagesApply for Scholarship FormRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Business Letter 6.12Document2 pagesBusiness Letter 6.12Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word MecvinaDocument37 pagesMicrosoft Word MecvinaRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Math30 5Document1 pageMath30 5Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic PressureDocument5 pagesHydrostatic PressureRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- E306Document3 pagesE306Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- E302 Conclusion QuestionsDocument1 pageE302 Conclusion QuestionsRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Phy11 Lesson 7 SHMDocument17 pagesPhy11 Lesson 7 SHMRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- EIE Resume FormatDocument1 pageEIE Resume FormatRakesh MandalNo ratings yet
- Natural Fibres For Composites in EthiopiaDocument12 pagesNatural Fibres For Composites in EthiopiaTolera AderieNo ratings yet
- Drilling Products and Solutions CatalogDocument141 pagesDrilling Products and Solutions CatalogAlex Boz100% (1)
- Collective Fleet Agreement TermsDocument25 pagesCollective Fleet Agreement TermskjdckncknsNo ratings yet
- DataSheet ULCAB300Document2 pagesDataSheet ULCAB300Yuri OliveiraNo ratings yet
- mPassBook 161022 150423 2918Document4 pagesmPassBook 161022 150423 2918Ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- Plan & Elevation of Dog-Legged StaircaseDocument1 pagePlan & Elevation of Dog-Legged Staircasesagnik bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Premier League 2024 Schedule, Live Scores and ResultsDocument5 pagesBangladesh Premier League 2024 Schedule, Live Scores and Resultsmoslahuddin2022No ratings yet
- Fin4010 Assignment 3Document3 pagesFin4010 Assignment 3Grace AtteNo ratings yet
- Matrix 210N Reference Manual 2017 PDFDocument167 pagesMatrix 210N Reference Manual 2017 PDFiozsa cristianNo ratings yet
- Describe The Financial and Non-Financial Benefits of Strategic Management 4.1 Financial Benefits of Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesDescribe The Financial and Non-Financial Benefits of Strategic Management 4.1 Financial Benefits of Strategic ManagementAlemayehu Demeke80% (5)
- Blue Assured Individual Health PlanDocument5 pagesBlue Assured Individual Health PlanahsanNo ratings yet
- Filiation and Support ClaimsDocument3 pagesFiliation and Support ClaimsEugene BalagotNo ratings yet
- Lista Carti Audio Dezvoltare PersonalaDocument4 pagesLista Carti Audio Dezvoltare PersonalaNicu Osan50% (2)
- Column:C2 900X900: Basic Design ParametersDocument2 pagesColumn:C2 900X900: Basic Design ParametersAnonymous tBhJoH5wgMNo ratings yet
- Arpit Y2Document7 pagesArpit Y2swapnil jainNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structure and Management RolesDocument26 pagesOrganisation Structure and Management RolesFiona TauroNo ratings yet
- Ssnt Question BankDocument32 pagesSsnt Question Bankhowise9476No ratings yet
- Macalintal v. PETDocument5 pagesMacalintal v. PETJazem AnsamaNo ratings yet
- Career Profile: Nidhi PathakDocument4 pagesCareer Profile: Nidhi PathaknidhipathakNo ratings yet
- Juno Gi BrochureDocument2 pagesJuno Gi BrochureJerry VagilidadNo ratings yet
- Routine Pile Load Test-Ga-13.04.2021Document1 pageRoutine Pile Load Test-Ga-13.04.2021Digambar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Tax2win's Growth Strategy Through Comprehensive Tax SolutionsDocument6 pagesTax2win's Growth Strategy Through Comprehensive Tax SolutionsAhmar AyubNo ratings yet