Professional Documents
Culture Documents
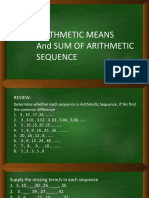
Arithmetic Series
Uploaded by
JayczarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arithmetic Series
Uploaded by
JayczarCopyright:
Available Formats
1st Quarter: Lesson 4 August 31, 2022
ARITHMETIC SERIES
is the sum of a sequence in which each term is computed from the
previous one by adding or subtracting a constant “d” (common
difference).
F O R M U L A
Sn = n/2(2a1 + (n – 1)d)
Sn = (n(a1 + an))/2 Sn = (n/2)(a1 + an)
Let’s Try:
n = 100
Sum of all first 100 positive integers.
a1 = 1
an = 100
Solve: Sn = (n/2)(a1 + an)
S100 = (100/2)(1 + 100)
S100 = (50)(101)
S100 = 5050
Solve: Sn = n/2(2a1 + (n – 1)d)
S100 = 100/2(2(1) + (100 – 1)1)
Solve: Sn = (n(a1 + an))/2
S100 = 50/2(2 + (99)1)
S100 = (100(1 + 100))/2
S100 = 50/2(101)1)
S100 = (100(101))/2
S100 = 50/2(101)
S100 = (10100)/2
S100 = 5050
S100 = 5050
Therefore,
1 + 2 + 3 + … + 99 + 100
5050
You might also like
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Reliability & Maintainability Engineering Ebeling Chapter 2 Book Solutions - Failure Distribut PDFDocument12 pagesReliability & Maintainability Engineering Ebeling Chapter 2 Book Solutions - Failure Distribut PDFNaveenMatthewNo ratings yet
- Precalculus ReviewerDocument6 pagesPrecalculus ReviewerIna Louise MagnoNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Sequences and SeriesDocument37 pagesArithmetic Sequences and Seriesikatal2033% (3)
- An Introduction To Reliability and Maintainability Engineering PDFDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To Reliability and Maintainability Engineering PDFMahmoud. Hlelai100% (3)
- Topic 2 MMW Arithmetic SeriesDocument20 pagesTopic 2 MMW Arithmetic SeriesMarlyn CuregNo ratings yet
- Đáp ÁnDocument2 pagesĐáp Ánstu725121007No ratings yet
- SumsDocument12 pagesSumsJohn Kyle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- MetodoDocument1 pageMetododannyNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Series: Mathematics 10 By: Sir John Ry T. JonilasDocument10 pagesArithmetic Series: Mathematics 10 By: Sir John Ry T. JonilasAndrea ElcanoNo ratings yet
- Sequence & Series - Practice Sheet - Varun JEE Advanced 2024Document3 pagesSequence & Series - Practice Sheet - Varun JEE Advanced 2024shikharvashishtha1729No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Handouts 7 and 8Document3 pages1st Quarter Handouts 7 and 8Louise CruzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10: Bauko Catholic SchoolDocument2 pagesMathematics 10: Bauko Catholic SchoolKevinRick B MalicdanNo ratings yet
- Act Assignment PDFDocument14 pagesAct Assignment PDFchan hkNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Mean 4Document9 pagesArithmetic Mean 4alvinder acebedoNo ratings yet
- Maranatha Christian Academy: 9029 National Road Batong Malake, Los Baños, Laguna Tel. No.: (049) 501-1273Document3 pagesMaranatha Christian Academy: 9029 National Road Batong Malake, Los Baños, Laguna Tel. No.: (049) 501-1273Mario GamboaNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic SeriesDocument13 pagesArithmetic SeriesRedginald CalderonNo ratings yet
- Progression (Sol. + Level)Document29 pagesProgression (Sol. + Level)sanket sinhaNo ratings yet
- Sequence Series Solutions MathongoDocument9 pagesSequence Series Solutions MathongoMehal KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying & Cost Estimation CE-372 XEN Shahid HussainDocument4 pagesQuantity Surveying & Cost Estimation CE-372 XEN Shahid HussainAli TariqNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying & Cost Estimation CE-372 XEN Shahid HussainDocument4 pagesQuantity Surveying & Cost Estimation CE-372 XEN Shahid HussainAli TariqNo ratings yet
- A.1.3 SolutionsDocument2 pagesA.1.3 SolutionsOmer ShareefNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 TCE 5102Document6 pagesAssignment 2 TCE 5102Samuel TemboNo ratings yet
- SSG 811 Solution To AssignmentDocument15 pagesSSG 811 Solution To AssignmentSmartLeoMekilisNo ratings yet
- 1 4 Arithmetic SeriesDocument25 pages1 4 Arithmetic SeriesZender DrofNo ratings yet
- General Formula For A Finite Arithmetic Series: EmcdyDocument1 pageGeneral Formula For A Finite Arithmetic Series: EmcdyreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Mathematics and Allied SciencesDocument9 pagesBasic Engineering Mathematics and Allied SciencesHajji BañocNo ratings yet
- EEE212 Week1Document66 pagesEEE212 Week1melikeNo ratings yet
- Math 102, Winter 2010, Final Exam Review Problems, Part IIDocument6 pagesMath 102, Winter 2010, Final Exam Review Problems, Part IIJordan RamseyNo ratings yet
- hw3 - Solution Grade 100Document4 pageshw3 - Solution Grade 100Ravid CohenNo ratings yet
- Lathi Ls SM Chapter 4Document88 pagesLathi Ls SM Chapter 4Dr Satyabrata JitNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solution To Finals Long QuizDocument5 pagesSuggested Solution To Finals Long QuizJamil MacabandingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 State-Space Solutions and Realization - v1Document76 pagesLecture 3 State-Space Solutions and Realization - v1Md Nur-A-Adam DonyNo ratings yet
- Corre Part1 AlgebraDocument11 pagesCorre Part1 AlgebraJoshua ColladoNo ratings yet
- SPWM Inverter UnipolarDocument13 pagesSPWM Inverter UnipolarFerdy AhmadNo ratings yet
- Positive Solutions For Boundary Value Problem of Nonlinear Fractional Differential EquationDocument11 pagesPositive Solutions For Boundary Value Problem of Nonlinear Fractional Differential EquationBoutiara AbdellatifNo ratings yet
- Sequences and SeriesDocument38 pagesSequences and Seriesfmukuka12No ratings yet
- School of Mathematics and Statistics Spring Semester 2013-2014 Mathematical Methods For Statistics 2 HoursDocument2 pagesSchool of Mathematics and Statistics Spring Semester 2013-2014 Mathematical Methods For Statistics 2 HoursNico NicoNo ratings yet
- QUAN-Digital BSCIT DescriptiveDocument31 pagesQUAN-Digital BSCIT DescriptiveDebanjan PatraNo ratings yet
- DPP - 1 - MathematicsDocument2 pagesDPP - 1 - Mathematicsnot meNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. What Is Advance Algebra?: Quadratic FormulaDocument42 pagesChapter 1. What Is Advance Algebra?: Quadratic FormulaArlene VictoryNo ratings yet
- Answer Key CHP 18 Derivatives MarketDocument5 pagesAnswer Key CHP 18 Derivatives MarketMuhammad Luthfi Al AkbarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Algebra (Arithmetic Series) Presentation-WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesLesson Plan in Algebra (Arithmetic Series) Presentation-WPS OfficeWonyoung IveNo ratings yet
- Me 343 - Control Systems - Fall 2008 Second Exam - October 29, 2008Document7 pagesMe 343 - Control Systems - Fall 2008 Second Exam - October 29, 2008Sérgio SilvaNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument10 pagesRESEARCHRayan H BarwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Midpoint - Line ExampleDocument26 pagesLecture - Midpoint - Line ExampleAlif hasanNo ratings yet
- Day 2 GROUPED DATADocument7 pagesDay 2 GROUPED DATAZhyrra ViganNo ratings yet
- Two Limiting Cases Ne: 1.3 Solutions 83Document1 pageTwo Limiting Cases Ne: 1.3 Solutions 83Sano ManjiroNo ratings yet
- Li Thuyet DK Tu Dong Giua KyDocument3 pagesLi Thuyet DK Tu Dong Giua KyTuấn Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Unit 1 Lesson 3 ModuleDocument5 pagesMath 10 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Modulemary joy buliagNo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval, Model Fitness and Prediction: S S T BDocument8 pagesConfidence Interval, Model Fitness and Prediction: S S T BtinkitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document51 pagesChapter 01MJoyce Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression, Cont.: BIOST 515 January 13, 2004Document23 pagesSimple Linear Regression, Cont.: BIOST 515 January 13, 2004HazemIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Exponential FunctionsDocument4 pagesExponential FunctionsAnnie FreebiesNo ratings yet
- Covariance, Correlation CoefficientDocument4 pagesCovariance, Correlation CoefficientIvan ZhuravlevNo ratings yet
- Sum APDocument7 pagesSum APIng Ding LonNo ratings yet
- DC 02 Problems With SolutionsDocument7 pagesDC 02 Problems With SolutionsYato QtNo ratings yet
- Pineda, Maricar R. CBET-01-601E: Produced (X1) Purchased (X2) TotalDocument4 pagesPineda, Maricar R. CBET-01-601E: Produced (X1) Purchased (X2) TotalMaricar PinedaNo ratings yet
- Black Book SolutionsDocument15 pagesBlack Book SolutionsSaikat Das0% (3)
- Handouts Q3 L3 Mechanics RWSDocument3 pagesHandouts Q3 L3 Mechanics RWSJayczarNo ratings yet
- Handouts Q3 L3 Language-Use RWSDocument4 pagesHandouts Q3 L3 Language-Use RWSJayczarNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Uniqueness of EarthDocument1 pageHandouts For Uniqueness of EarthJayczarNo ratings yet
- Relation Among The Arcs and The Inscribed Angles of The CircleDocument3 pagesRelation Among The Arcs and The Inscribed Angles of The CircleJayczarNo ratings yet