Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solved Repeat Problem 10.5 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....
Uploaded by
Cristian A. GarridoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solved Repeat Problem 10.5 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....
Uploaded by
Cristian A. GarridoCopyright:
Available Formats
! " Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Practice NEW!
Find solutions for your homework Search
home / study / engineering / civil engineering / building materials and theory of constructions / building materials and
theory of constructions solutions manuals / principles of geotechnical engineering / 9th edition / chapter 10 / problem 6p
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (9th Edition)
See this solution in the app
Chapter 10, Problem 6P 9 Bookmarks Show all steps: ON
Post a question
Answers from our experts for your tough
homework questions
Problem
Enter question
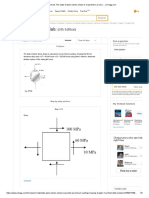
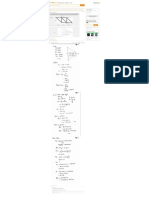
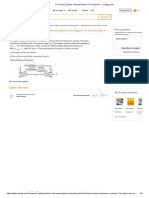
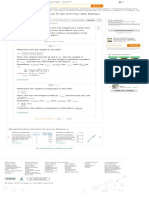
Repeat Problem 10.5 for the element shown in Figure 10.39.
Next
Figure 10.34 Continue to post
20 questions remaining
Snap a photo from your
phone to post a question
We'll send you a one-time
download link
888-888-8888 Text me
Figure 10.35 By providing your phone number, you agree to receive
a one-time automated text message with a link to get
the app. Standard messaging rates may apply.
My Textbook Solutions
Figure 10.36 Principles of... Mechanics of Mechanics of
Materials Materials
9th Edition 8th Edition 7th Edition
View all solutions
Chegg tutors who can help
right now
S
Rensselaer Polytec… 1465
Figure 10.37
Alfredo
Rasmussen College 372
Hannah
Brigham Young Uni… 1013
Find me a tutor
Figure 10.38
Figure 10.39
Step-by-step solution
Step 1 of 13
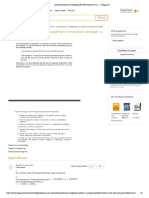
Consider the soil element as follows:
Comment
Step 2 of 13
Find the center of Mohr’s circle by using the following formula:
Comment
Step 3 of 13
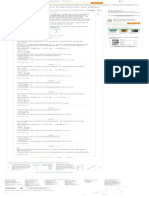
Procedure to draw Mohr’s circle.
• Locate the center of Mohr’s circle O on the graph
• Draw the lines for normal stresses (15 and 25) and shear
stress (6 and -6) on the graph.
• Represent the intersection points w,x,y, and z as shown in
figure.
• Draw a circle with radius of Ow as shown in figure.
Comment
Step 4 of 13
Draw the Mohr’s circle.
Comment
Step 5 of 13
Procedure to determine the pole point.
• Draw a vertical line from the point (15,-6) onto the Mohr’s
circle.
• Draw a horizontal line from the point (25,6) onto the Mohr’s
circle.
• The intersection point (w) is the pole point.
Comment
Step 6 of 13
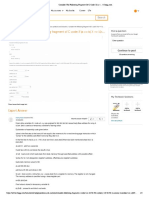
Represent the Pole point on the graph as follows:
Comment
Step 7 of 13
Procedure to determine the normal and shear stresses on the
plane AB:
• Draw a line from the pole point (parallel to plane AB) with an
angle of with horizontal axis onto Mohr’s circle.
• The intersection point (P) gives normal and shear stresses on
plane AB.
Comment
Step 8 of 13
Determine the major, minor principal stresses and normal stress,
shear stress on the plane AB as shown in figure.
Comment
Step 9 of 13
(a)
Obtain the values of minor and major principal stresses from the
graph.
Therefore, the major principal stress is and the minor
principal stress is .
Comments (1)
Step 10 of 13
(b)
Obtain the values of normal stress and shear stress on plane AB
from the graph.
Therefore, the normal stress on plane AB is and the
shear stress on plane AB is .
Comment
Step 11 of 13
Check:
Check the obtained stresses from pole method by using
mathematical approach.
Calculate the maximum principal stress by using the following
formula:
Calculate the minimum principal stress by using the following
formula:
Hence, the minimum and maximum principal stresses which are
calculated by using mathematical approach are equal to the
stresses calculated by using pole method.
Therefore, Check is correct.
Comment
Step 12 of 13
Calculate the normal stress on plane AB by using the
mathematical approach as follows:
Comment
Step 13 of 13
Calculate the shear stress on plane AB by using the
mathematical approach as follows:
Hence, the normal and shear stresses which are calculated by
using mathematical approach are equal to the stresses
calculated by using pole method.
Therefore, Check is correct.
Comment
Was this solution helpful? 4 1
Recommended solutions for you in Chapter 10
Chapter 10, Problem 22P Chapter 10, Problem 21P
Refer to Figure 10.49. Refer to Figure 10.48. If R = 4 m and hw = height of
For the linearly increasing water = 5 m, determine the vertical stress increases
vertical loading on an 2 m below the loaded area at radial distances
infinite strip of width 5 m, where r = 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 m.
determine the vertical...
See solution
See solution
See more problems in subjects you study
ABOUT CHEGG LEGAL & POLICIES CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CHEGG NETWORK CUSTOMER SERVICE
Become a Tutor Advertising Choices Cheap Textbooks Online Tutoring EasyBib Customer Service
Chegg For Good Cookie Notice Chegg Coupon Sell Textbooks Internships.com Give Us Feedback
College Marketing General Policies Chegg Play Solutions Manual Studyblue Help with Chegg Tutors
Corporate Development Intellectual Property Chegg Study Help Study 101 Thinkful Help with eTextbooks
Investor Relations Rights College Textbooks Test Prep Help to use EasyBib Plus
Jobs Terms of Use eTextbooks Textbook Rental Manage Chegg Study
Join Our Affiliate Program Chegg Tutors Terms of Chegg Math Solver Used Textbooks Subscription
Service Return Your Books
Media Center Mobile Apps Digital Access Codes
Global Privacy Policy Textbook Return Policy
Site Map
DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Honor Code
© 2003-2020 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Solved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 10.48 Shows The Schematic of A Circular Water St...Document1 pageSolved Figure 10.48 Shows The Schematic of A Circular Water St...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A 10-M-Thick Layer of Stiff Saturated Clay Is Underlain...Document1 pageSolved A 10-M-Thick Layer of Stiff Saturated Clay Is Underlain...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Document1 pageSolved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Document1 pageSolved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Layered Soil Is Shown in Figure 7.33. Given - H1 1....Document1 pageSolved A Layered Soil Is Shown in Figure 7.33. Given - H1 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An AluDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An AluTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved Results of A Standard Proctor Compaction Test On A Silt...Document1 pageSolved Results of A Standard Proctor Compaction Test On A Silt...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- 6.9 For The La For The Plane Strain Elements Shown...Document4 pages6.9 For The La For The Plane Strain Elements Shown...EdilunarNo ratings yet
- Question: Integrate 0 Between 3 Root 3/2 X 3/ (4x 2+9) 3/2: Continue To PostDocument1 pageQuestion: Integrate 0 Between 3 Root 3/2 X 3/ (4x 2+9) 3/2: Continue To PostElite SaNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 8.23. Given - H1 6 M - H2 1.5 M - D ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 8.23. Given - H1 6 M - H2 1.5 M - D ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F...Document1 pageSolved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- A Two-Start Worm Gear Rotating at 800 RPM Drives A...Document1 pageA Two-Start Worm Gear Rotating at 800 RPM Drives A...johan razakNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- As An Expert in Thermodynamics, You Are Attempting...Document6 pagesAs An Expert in Thermodynamics, You Are Attempting...melisa.serpamNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 7.32 Shows The Cross Section of A Levee Which Is...Document1 pageSolved Figure 7.32 Shows The Cross Section of A Levee Which Is...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- The Demand Curve Facing A Competitive Firm The ...Document3 pagesThe Demand Curve Facing A Competitive Firm The ...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: 10. A Rigid Insulated Tank Is Separated Into Two Rooms by A Stiff PDocument2 pagesQuestion: 10. A Rigid Insulated Tank Is Separated Into Two Rooms by A Stiff PIllion IllionNo ratings yet
- Question: (Practicing International Management Case BT in LocDocument1 pageQuestion: (Practicing International Management Case BT in LocMartinah Ross CoderaNo ratings yet
- If A Yield Curve Looks Like The One Shown in The...Document3 pagesIf A Yield Curve Looks Like The One Shown in The...Muiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Company Case Virgin America - Flight Service For Th...Document1 pageCompany Case Virgin America - Flight Service For Th...Ayu ParlindaNo ratings yet
- Problem 6.3-4 The Composite Beam Shown in The Figu...Document3 pagesProblem 6.3-4 The Composite Beam Shown in The Figu...Gary RenfronNo ratings yet
- Image Processing ExampleDocument3 pagesImage Processing ExampleAlperen ŞentürkNo ratings yet
- Question: Case Study. For Your Better Understanding, Let Us Practice How TDocument1 pageQuestion: Case Study. For Your Better Understanding, Let Us Practice How Tfahad BataviaNo ratings yet
- Question: Problem On Accrual E. Gevera Realty Co. Who Owns A BuildingDocument2 pagesQuestion: Problem On Accrual E. Gevera Realty Co. Who Owns A BuildingKen SannNo ratings yet
- Consider A Three-Dimensional Differential Fluid El...Document1 pageConsider A Three-Dimensional Differential Fluid El...Mergen KhanNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- The Following Data Apply To The Four-Bar Linkage S...Document7 pagesThe Following Data Apply To The Four-Bar Linkage S...Ömer faruk SilNo ratings yet
- Section 4. Asymmetric Shock (24 Points) Consider A...Document4 pagesSection 4. Asymmetric Shock (24 Points) Consider A...Noor FatimaNo ratings yet
- The Members Are Connected by The Details As Shown...Document2 pagesThe Members Are Connected by The Details As Shown...joizz rizzelle hilarioNo ratings yet
- Question: Q3. Consider A Cylindrical Specimen of A Steel Alloy (See FigureDocument3 pagesQuestion: Q3. Consider A Cylindrical Specimen of A Steel Alloy (See FigureVanesaaNo ratings yet
- In The Gas Turbine Thermal Plant in The Figure It ...Document4 pagesIn The Gas Turbine Thermal Plant in The Figure It ...Juan DiegoNo ratings yet
- The Cable AE Supports Three Vertical Loads From...Document3 pagesThe Cable AE Supports Three Vertical Loads From...BruhNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 3Document1 pageSolved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 3Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- A Businesswoman Is Budgeting For Her Products Cam.Document4 pagesA Businesswoman Is Budgeting For Her Products Cam.Keith GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 9.34 Two P-Electrons Are in The State Lim1112) 1...Document2 pages9.34 Two P-Electrons Are in The State Lim1112) 1...Azina KhanNo ratings yet
- Question: Match Each Discrete-Time Signal With Its DFT. You Should Be AblDocument3 pagesQuestion: Match Each Discrete-Time Signal With Its DFT. You Should Be AblThePositive GuyNo ratings yet
- Question: Problem 3 103 10 in Freshly Poured Concrete Approximates ADocument3 pagesQuestion: Problem 3 103 10 in Freshly Poured Concrete Approximates AWalter CatapangNo ratings yet
- For The Plane Strain Element Shown in Figure 22, T...Document6 pagesFor The Plane Strain Element Shown in Figure 22, T...EdilunarNo ratings yet
- Question: Consider The Following Fragment of C Code: If (A B) X + 10Document3 pagesQuestion: Consider The Following Fragment of C Code: If (A B) X + 10HJFNo ratings yet
- Solved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Document1 pageSolved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pretzel, A Pretzel Shop, Has The Followin...Document3 pagesUltimate Pretzel, A Pretzel Shop, Has The Followin...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Question: Sketch The Signal X Sin (2 Pi (0:7) /8) and ND The DFT of X. DoDocument2 pagesQuestion: Sketch The Signal X Sin (2 Pi (0:7) /8) and ND The DFT of X. DoThePositive GuyNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: Problem 1 (25 Marks) Design A Hard Steel (Screw and Nut) LubriDocument6 pagesQuestion: Problem 1 (25 Marks) Design A Hard Steel (Screw and Nut) Lubrimahdi najehNo ratings yet
- Create An HTML Page To Place 4 Div Elements Si...Document3 pagesCreate An HTML Page To Place 4 Div Elements Si...αlífNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F...Document1 pageSolved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 91Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 91Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Element Is Shown in Figure 10.38. Using The Pole...Document1 pageSolved A Soil Element Is Shown in Figure 10.38. Using The Pole...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 3Document1 pageSolved A Soil Profile Consisting of Three Layers Is Shown in F... Chegg - Com 3Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Layered Soil Is Shown in Figure 7.33. Given - H1 1....Document1 pageSolved A Layered Soil Is Shown in Figure 7.33. Given - H1 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Determine The Factor of Safety Against Heave On The Dow...Document1 pageSolved Determine The Factor of Safety Against Heave On The Dow...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Given Soil, The Following Are Known Gs 2.74, M...Document1 pageSolved For A Given Soil, The Following Are Known Gs 2.74, M...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved The Maximum and Minimum Dry Unit Weights of A Sand Were...Document1 pageSolved The Maximum and Minimum Dry Unit Weights of A Sand Were...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To The Silty Clay Soil at The Construction Site I...Document1 pageSolved Refer To The Silty Clay Soil at The Construction Site I...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Results of A Standard Proctor Compaction Test On A Silt...Document1 pageSolved Results of A Standard Proctor Compaction Test On A Silt...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Document1 pageSolved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Document1 pageSolved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To The Field Compaction of The Clayey Sand in Pro...Document1 pageSolved Refer To The Field Compaction of The Clayey Sand in Pro...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Proposed Embankment Fill Requires 7500 m3 of Compacte...Document1 pageSolved A Proposed Embankment Fill Requires 7500 m3 of Compacte...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 10Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 10Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 8Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 8Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Soil With Gs 2.7, Calculate and Plot The Variat...Document1 pageSolved For A Soil With Gs 2.7, Calculate and Plot The Variat...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 9Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 9Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 7Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 7Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 208Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 208Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 209Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 209Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- 1-Intro and First UnitDocument39 pages1-Intro and First Unitsahale sheraNo ratings yet
- G631/631 Series Installation and Operation Instruction: Electrohydraulic ServovalveDocument4 pagesG631/631 Series Installation and Operation Instruction: Electrohydraulic ServovalvenoaservicesNo ratings yet
- Mec30 - Quiz 2Document1 pageMec30 - Quiz 2John Andrae MangloNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document27 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Garuda MudaNo ratings yet
- Control System ModelingDocument88 pagesControl System Modelingcantik cuteNo ratings yet
- 08a. Phy 2nd Paper Cadet TP (MCQ) 01Document19 pages08a. Phy 2nd Paper Cadet TP (MCQ) 01Mustafa Nabeel ZamanNo ratings yet
- SOM Project Diploma CLGDocument9 pagesSOM Project Diploma CLGJoshua KondkarNo ratings yet
- Piping QC Guide (For Saudi Aramco Project)Document11 pagesPiping QC Guide (For Saudi Aramco Project)Heng100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Design Module 7 Subject: CE 74A-Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument25 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Module 7 Subject: CE 74A-Reinforced Concrete DesignJemson VictorioNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology and Its ApplicationDocument28 pagesNanotechnology and Its ApplicationsorinamotocNo ratings yet
- Soal Un English PDFDocument6 pagesSoal Un English PDFRadiatul Awalia AmirNo ratings yet
- Plasma TechnologyDocument27 pagesPlasma TechnologyAtul Mittal100% (2)
- Validity Criteria of Oedometric and Triaxial Test Results: December 2012Document8 pagesValidity Criteria of Oedometric and Triaxial Test Results: December 2012juan muneraNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Material Number Country DesignationsDocument3 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Material Number Country Designationsdanaandrei74No ratings yet
- Reiki First Degree Level 1 Training ScriptDocument199 pagesReiki First Degree Level 1 Training ScriptJohn LeahyNo ratings yet
- The Steering System - SummaryDocument7 pagesThe Steering System - SummaryPagg Dē TygerNo ratings yet
- Uganda Technical College - Lira: IMPORTANT SAMPLE QUESTIONS (Design of Concrete Structures To Eurocode 2)Document38 pagesUganda Technical College - Lira: IMPORTANT SAMPLE QUESTIONS (Design of Concrete Structures To Eurocode 2)Mugara Waitega PeterNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Formative TestDocument2 pagesMagnetism: Formative TestswapnaNo ratings yet
- Introductory LAMMPS Hands-On Tutorial: Prepared By: &Document14 pagesIntroductory LAMMPS Hands-On Tutorial: Prepared By: &Yongjia ShiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2A - Physics 1: General Physics 1 Grade Level/Section: Subject TeacherDocument7 pagesMODULE 2A - Physics 1: General Physics 1 Grade Level/Section: Subject TeacherJessica AngayenNo ratings yet
- Elementary Algebra For College Students 9th Edition by Ange Runde Gilligan and Semmler ISBN Test BankDocument48 pagesElementary Algebra For College Students 9th Edition by Ange Runde Gilligan and Semmler ISBN Test Bankgeorge100% (27)
- Mcknight Biasing PDFDocument4 pagesMcknight Biasing PDFIordan Dan FfnNo ratings yet
- Identification of Potential Inhibitors For Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase-3: A Molecular Docking and Dynamics StudyDocument15 pagesIdentification of Potential Inhibitors For Klebsiella Pneumoniae Carbapenemase-3: A Molecular Docking and Dynamics StudyDamián MoisaNo ratings yet
- Cantillo 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1386 012038Document7 pagesCantillo 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1386 012038David MoralesNo ratings yet
- MechYr1 Chp10 ForcesAndMotionDocument15 pagesMechYr1 Chp10 ForcesAndMotionmanojNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Lesson 3 The Atomic Structure and The Chemical ElementsDocument16 pagesPhysical Sciences Lesson 3 The Atomic Structure and The Chemical ElementsJustin BirdNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar 3412D MARINE ENGINE Workshop Repair Service Manual PDF DownloadDocument405 pagesCaterpillar 3412D MARINE ENGINE Workshop Repair Service Manual PDF Downloadben threadwell75% (4)
- TDS ATLANTIC CHT81Ni1Document1 pageTDS ATLANTIC CHT81Ni1Andi Baso Temalala STNo ratings yet
- Double Sided Drift Method Reduces The Effect of Crystals' Inhomogeneity To Si (Li) Detector's ElectroPysicsal CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesDouble Sided Drift Method Reduces The Effect of Crystals' Inhomogeneity To Si (Li) Detector's ElectroPysicsal CharacteristicsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Loads - Part 1 - Piping Engineering - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesNozzle Loads - Part 1 - Piping Engineering - Knowledge BaseNitinNo ratings yet