Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Are The Tools That Biologists Use To Study Cells?
Uploaded by
Connie PhungOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are The Tools That Biologists Use To Study Cells?
Uploaded by
Connie PhungCopyright:
Available Formats
Tuesday, September 06, 2011 Organization of cells The organization and small size of cells allow them o maintain
ntain an appropriate internal environment (homeostasis) To maintain homeostasis, the plasma membrane acts as a selective barrier between cell contents and the environment Most cells have internal structures (organelles) specialized to carry out metabolic activities Each cell has genetic instructions coded in DNA and passed to each new generation of cells during cell division (cell reproduction) Similarities among cells of different organisms suggest evolutionary relationships Cell theory Cells are the basic units of organization and function in all living organisms All cells come from preexisting cells All living cells have evolved from a common ancestor. Evidence that all living cells have a common origin is provided by basic similarities in their structures and molecules of which they are made. Cell size is limited: surface area-to-volume ratio What are the tools that biologists use to study cells? Light microscope (LM) o Magnification: 2000X o Resolution 0.2 micrometer Dead or alive cells Stains: orcein (proteins), Acetocarmine (DNA). Types of LM: o Bright/dark field o Phase contrast o Fluorescent o Confocal Electron microscope (EM) o Magnification: 10,000,000X o Resolution 1-2.0 nm Dead Sections/surface cell Types of EM o Scanning (SEM) o Transmission (TEM)
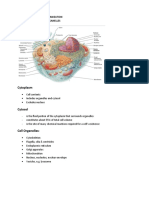
Tuesday, September 06, 2011 What methods do biologists use to study cells? Biochemical techniques to study cells The two main categories of cells Prokaryotic cell o Characteristics Bacteria and Archae Ecological successful Small size range 10 micrometer Nuclear area, circular DNA Plasma membrane No endomembrane system Ribosomes Cell wall: peptidoglucan Capsule Flagella Eukaryotic cell o Characterized by membrane-enclosed organelles Nucleus contains DNA The part of the cell outside the nucleus is cytoplasm The fluid component of cytoplasm is cytosol Supporting framework (cytoskeleton) Some organelles are present only in specific cells Plasma membrane and fluid mosaic model Plasma membrane forms the outer surface of every cell (all) Structure: fluid mosaic model -fluid mosaic model (double layer of phospholipids with proteins embedded and protruding from it Plasma membrane functions: The endomembrane system Membranes divide the cell into many compartments: Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Tuesday, September 06, 2011 Golgi complex Lysosomes Vacuoles Vesicles Vesicles move materials from one organelle to another Endomembrane system: Nucleus Nuclear envelope with nuclear pores Chromatin: DNA and protein make up the chromosomes Nucleolus: site of ribosome assembly Endomembrane system: The endoplasmic reticulum Smooth ER o o o o Outer surface without ribosomes Enzymes in the membranes catalyze synthesis of many lipids and carbohydrates (phospholipids, cholesterol, steroid hormones) Stores calcium ions (signaling) In liver cells, smooth ER breaks down stored glycogen and detoxifies chemicals
Golgi apparatus and proteins o Transport vesicles carrying proteins from the ER move along microtubules to the cis face of the Golgi complex
You might also like
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Chap. 04+Document49 pagesGeneral Biology - Chap. 04+정서진No ratings yet
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionDocument62 pagesCHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- 01cell Lecture 01Document42 pages01cell Lecture 01Phillip WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument36 pagesThe CellSam MumoNo ratings yet
- 6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Document7 pages6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Sadasivarao GaddeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Biology & GeneticsDocument7 pagesChapter 3: Cell Biology & GeneticsansleybarfieldNo ratings yet
- CellDocument28 pagesCellJanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-1 - The CellDocument33 pagesHDTD-B-1 - The CellMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- Cell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADDocument44 pagesCell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Biology Review: 1° Central Dogma of Molecular Biology and ImplicationsDocument19 pagesBiology Review: 1° Central Dogma of Molecular Biology and Implicationsdjxela89No ratings yet
- IB Biology A Unity and Diversity pt1Document18 pagesIB Biology A Unity and Diversity pt1rellomharazNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 BioDocument39 pagesTopic 3 BioTsukiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell StructureDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Cell StructureDeana NamirembeNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 6Document9 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 6Sarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesProkaryotic CellsRoshinne Lea Ang BialaNo ratings yet
- Biyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsDocument81 pagesBiyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsAkshay chandrakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cellular Level Part 2Document12 pagesLecture 3 Cellular Level Part 2Pia GalagalaNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleroavNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelDocument56 pages2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelVe LinNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 The CellDocument54 pagesBIO 1 The CellElyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument35 pagesLecture 9. Cell and Cell OrganellesSaksham JainNo ratings yet
- Biology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahDocument52 pagesBiology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahSophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cells and TissuesDocument21 pagesModule 2 Cells and TissuesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- CELL THE UNIT OF LIFE Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesCELL THE UNIT OF LIFE Important QuestionsAli WarisNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument108 pagesBiochemJangNo ratings yet
- Biology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahDocument52 pagesBiology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahSophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- Cell QuizDocument3 pagesCell QuizEuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Notes Chapter 7Document5 pagesBiology Lecture Notes Chapter 7Lady Rei RachoNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument24 pagesPlant and Animal CellMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- Cells: Structure and FunctionDocument51 pagesCells: Structure and FunctionmalaitamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 A Tour of The Cell: Lecture OutlineDocument17 pagesChapter 7 A Tour of The Cell: Lecture Outlinerashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Stem 12 Cell DivisionDocument38 pagesStem 12 Cell DivisionJohnson FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Document21 pagesCellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Maryum JavedNo ratings yet
- As OCR Biology Revision PackDocument28 pagesAs OCR Biology Revision PackJoel TrelivingNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument28 pagesCell OrganellesPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cells: Structure and FunctionsDocument13 pagesCells: Structure and Functionsrocen jerlyNo ratings yet
- CH - 03 The CellDocument29 pagesCH - 03 The Celllourd nabNo ratings yet
- Nature of CellsDocument7 pagesNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNo ratings yet
- Biology Mocks NotesDocument3 pagesBiology Mocks NotesAadit ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsDocument5 pagesCell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsPriyanshu Priyadarshi MeherNo ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell OrganellesSefLRho100% (1)
- Cell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSDocument51 pagesCell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSkittypattyNo ratings yet
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDocument7 pagesCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam #1 Study GuideDocument12 pagesBiology Exam #1 Study GuideKevin TranNo ratings yet
- w1 Introduction of CellsDocument60 pagesw1 Introduction of CellsNur Bahiyah Binti Abdul Wahab IPGKTINo ratings yet
- Cells 2020Document23 pagesCells 2020api-496612814No ratings yet
- Cell Theory1Document62 pagesCell Theory1Micoper ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Final School TranscriptDocument3 pagesFinal School TranscriptSteven TeguhNo ratings yet
- Jan 2019 3h - UnlockedDocument24 pagesJan 2019 3h - UnlockedahmedNo ratings yet
- Special Types of Matrices: By: Engr. Glenda Alega - de MesaDocument22 pagesSpecial Types of Matrices: By: Engr. Glenda Alega - de Mesasairin parkNo ratings yet
- PipephaseDocument32 pagesPipephaseZadeh NormanNo ratings yet
- Rubik's Revenge (4x4x4)Document5 pagesRubik's Revenge (4x4x4)Febbi Abdul MuktiNo ratings yet
- 2008 Bruce VandermeerDocument11 pages2008 Bruce Vandermeermadhumster1240No ratings yet
- Planning CriteriaDocument23 pagesPlanning CriteriaKiran TejaNo ratings yet
- HW 5 SolDocument20 pagesHW 5 SolKhoa Le TienNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Aperture Focussing Technique For Testing The Defects in Concrete Using LS DynaDocument27 pagesSynthetic Aperture Focussing Technique For Testing The Defects in Concrete Using LS DynaAnishu RahmanNo ratings yet
- Hot Rolled Bulb Flats PDFDocument4 pagesHot Rolled Bulb Flats PDFLaurentiu GavrilaNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 Final SAMPLEDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 Final SAMPLEJonah the mixerNo ratings yet
- To Estimate The Charge Induced On Each One of The Two Identical Styrofoam BallsDocument15 pagesTo Estimate The Charge Induced On Each One of The Two Identical Styrofoam Ballskiran ViratNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Extraction 3 Trimyristin From Nutmeg FS2010Document3 pagesLab 5 Extraction 3 Trimyristin From Nutmeg FS2010Sandip ThorveNo ratings yet
- Bionanotechnology - E. Papazoglou, A. Parthasarathy (2007) WWDocument148 pagesBionanotechnology - E. Papazoglou, A. Parthasarathy (2007) WWbicarbonat100% (2)
- Instructions HMG 47-48Document2 pagesInstructions HMG 47-48arindamdhar2004No ratings yet
- NES 838 Part2Document42 pagesNES 838 Part2QTESNo ratings yet
- Junior Design Project Meat Grinder 2016 2Document44 pagesJunior Design Project Meat Grinder 2016 2api-328800450100% (10)
- CH 10 Lecture 3 Angular Overlap: I. Ligand Field Theory and Square Planar ComplexesDocument16 pagesCH 10 Lecture 3 Angular Overlap: I. Ligand Field Theory and Square Planar ComplexesIsrael PobleteNo ratings yet
- Nuclear and Particle Physics - Unit 8 - Week 6: Particle Detectors and Elementary ParticlesDocument1 pageNuclear and Particle Physics - Unit 8 - Week 6: Particle Detectors and Elementary ParticlesSamarjeet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Flyback Diode PDFDocument3 pagesFlyback Diode PDFmarkgaloNo ratings yet
- La Teoria SintergiaDocument17 pagesLa Teoria SintergiaCarlos CárdenasNo ratings yet
- How To Carry Out Tack WeldingDocument2 pagesHow To Carry Out Tack WeldingwentropremNo ratings yet
- 7PPX0 2021 2022 AM Exercise BookDocument131 pages7PPX0 2021 2022 AM Exercise BookTeun JenniskensNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture Week 6 Chapter 2 PPT With NotesDocument40 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture Week 6 Chapter 2 PPT With NotesJake CanlasNo ratings yet
- R 2008 M.E. Power System SyllabusDocument24 pagesR 2008 M.E. Power System SyllabuskarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Simplified Model For Evaluating Soil Liquefaction Potential Using CPTUDocument8 pagesSimplified Model For Evaluating Soil Liquefaction Potential Using CPTUIbrahim SuryaNo ratings yet
- Higher Mathematics 1 (H & B)Document3 pagesHigher Mathematics 1 (H & B)joseph.kabaso96No ratings yet
- Rectifier Comissiong and Alarm SimulationDocument12 pagesRectifier Comissiong and Alarm SimulationsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Lec# 8 (Higher Order DE)Document22 pagesLec# 8 (Higher Order DE)Faraz KashifNo ratings yet
- The Inclined Plane (George Ricarrson - 2501987261)Document12 pagesThe Inclined Plane (George Ricarrson - 2501987261)George RYNo ratings yet