Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screenshot 2023-06-17 at 10.25.07 PM
Uploaded by
Noah GreenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screenshot 2023-06-17 at 10.25.07 PM
Uploaded by
Noah GreenCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Notes
Name: _______________________________________
Topic: Enzymes Period:_______________________________________
Date: _______________________________________
Questions/Main Idea:
Notes:
• Enzymes are proteins that help molecules react with one
What are enzymes?
another
• Their monomers are amino acids.
• Enzymes are used by cells to trigger and control
chemical reactions.
• Without enzymes, several reactions in cells would never
occur or happen too slowly to be useful.
• In digestive enzymes, often end in “-ase”
• It is the process of changing one set of chemicals
(reactants) into another set of chemicals (products) by
What is a chemical
rearranging the atoms.
reaction?
• Reactants’ bonds are broken and new ones are formed in
the products.
What is a catalyst? • It is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical
reaction.
• It lowers the activation energy.
• It participates in the reaction but doesn’t change itself;
therefore it can be used over and over.
What is activation • It is the amount of energy needed to start a chemical
energy? reaction.
• Catalysts speed up chemical reactions by lowering their
activation energy.
• Enzymes are catalysts because they lower the activation
energy by holding molecules together to either help them
bind (synthesize) or help them break apart (decompose).
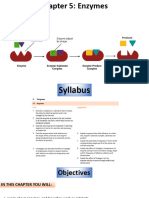
• Enzymes bind to or break molecules called substrates.
What is a substrate? • These substrates are the reactants that are catalyzed by
the enzyme.
What is the active site? • Each substrate and enzyme has a specific shape,
therefore enzymes bind to substrates based on shape.
• The site on the enzyme where the substrates bind is
called the active site.
What is the Lock and Key • Enzymes bind to the substrates based on their
Hypothesis? complementary shape.
• The fit is so exact that the active site and substrates are
compared to a lock and key.
• Most digestive enzymes are named for the foods
(molecules) they help react—lactase helps break down
lactose (milk sugar)
What are other examples of • Lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose
enzymes and what they • Sucrase (the “sugar-clipper”): breaks down sucrose
break down? (common table sugar) into glucose and fructose
• Amalyse breaks down starch in your mouth and
stomach
• Lipase breaks down ats
• Pepsin breaks down proteins
How are enzymes affected Enzymes are NOT changed by the reactions they catalyze,
by the reaction? therefore they are reusable!
How can enzymes be • Enzymes each work best at a specific temperature and
affected? pH.
• Temperatures outside the correct range can cause
enzymes to break down or change shape.
• This break down is called denaturation.
Why are enzymes • Nearly every reaction in your body is helped by an
considered the body’s enzyme!
“workers”? • Remember—enzymes are proteins!
Summary:
You might also like
- 15 Enzymescornell NotesDocument2 pages15 Enzymescornell NotesRusselNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 EnzymesDocument21 pagesLecture5 EnzymesassmmNo ratings yet
- "Helper" Protein Molecules: EnzymesDocument7 pages"Helper" Protein Molecules: EnzymesMuhammad Junaid IqbalNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesDavid PetalcurinNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and EnzymesDocument11 pagesMetabolism and Enzymessherylmatchado07No ratings yet
- Enzymes PresDocument34 pagesEnzymes PresRasmia SalamNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PPT BioDocument22 pagesEnzymes PPT Biovoyav37617No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Exploring EnzymesDocument17 pages2.4 Exploring EnzymesIsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - EnzymesDocument84 pagesChapter 1 - EnzymesNorsuzianaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionDocument35 pagesEnzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionAnonymous cgKtuWzNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PresentationDocument9 pagesEnzymes PresentationMile •No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument14 pagesEnzymesCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Enzymes PreAP 1st 3Document16 pagesChemical Reactions and Enzymes PreAP 1st 3Cardin PatrickNo ratings yet
- Enzymes As Biological CatalystDocument19 pagesEnzymes As Biological CatalystJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 EnzymeDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Enzymejzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Notes PPT Pre APDocument37 pagesEnzymes Notes PPT Pre APTed Dian TejadoNo ratings yet
- Title: Lecture (9) Enzymes Present By: Associate Prof - Ingy BadawyDocument58 pagesTitle: Lecture (9) Enzymes Present By: Associate Prof - Ingy BadawyAbdo ElsaidNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument26 pagesEnzymesrabiullah.edu987No ratings yet
- Slide EnzymeDocument27 pagesSlide EnzymeReni Fatmawati100% (1)
- Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsDocument61 pagesEnzyme and Enzyme KineticsNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Lasaca Report (Enzymes)Document43 pagesLasaca Report (Enzymes)MaryAnn LasacaNo ratings yet
- EnzymologyDocument47 pagesEnzymologyTererai Lalelani Masikati Hove100% (1)
- ENZYMES Semester 1Document51 pagesENZYMES Semester 1asadullah2315No ratings yet
- Enzymes (Bio Chem) : Mariano Marcos State University College of Teacher Education Laoag CityDocument34 pagesEnzymes (Bio Chem) : Mariano Marcos State University College of Teacher Education Laoag CityJared TabangcuraNo ratings yet
- Description of The Components of EnzymeDocument28 pagesDescription of The Components of EnzymeJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCDocument69 pagesBiomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCAmon Sangulube100% (1)
- 2.4 EnzymesDocument21 pages2.4 EnzymesMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Enzyme Action PowerpointDocument18 pagesLesson 1 Enzyme Action Powerpointtbrook2017No ratings yet
- Wajeeh Un Nisa#27Document20 pagesWajeeh Un Nisa#27Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - EnzymesDocument48 pagesChapter 5 - EnzymesKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- Lesson Objectives: - Enzyme Unit OverviewDocument14 pagesLesson Objectives: - Enzyme Unit OverviewMatt BarhamNo ratings yet
- Enzymes L1 2023 2024Document33 pagesEnzymes L1 2023 20249829c7fchsNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: How Does CF Affect Other Body System?Document3 pagesEnzymes: How Does CF Affect Other Body System?Tamara MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and SubstratesDocument11 pagesEnzymes and Substratesapi-252152558No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument27 pagesEnzymesRussNo ratings yet
- F EnzymesDocument27 pagesF Enzymeshazharomar958No ratings yet
- Pure Biology CHP 5 Enzymes 1Document35 pagesPure Biology CHP 5 Enzymes 1rabiayub21No ratings yet
- Enzyme NotesDocument1 pageEnzyme NotesGabrielNo ratings yet
- Module 8: Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways MetabolismDocument4 pagesModule 8: Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways MetabolismThiody Hope Mongas100% (2)
- Enzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionDocument31 pagesEnzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionCathrine CruzNo ratings yet
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDocument27 pagesEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesLyan Joy PalmesNo ratings yet
- Module 11: EnzymesDocument3 pagesModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 A EnzymesDocument3 pagesUnit 3 A EnzymesseecatpNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Are The Tools of LifeDocument31 pagesEnzymes Are The Tools of LifedrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- Bio G11 Unit 3 Enzymes PPXDocument14 pagesBio G11 Unit 3 Enzymes PPXBereket NetsanetNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of EnzymesDocument44 pagesBiochemistry of EnzymesShaira Elyze GabrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Biocatalysis: SUBTOPIC: 4.1 Properties of Enzymes and Mechanism of Actions Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesChapter 4: Biocatalysis: SUBTOPIC: 4.1 Properties of Enzymes and Mechanism of Actions Learning OutcomesNURUL HIDAYAH BINTI SAIFUL ANUAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Enzymes As Biological CatalystsDocument23 pagesEnzymes As Biological CatalystsLailatul BadriyahNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PresentationDocument25 pagesEnzymes Presentationmmpanjwani4No ratings yet
- Enzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriDocument71 pagesEnzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriIkhsan muttaqinNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesKim TanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument9 pagesEnzymesMaria AnghelacheNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument44 pagesEnzymesYumul, Jewel B.No ratings yet
- BiocatalysisDocument8 pagesBiocatalysisHanithra AnanthanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesMarie Veatrice Jacomille100% (1)
- Enzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Document26 pagesEnzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Nur AishaNo ratings yet
- Babi Pandey Biochemistry Vii Semester: Submitted To: Anil RegmiDocument38 pagesBabi Pandey Biochemistry Vii Semester: Submitted To: Anil RegmiBabi PandeyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes StructureDocument20 pagesEnzymes StructureBrandonNo ratings yet