Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scalar Multiplication
Uploaded by
Pei Sekar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesScalar Multiplication
Uploaded by
Pei SekarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
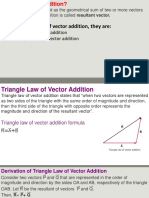
Multiplication of vectors
Scalar product Vector Product
(Dot product) (Cross product)
These are two ways in which a vector can be multiplied by another
vector
1) One way produces a Scalar and is known as Scalar product
A.B = ABcosθ
Where θ is the angle between the to vectors
Example:
Work done = Force x displacement
W = F.S
Power = Force x Velocity
P = F.v
Magnetic flux = Magnetic induction x Area vector
φ = B.A
2) Another way produces a new vector and is known as vector
product
Example:
Torque = position vector x Force
τ=rxF
Angular momentum = position vector x linear momentum
L=rxP
Properties of Scalar Product
1) Scalar product is commutative
A.B = B.A
2) The scalar product is distributive over addition
A.(B + C) = A.B + A.C
3) If A and B are two vectors perpendicular to each other then their
scalar product is zero
A.B = AB cos 90 = 0
4) If A and B are two vectors parallel to each other and acting in the
same direction then their scalar product has the maximum positive
magnitude
A.B = AB cos 0 = AB
5) If A and B are two vectors parallel to each other and acting in the
opposite direction then their scalar product has the maximum negative
magnitude
A.B = AB cos 180 = - AB
6) The scalar product of a vector with itself is equal to the square of
its magnitude
A.A = AAcos 0 = A2
7) Scalar product of two similar base vectors is unity and that of two
different base vectors is zero
i.i = j.j = k.k = 1
i.j = j.k = k.i = 0
8) A = Ax + Ay + Az B = Bx + By + Bz
A.B = Ax Bx + Ay By + Az Bz
9) A.B = │A││B │Cosθ
Cosθ = A.B / │A││B │
= (Ax Bx + Ay By + Az Bz) / √( A2x + A2y + A2z) √ ( B2x + B2y + A2z)
You might also like
- Physical Quantities Vectors & ScalarsDocument41 pagesPhysical Quantities Vectors & ScalarsLin Xian Xing100% (1)
- Problems and Worked Solutions in Vector AnalysisFrom EverandProblems and Worked Solutions in Vector AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Vectors 3. Product of Vectors: Points To RememberDocument11 pagesVectors 3. Product of Vectors: Points To RememberReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities & MEASUREMENTS (3 Hours)Document63 pagesPhysical Quantities & MEASUREMENTS (3 Hours)Muhd Fadhlan NaqiuddinNo ratings yet
- 2-Vector Analysis-Dot, Vector and Triple Scalar Product SY 2021-2022 EEDocument37 pages2-Vector Analysis-Dot, Vector and Triple Scalar Product SY 2021-2022 EEMarc RiveraNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Vector Analysis-A Language of PhysicsDocument15 pagesVectors: Vector Analysis-A Language of Physicsprabhu81No ratings yet
- Vectors: Introduction of VectorDocument9 pagesVectors: Introduction of Vectorskj6272No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument46 pagesVectorsmonika gompa100% (1)
- ScalarsDocument11 pagesScalarsbisratbirhanu52No ratings yet
- Teaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsDocument10 pagesTeaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Vector OperationsDocument19 pagesVector OperationsPuji NurrahmawatiNo ratings yet
- M O T I O N I N P L A N E: Learners AcademyDocument6 pagesM O T I O N I N P L A N E: Learners Academymujeebc 1972No ratings yet
- 3 VectorsDocument14 pages3 VectorsArvindhkandhavel RNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument9 pagesVectorsImash MinokaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 ElevenhDocument4 pagesChapter - 2 ElevenhsaqibrahimkchiNo ratings yet
- Gelombang Dan Optik Nelly ZamrianiDocument8 pagesGelombang Dan Optik Nelly ZamrianiNelly zamrianiNo ratings yet
- Phy10 Wk01 Vector 1Document69 pagesPhy10 Wk01 Vector 1Jed Efraim EspanilloNo ratings yet
- Physics - Class 11 CHAPTER 4 MOTION IN A PLANE-NOTESDocument8 pagesPhysics - Class 11 CHAPTER 4 MOTION IN A PLANE-NOTESAditya MauriyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes ON: Engineering PhysicsDocument133 pagesLecture Notes ON: Engineering PhysicsVishwa bandhu knNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument17 pagesChapter IMD NAYM MIANo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument12 pagesMotion in Straight LineamitctoNo ratings yet
- Units Physical Quantities and VectorsDocument33 pagesUnits Physical Quantities and VectorsWaffleNo ratings yet
- XI PHYSICS - IMPORTANT SOLVED LONG Q/A - 2023 - By: Sir AMMR BIN AHSANDocument20 pagesXI PHYSICS - IMPORTANT SOLVED LONG Q/A - 2023 - By: Sir AMMR BIN AHSANAmmar Bin AhsanNo ratings yet
- 4 - Motion in A PlaneDocument16 pages4 - Motion in A PlanePhysics with GurmeetNo ratings yet
- Phys245 Notes PDFDocument117 pagesPhys245 Notes PDFfuckitNo ratings yet
- Vector Notes: Modulus of A VectorDocument6 pagesVector Notes: Modulus of A VectorAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 VectorsDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Vectorsfatimaizzah24No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument48 pagesVectorsUltra Gamer (sishant)No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Vector Cross and Dot ProductDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Vector Cross and Dot ProductRyan Philip CatapangNo ratings yet
- 1lecture 1Document18 pages1lecture 1HIMA PARDHAV JASTINo ratings yet
- Motion 2d AakashDocument10 pagesMotion 2d AakashNavin RaiNo ratings yet
- SPH 110 - Full NotesDocument101 pagesSPH 110 - Full NotesErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics L2 PDFDocument50 pagesMechanics L2 PDFCharlie LaiNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 2Document13 pagesPhysics Chapter 2RaheEl Mukhtar0% (1)
- Newtonian MechanicsDocument15 pagesNewtonian Mechanicsvarsha gatlaNo ratings yet
- Dot ProdukDocument6 pagesDot ProdukTri AdiantoNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane Part 1Document8 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane Part 1ShashankAnil50% (2)
- Physics Notes Class 11 Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane Part 1Document8 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane Part 1TajiriMollel0% (1)
- Lecture 01 Scalars and Vectors (Module Version)Document10 pagesLecture 01 Scalars and Vectors (Module Version)John Lloyd GaringNo ratings yet
- EC8451 Unit IDocument19 pagesEC8451 Unit INagai KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Vector Algebra: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnDocument8 pagesVector Algebra: Complete Study Guide & Notes Onsharan1281No ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Griffiths-Vector Analysis - 1.1 1.2Document24 pagesChapter 1. Griffiths-Vector Analysis - 1.1 1.2Hazem TawfikNo ratings yet
- Privatisation of Indian Railways.Document34 pagesPrivatisation of Indian Railways.Aniket BabutaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Notes Vector AlgebraDocument8 pagesClass 12 Revision Notes Vector Algebrashubham upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument10 pagesVector AlgebraSamrat JanjanamNo ratings yet
- A Three Five Kilograms Twenty-Two Degrees Celsius: Scalar QuantitiesDocument6 pagesA Three Five Kilograms Twenty-Two Degrees Celsius: Scalar QuantitiesDars- Limos SaludezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Dsu PDFDocument32 pagesModule 1 Dsu PDFVinu RamadhasNo ratings yet
- Vectors Fundamentals CBSEDocument53 pagesVectors Fundamentals CBSEcpawan_699508No ratings yet
- Ec8451 Emf Lecture NotesDocument61 pagesEc8451 Emf Lecture NotesNarenthra BaalaNo ratings yet
- Vectors Note 2Document30 pagesVectors Note 2dhausa basnetNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Iit-Physics - Set - IDocument24 pagesVectors: Iit-Physics - Set - IHemant Kumar100% (1)
- Resolution of Vectors, Scalar & Vector ProductsDocument14 pagesResolution of Vectors, Scalar & Vector ProductsZahraNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 - TMT 20303Document13 pagesLect 1 - TMT 20303Arif FahmiNo ratings yet
- Notes1 2 76 12 11 2020 14 09Document75 pagesNotes1 2 76 12 11 2020 14 09Oo-baid U-safzaiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 VectorsDocument16 pagesModule 2 VectorsKrizel CalasaraNo ratings yet
- Learner Activity Sheet Dot Scalar ProductDocument2 pagesLearner Activity Sheet Dot Scalar ProductMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Tipos de Magnitudes Físicas: Magnitud Escalar: Definida Mediante Un Número yDocument20 pagesTipos de Magnitudes Físicas: Magnitud Escalar: Definida Mediante Un Número yjaviNo ratings yet
- Vectors and ScalarsDocument26 pagesVectors and ScalarsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Vector Operations - Part 2: General Physics 1 Learning Material 4Document6 pagesLesson 3: Vector Operations - Part 2: General Physics 1 Learning Material 4Justeny TabbayNo ratings yet