Professional Documents
Culture Documents
USP-NF Alcohol
Uploaded by
Rasmi PCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
USP-NF Alcohol
Uploaded by
Rasmi PCopyright:
Available Formats
6/14/23, 3:43 PM USP-NF Alcohol
Printed on: Wed Jun 14 2023, 15:43:10 pm
Printed by: Rasmi Pulakizhi
Status: Currently Official on 14-Jun-2023
Official Date: Official as of 01-Dec-2021
Document Type: USP & NF
DocId: GUID-81E046F1-D3BE-49C5-B216-BCA4E55F6E78_5_en-US
DOI: https://doi.org/10.31003/USPNF_M1238_05_01
DOI Ref: 8vnv1
Do not distribute
© 2023 USPC
Alcohol
Portions of this monograph that are national USP text, and are not part of the harmonized text, are marked with symbols (◆◆) to specify this fact.
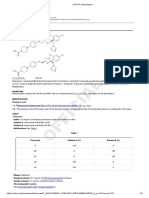
C2H6O 46.07
Ethanol;
Ethyl alcohol CAS RN®: 64-17-5.
DEFINITION
◆Alcohol contains NLT 92.3% and NMT 93.8%, by weight, corresponding to NLT 94.9% and NMT 96.0%, by volume, at 15.56°, of ethanol
(C2H5OH).◆
IDENTIFICATION
• A. It meets the requirements of the test for Specific Gravity 〈841〉.
• B. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197F or 197S: Neat
• ◆ C. Limit of Methanol
[Note—This test must be performed to be in compliance with USP, in addition to Identification A and B above.]
AL
Sample solution A, Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Chromatographic system, and System suitability: Proceed as directed in Organic
Impurities.
Analysis: Proceed as directed in the Organic Impurities test, Methanol calculation.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements in Table 2 for methanol.◆
IMPURITIES
I
• Limit of Nonvolatile Residue
Sample: 100 mL of Alcohol
IC
Analysis: Evaporate the Sample in a tared dish on a water bath, and dry at 100°–105° for 1 h.
Acceptance criteria: The weight of the residue is NMT 2.5 mg.
• Organic Impurities
Sample solution A: Alcohol (substance under test)
FF
Sample solution B: 300 µL/L of 4-methylpentan-2-ol in Sample solution A
Standard solution A: 200 µL/L of methanol in Sample solution A
◆[Note—To be prepared for use in Identification C]◆
Standard solution B: 10 µL/L each of methanol and acetaldehyde in Sample solution A
Standard solution C: 30 µL/L of acetal in Sample solution A
O
Standard solution D: 2 µL/L of benzene in Sample solution A
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 0.32-mm × 30-m fused-silica capillary; bonded with a 1.8-µm layer of phase G43
Injection type: Split; split ratio 20:1
Temperatures
Injection port: 200°
Detector: 280°
https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-81E046F1-D3BE-49C5-B216-BCA4E55F6E78_5_en-US?source=Search Results&highlight=et… 1/4
6/14/23, 3:43 PM USP-NF Alcohol
Column: See Table 1.
Table 1
Hold Time at Final
Initial Temperature Temperature Ramp Final Temperature Temperature
(°) (°/min) (°) (min)
40 0 40 12
40 10 240 10
Linear velocity: 35 cm/s
Carrier gas: Helium
Injection volume: 1.0 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution B
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the first major peak (acetaldehyde) and the second major peak (methanol)
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution A, Sample solution B, Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Standard solution D
Methanol calculation
◆
[Note—To be performed as a part of Identification C.]◆
Result = (rU/rS)
rU = peak area of methanol from Sample solution A
AL
rS = peak area of methanol from Standard solution A
Acetaldehyde calculation (sum of acetaldehyde and acetal)
Result = {[AE/(AT − AE)] × CA} + {[DE/(DT − DE)] × CD × (Mr1/Mr2)}
I
AE = peak area of acetaldehyde from Sample solution A
IC
AT = peak area of acetaldehyde from Standard solution B
CA = concentration of acetaldehyde in Standard solution B (µL/L)
FF
DE = peak area of acetal from Sample solution A
DT = peak area of acetal from Standard solution C
CD = concentration of acetal in Standard solution C (µL/L)
O
Mr1 = molecular weight of acetaldehyde, 44.05
Mr2 = molecular weight of acetal, 118.2
Benzene calculation
Result = [BE/(BT − BE)] × CB
BE = peak area of benzene from Sample solution A
BT = peak area of benzene from Standard solution D
CB = concentration of benzene in Standard solution D (µL/L)
[Note—If necessary, the identity of benzene can be confirmed using another suitable chromatographic system (stationary phase with a
different polarity).]
Any other impurity calculation
Result = (rU/rM) × CM
https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-81E046F1-D3BE-49C5-B216-BCA4E55F6E78_5_en-US?source=Search Results&highlight=et… 2/4
6/14/23, 3:43 PM USP-NF Alcohol
rU = peak area of each impurity in Sample solution B
rM = peak area of 4-methylpentan-2-ol in Sample solution B
CM = concentration of 4-methylpentan-2-ol in Sample solution B (µL/L)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2.
Table 2
Name Acceptance Criteria
Methanol NMT 0.5, corresponding to 200 µL/L
Acetaldehyde and acetal NMT 10 µL/L, expressed as acetaldehyde
Benzene NMT 2 µL/L
Sum of all other impuritiesa NMT 300 µL/L
a Disregard any peaks of less than 9 µL/L (0.03 times the area of the peak corresponding to 4-methylpentan-2-ol in Sample solution B).
SPECIFIC TESTS
Change to read:
• ◆ Specific Gravity 〈841〉: 0.812–0.816 at 15.56°, indicating 92.3%–93.8%, by weight, or 94.9%–96.0%, by volume, of ethanol (C2H5OH)
▲[Note—In the event that a temperature of 15.56° cannot be reached, the Alcoholometric Table found in the Reagents and Reference Tables section
of USP-NF can be used to provide the conversion factors needed to complete this test at other temperatures.◆]▲ (USP 1-Dec-2021)
• Ultraviolet Absorption
Analytical wavelength: 235–340 nm
AL
Cell: 5 cm
Reference: Water
Acceptance criteria
Absorbance: NMT 0.40 at 240 nm; NMT 0.30 between 250 nm and 260 nm; NMT 0.10 between 270 nm and 340 nm
I
Curve: The spectrum shows a steadily descending curve with no observable peaks or shoulders.
IC
• ◆ Clarity of Solution
[Note—Compare each Sample solution to Standard suspension A and to water in diffused daylight 5 min after preparation of Standard suspension
A.]
Hydrazine solution: 10 mg/mL of hydrazine sulfate in water. Allow to stand for 4–6 h.
Methenamine solution: Transfer 2.5 g of methenamine to a 100-mL glass-stopper flask, add 25.0 mL of water, insert the glass stopper, and mix
FF
to dissolve.
Primary opalescence suspension: Transfer 25.0 mL of Hydrazine solution to the Methenamine solution in the 100-mL glass-stopper flask. Mix,
and allow to stand for 24 h. This suspension is stable for 2 months, provided it is stored in a glass container free from surface defects. The
suspension must not adhere to the glass and must be well mixed before use.
Opalescence standard: Transfer 15.0 mL of the Primary opalescence suspension to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
O
This suspension should not be used beyond 24 h after preparation.
Standard suspension A: Opalescence standard and water (1 in 20)
Standard suspension B: Opalescence standard and water (1 in 10)
Sample solution A: Substance to be examined
Sample solution B: Dilute 1.0 mL of Sample solution A with water to 20 mL, and allow to stand for 5 min before testing.
Blank: Water
Analysis
Samples: Standard suspension A, Standard suspension B, Sample solution A, Sample solution B, and Blank
Transfer a sufficient portion of Sample solution A and Sample solution B to separate test tubes of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a
flat base and an internal diameter of 15–25 mm to obtain a depth of 40 mm. Similarly transfer portions of Standard suspension A,
Standard suspension B, and Blank to separate matching test tubes. Compare the Samples in diffused daylight, viewing vertically against a
black background (see Visual Comparison 〈630〉). The diffusion of light must be such that Standard suspension A can readily be
distinguished from water, and Standard suspension B can readily be distinguished from Standard suspension A.
Acceptance criteria: Sample solution A and Sample solution B show the same clarity as that of water or their opalescence is not more
pronounced than that of Standard suspension A.◆
• Acidity or Alkalinity
Phenolphthalein solution: Dissolve 0.1 g of phenolphthalein in 80 mL of alcohol, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Sample: 20 mL of Alcohol
https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-81E046F1-D3BE-49C5-B216-BCA4E55F6E78_5_en-US?source=Search Results&highlight=et… 3/4
6/14/23, 3:43 PM USP-NF Alcohol
Analysis: To the Sample add 20 mL of freshly boiled and cooled water and 0.1 mL of Phenolphthalein solution. The solution is colorless. Add 1.0
mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide.
Acceptance criteria: The solution is pink (30 µL/L, expressed as acetic acid).
• ◆ Color of Solution
Standard stock solution: Combine 3.0 mL of ferric chloride CS, 3.0 mL of cobaltous chloride CS, 2.4 mL of cupric sulfate CS, and 1.6 mL of dilute
hydrochloric acid (10 mg/mL).
Standard solution: Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with dilute hydrochloric acid (10 mg/mL).
Prepare the Standard solution immediately before use.
Sample solution: Substance under test
Blank: Water
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank
Transfer a sufficient portion of the Sample solution to a test tube of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal
diameter of 15–25 mm to obtain a depth of 40 mm. Similarly transfer portions of the Standard solution and Blank to separate, matching
test tubes. Compare the Samples in diffused daylight, viewing vertically against a white background (see Visual Comparison 〈630〉).
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution has the appearance of water or is not more intensely colored than the Standard solution.◆
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers, protected from light.
• USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Alcohol RS
Auxiliary Information - Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Topic/Question Contact Expert Committee
ALCOHOL Jenny Liu
AL SE2020 Simple Excipients
Senior Scientific Liaison
Chromatographic Database Information: Chromatographic Database
I
IC
Most Recently Appeared In:
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 46(4)
Page Information:
FF
USPNF 2021 ISSUE 3 - online
USP43-NF38 - 113
USP42-NF37 - 114
Current DocID: GUID-81E046F1-D3BE-49C5-B216-BCA4E55F6E78_5_en-US
DOI: https://doi.org/10.31003/USPNF_M1238_05_01
DOI ref: 8vnv1
O
https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-81E046F1-D3BE-49C5-B216-BCA4E55F6E78_5_en-US?source=Search Results&highlight=et… 4/4
You might also like
- USP-NF AlcoholDocument4 pagesUSP-NF AlcoholOIL TEST INTERNACIONAL DE COLOMBIA S.A.SNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Stage 6 Harmonization of Alcohol StandardsDocument2 pagesStage 6 Harmonization of Alcohol Standardssaif aliNo ratings yet
- Stage 6 Harmonization of Alcohol Monograph StandardsDocument2 pagesStage 6 Harmonization of Alcohol Monograph StandardsSilvia RefreskateNo ratings yet
- Acid Value - Metrohm Application Balletin No. 80-3 eDocument7 pagesAcid Value - Metrohm Application Balletin No. 80-3 e陳丹庭No ratings yet
- USP-NF Cabergoline TabletsDocument4 pagesUSP-NF Cabergoline Tabletsanon_993394650No ratings yet
- Determine TBN in petroleum products via potentiometric titrationDocument10 pagesDetermine TBN in petroleum products via potentiometric titrationmbusairiNo ratings yet
- USP-NF AcetoneDocument3 pagesUSP-NF AcetoneyoussufNo ratings yet
- Hydroxypropyl Betadex NMR MSDocument8 pagesHydroxypropyl Betadex NMR MSLeidy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Get AttachmentDocument7 pagesGet AttachmentGaurav PatelNo ratings yet
- Anastrozolum: AnastrozoleDocument2 pagesAnastrozolum: AnastrozolelinhkhanhNo ratings yet
- For METTLER TOLEDO Titration Excellence Line: Selected ApplicationsDocument31 pagesFor METTLER TOLEDO Titration Excellence Line: Selected ApplicationsKeila ChavesNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Acebutolol HydrochlorideDocument4 pagesUSP-NF Acebutolol HydrochlorideStalin VacaNo ratings yet
- Ab-404 1 en PDFDocument8 pagesAb-404 1 en PDFVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- USP43 Methacholine ChlorideDocument2 pagesUSP43 Methacholine ChlorideAlejandro RestrepoNo ratings yet
- GUID - 4 en-USDocument1 pageGUID - 4 en-USLucélia ScachetiNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Aluminum MonostearateDocument3 pagesUSP-NF Aluminum MonostearateK.m. Ehsan Morshed RanaNo ratings yet
- N Methylpyrrolidone: Chemical Synonym General InformationDocument5 pagesN Methylpyrrolidone: Chemical Synonym General InformationMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Total Acid NumberDocument9 pagesDetermination of The Total Acid NumberAbu WildanNo ratings yet
- 5990 8068enDocument6 pages5990 8068enarnoldivanmtzfNo ratings yet
- Relevant Details of AminesDocument2 pagesRelevant Details of AminesdbothejuNo ratings yet
- Timolol Maleate 1susp40Document2 pagesTimolol Maleate 1susp40Ayu Febrina TunaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol FEUMDocument2 pagesAlcohol FEUMSajimars SajimarNo ratings yet
- Conductometric Determination of TBN in Petroleum Products According To IP 400Document2 pagesConductometric Determination of TBN in Petroleum Products According To IP 400luisry1990No ratings yet
- Valproic Acid PDFDocument3 pagesValproic Acid PDFazida59No ratings yet
- Methylphenidate HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesMethylphenidate HydrochlorideRezaul RazibNo ratings yet
- APAT 0116enDocument3 pagesAPAT 0116enU.s. Ezhil ArivudainambiNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Clopidogrel BisulfateDocument5 pagesUSP-NF Clopidogrel BisulfateRonald SalasNo ratings yet
- LetrozoleDocument3 pagesLetrozolelinhkhanhNo ratings yet
- Alpha Lipoic AcidDocument2 pagesAlpha Lipoic AcidRaquel Bc100% (1)
- USP-NF Acetyltriethyl CitrateDocument2 pagesUSP-NF Acetyltriethyl CitrateK.m. Ehsan Morshed RanaNo ratings yet
- Etia 07010 PDFDocument4 pagesEtia 07010 PDFrbdubey2020No ratings yet
- Determination of The Amine Value: Mettler Toledo Application M242Document4 pagesDetermination of The Amine Value: Mettler Toledo Application M242Hasan Zeki BayrakNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Total Acid Number in Petroleum ProductsDocument8 pagesDetermination of The Total Acid Number in Petroleum ProductsdianaNo ratings yet
- Substances and The Titration Method in The Assay With One HPLC Method For Both ProceduresDocument5 pagesSubstances and The Titration Method in The Assay With One HPLC Method For Both ProceduresRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesAtomoxetine Hydrochlorideehsan050628No ratings yet
- Experimental Chemistry IDocument60 pagesExperimental Chemistry IadminchemNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Combined: GC Method for 9 AlcoholsDocument6 pagesAlcohols Combined: GC Method for 9 AlcoholsMICROLABORATORIO S.A de C.VNo ratings yet
- AOCS Method Ce 1c-89Document4 pagesAOCS Method Ce 1c-89Lam Lai YanNo ratings yet
- Total Base Number TBN DIN ISO 3771 ASTM 2896 280KB English PDFDocument10 pagesTotal Base Number TBN DIN ISO 3771 ASTM 2896 280KB English PDFahmetNo ratings yet
- USP-NF KetoconazoleDocument3 pagesUSP-NF Ketoconazoleanon_993394650No ratings yet
- USP-NF Benzocaine GelDocument3 pagesUSP-NF Benzocaine GelayuwinaNo ratings yet
- M 5391 AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesM 5391 AripiprazoleFarell AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Iohexol USP42NF37Document5 pagesIohexol USP42NF37John Alejandro Restrepo GarciaNo ratings yet
- USP NF ButroDocument3 pagesUSP NF ButrosanthoshNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Acetyltributyl CitrateDocument2 pagesUSP-NF Acetyltributyl CitrateIVAN BERNALNo ratings yet
- Ethanol USP MonographDocument2 pagesEthanol USP MonographSarah Tahir100% (1)
- GUID - 4 en-USDocument2 pagesGUID - 4 en-USDilawar BakhtNo ratings yet
- Total Acid Number of Lubricant: Acid Base Titration (Non Aqueous) by Automatic Potentiometric TitratorDocument4 pagesTotal Acid Number of Lubricant: Acid Base Titration (Non Aqueous) by Automatic Potentiometric Titratorsugandaraj522No ratings yet
- CefaclorDocument3 pagesCefaclorLinh PhiNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel Bisulfate USPDocument2 pagesClopidogrel Bisulfate USPQC MahakamNo ratings yet
- Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium DetailsDocument11 pagesBetadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium DetailsLeidy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Oilpac eDocument85 pagesOilpac eAri CleciusNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic AcidDocument4 pagesTranexamic AcidJagdish ChanderNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl Value in Polyols (DIN 53240-2:2007-11) : Mettler Toledo Application M091-08Document6 pagesHydroxyl Value in Polyols (DIN 53240-2:2007-11) : Mettler Toledo Application M091-08hanna.costantinNo ratings yet
- 5991-hplc 1260 Mid DistDocument6 pages5991-hplc 1260 Mid Distمحمد محمودNo ratings yet
- MetoprololDocument3 pagesMetoprololIli MarinaNo ratings yet
- USP Etoricoxib MonographDocument4 pagesUSP Etoricoxib MonographNeng Ayu Fitryanita60% (5)
- 8 - Sucralose USP NFDocument2 pages8 - Sucralose USP NFasmae.labindusNo ratings yet
- Section - A: Holiday Homework For Grade XiDocument7 pagesSection - A: Holiday Homework For Grade XiGM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Examination of Power Electronics (Pel) : AnswerDocument10 pagesExamination of Power Electronics (Pel) : Answerves vegasNo ratings yet
- Sps 500 (STD) ProgramDocument164 pagesSps 500 (STD) Programwahyu100% (1)
- Jsa-0002 - CCTV Pipe Inspection RapidDocument8 pagesJsa-0002 - CCTV Pipe Inspection RapidMohamad AfifNo ratings yet
- THE LIVING MATRIX: A MODEL FOR THE PRIMARTY RESPIRATORY MECHANISMDocument69 pagesTHE LIVING MATRIX: A MODEL FOR THE PRIMARTY RESPIRATORY MECHANISMRukaphuongNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption Types and ProcessDocument18 pagesVolcanic Eruption Types and ProcessRosemarie Joy TanioNo ratings yet
- Humic Substances As Electron Acceptor For Microbial RespirationDocument4 pagesHumic Substances As Electron Acceptor For Microbial RespirationNed FlandersNo ratings yet
- Form Ibpr Haul Road PDFDocument2 pagesForm Ibpr Haul Road PDFelvandi100% (1)
- Online Medicine Industry Competitor AnalysisDocument14 pagesOnline Medicine Industry Competitor Analysispawangadiya1210No ratings yet
- WP Stratasys TopFiveReasonsDocument7 pagesWP Stratasys TopFiveReasonscititorulturmentatNo ratings yet
- Labrel 104-195Document1,014 pagesLabrel 104-195Maria Seleena HipolitoNo ratings yet
- 465 886 1 SMDocument8 pages465 886 1 SM17Annisa Muthmainnah067No ratings yet
- A Study On Satisfaction Level of Employees With Special Reference Textile IndustryDocument12 pagesA Study On Satisfaction Level of Employees With Special Reference Textile Industrysai kiran bade100% (1)
- Uganda National Urban ProfileDocument74 pagesUganda National Urban ProfileUnited Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT)No ratings yet
- GER Bangladesh EngDocument12 pagesGER Bangladesh Engfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet
- Site Comp End 02Document66 pagesSite Comp End 02Parameswararao BillaNo ratings yet
- 4 Dec - Elis Vs ElisDocument6 pages4 Dec - Elis Vs ElisRichard TenorioNo ratings yet
- Benign EntitiesDocument37 pagesBenign EntitiesleartaNo ratings yet
- Tugas UNtar 3Document28 pagesTugas UNtar 3Daniel Filemon PosoNo ratings yet
- NeseritideDocument28 pagesNeseritideNavojit Chowdhury100% (1)
- Arya Steels Ratings Remain StableDocument4 pagesArya Steels Ratings Remain StableData CentrumNo ratings yet
- The QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesThe QuestionnaireMaximo C. Nayanga Jr.No ratings yet
- Predicting Natural Hazards PowerPointDocument29 pagesPredicting Natural Hazards PowerPointZarlene SierraNo ratings yet
- MEH B1 Video Book Answer KeyDocument6 pagesMEH B1 Video Book Answer KeyTru CallingNo ratings yet
- Choosing the Right Handbag or Food Product (38 charactersDocument24 pagesChoosing the Right Handbag or Food Product (38 charactersNiceman NatiqiNo ratings yet
- Preserving Food Drying Fruits and VegetablesDocument12 pagesPreserving Food Drying Fruits and Vegetablespdxpharris100% (1)
- Different Mesh Sizes and Mesh To Micron ConversionDocument10 pagesDifferent Mesh Sizes and Mesh To Micron ConversionDevanandDongreNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Oral Presentation Peserta FIT-VIIIDocument26 pagesJadwal Oral Presentation Peserta FIT-VIIIKlinik FellitaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Technologist Resume SampleDocument2 pagesSurgical Technologist Resume Sampleresume7.com100% (3)
- D1553.140U1 German Braun Speed - Braun Card-Xi'an Yuanhua Instrument Co., LTDDocument2 pagesD1553.140U1 German Braun Speed - Braun Card-Xi'an Yuanhua Instrument Co., LTDTrong Hung NguyenNo ratings yet