Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Characterisitics of CILIA and FALGELLA
Uploaded by
Trần Quốc HuânOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Characterisitics of CILIA and FALGELLA
Uploaded by
Trần Quốc HuânCopyright:
Available Formats
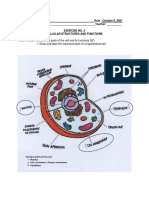
CILIA’s Characterisitics
Cilia are small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of all mammalian cells. They are
primitive in nature and could be single or many. Cilia play a major role in locomotion. They are also
involved in mechanoreception.
Cilia have several characteristics:
1. Structure: Cilia are long, thin structures with an actin-based core and a tubular membrane covering.
2. Movement: Cilia can undergo rhythmic, coordinated movements that result in the flow of fluids and
particles.
3. Directionality: The movement of cilia is unidirectional, meaning that it is directed in one direction only.
4. Function: Depending on the cell type and location, cilia can play a role in a variety of functions,
including the movement of fluids and particles, sensory detection, and cellular signaling.
5. Deficiency: Defects in cilia function can lead to the development of a variety of diseases, including
ciliary dyskinesia, primary ciliary dyskinesia, and some types of polycystic kidney disease.
Flagella’s Characteristics
Bacterial flagella are helically shaped structures containing the protein flagellin. The base of the
flagellum (the hook) near the cell surface is attached to the basal body enclosed in the cell envelope. The
flagellum rotates in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction, in a motion similar to that of a propeller.
Flagella are long, finger-like projections that protrude from the cell membrane of prokaryotic organisms
such as bacteria and archaea, and from some eukaryotic cells such as sperm cells. Flagella are used for
propulsion and for sensory functions in some organisms. Let me list the characteristics of flagella:
1. Structure: Flagella are composed of a single, central rod called the axoneme that is surrounded by a
sheath of fibrilous proteins.
2. Movement: Flagella can undergo metrical and rotational movements that are thought to be controlled
by a complex network of proteins.
3. Shape: Flagella can have different shapes depending on the organism, including straight, curved, or
wavy forms.
4. Function: Flagella play a role in the movement of microorganisms, including swimming and crawling.
They can also function as sensory organs, allowing microbes to sense their environment.
5. Deficiency: Defects in flagellar structure or function can lead to decreased motility or reduced sensory
capabilities in some organisms. This can impact their ability to survive and thrive in certain
environments.
You might also like
- Presented By: Jet Daniel Andrei Arellano Darwin Reigh Calub Aeryl Dierson MagahisDocument75 pagesPresented By: Jet Daniel Andrei Arellano Darwin Reigh Calub Aeryl Dierson MagahisDaniel Arellano85% (13)
- Cell ModificationsDocument8 pagesCell ModificationsOreeyoNo ratings yet
- Cell ModificationDocument2 pagesCell ModificationArwen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Cilia and Flagella: - by Neha LoharDocument18 pagesStructure of Cilia and Flagella: - by Neha Loharjoy parimalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Unit 1-2Document52 pagesCell Membrane Unit 1-2Kemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument4 pagesCilia and FlagellaGaurab Bhattarai100% (1)
- Cell ModificationsDocument38 pagesCell ModificationsMarlennete Urbano Ligas100% (1)
- Divyasparshi: Healer Suresh NagarsekarDocument21 pagesDivyasparshi: Healer Suresh Nagarsekarprashant borgeNo ratings yet
- Elsc Easy Learn Singh Classes: Cell OrganelleDocument13 pagesElsc Easy Learn Singh Classes: Cell OrganelleNandini SinghNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Differences Between Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesStudy Notes - Differences Between Plant and Animal Cellsuserdev987No ratings yet
- Microtubules: Organization: Single Microtubules Are Distributed Within The Cytoplasm. Also, MicrotubulesDocument6 pagesMicrotubules: Organization: Single Microtubules Are Distributed Within The Cytoplasm. Also, MicrotubulesArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- CELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonDocument19 pagesCELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BIO564Document334 pagesChapter 2 BIO564wannuraihanfadzilNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Cell ModificationDocument35 pagesGen Bio 1 Cell Modificationizy nicole bugalNo ratings yet
- Flagella DefinitionDocument11 pagesFlagella DefinitionShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEDocument3 pagesAnatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Unicellular OrganismsDocument10 pagesGrade 7 Unicellular OrganismsGadgetGlitchKillNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Week 3Document8 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Week 3Liamie MedezNo ratings yet
- CilliumDocument5 pagesCilliumMuhammad ZairulfikriNo ratings yet
- Microbial Anatomy - Prokaryotic MicrobesDocument55 pagesMicrobial Anatomy - Prokaryotic MicrobesRoel Jason TuboNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 6Document3 pagesHes 029 Lab Sas 6Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles DefinitionDocument40 pagesCell Organelles Definitionmuhammad aslam0% (1)
- Cell Modifications: Microvilli Cilia FlagellaDocument19 pagesCell Modifications: Microvilli Cilia FlagellaDaniel CraigNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsJohn TacordaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Epithelial TissueDocument6 pagesExercise 1: Epithelial TissueTherese RiveraNo ratings yet
- Gen Zoology ReviewerDocument19 pagesGen Zoology ReviewerDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantDocument3 pagesCell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantPauline Grace MontifalconNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio 1 Module 2Document6 pagesGen. Bio 1 Module 2Evelyn MagbarilNo ratings yet
- Histology (Epithelial Tissue)Document23 pagesHistology (Epithelial Tissue)FazilaNo ratings yet
- Bpes2 SemDocument95 pagesBpes2 Semnishthabanga1525No ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Cellular Structure of Bacteria (Part2) : MSC Somya H. TrurkiDocument9 pagesLecture 3: Cellular Structure of Bacteria (Part2) : MSC Somya H. Trurkiعبدالحق صادقNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell StructureDocument2 pagesBiology Cell StructureCut Rizka RahmiNo ratings yet
- LAS 3 Cell ModificationDocument5 pagesLAS 3 Cell ModificationJeremie CataggatanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Structures WorksheetCharlene BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell Lesson PlanGilda Genive AriolaNo ratings yet
- Cell ModificationDocument28 pagesCell ModificationIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science BDocument5 pagesReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomNo ratings yet
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocument14 pagesKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- ProtistDocument5 pagesProtistGerald Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- Unite 3 CellsDocument44 pagesUnite 3 CellsJo AnNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesMUTWIRINo ratings yet
- Ch#4Document5 pagesCh#4surprisinglysarahytNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Cell Structure-Group #4Document17 pagesCell Structure-Group #4Andrea MorochoNo ratings yet
- Membrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesMembrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemFarah Jaye Verde CayayanNo ratings yet
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailNo ratings yet
- Structure of Prokaryotic CellDocument16 pagesStructure of Prokaryotic CellShahzad AslamNo ratings yet
- Class NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Document28 pagesClass NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Cyril Josh MaisogNo ratings yet
- Cell ModificationsDocument35 pagesCell ModificationsIvan GalletoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument43 pagesLecture 2-The CellMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusNo ratings yet
- Bagian IsiDocument16 pagesBagian IsiKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CellDocument11 pagesStructure and Function of CellWoobin RealNo ratings yet
- Cell Modification EditedDocument44 pagesCell Modification EditedGian Miguel FernandezNo ratings yet
- NUDES Lab Activity 2Document5 pagesNUDES Lab Activity 2Ella RetizaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Cell Organelles 2Document29 pagesStructure and Function of Cell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument3 pagesProkaryotic CellWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Part 4 FinalDocument23 pagesCell Biology Part 4 FinalVittal Athul RNo ratings yet