Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity No.1 - The Cell
Uploaded by
Celestine Mambulao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Activity-No.1_The-Cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesActivity No.1 - The Cell
Uploaded by
Celestine MambulaoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Name: Mambulao, Celestine M. Date: February 12, 2023.
Course & Section: BSBIO-2A Subject: Lecture / Biomolecules
Assignment: Identity different type of organelles of plant and animals.
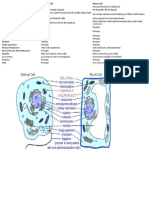
Animal cell organelles.
Nucleus – rounded, darkly-skinned structure separated from the cytoplasm by
double-walled nuclear envelope, the nuclear membrane. Control cell direct cell
division since it contains all hereditary in the form of genes. Control protein
synthesis.
Peroxisomes – similar to lysosomes in that they are membrane bound sacs
which contain enzymes. Involved either in the production of hydrogen peroxide
(product of the reduction of O2) or the destruction of hydrogen peroxide to water.
Centrosome and centrioles – granules structure located just outside the
nucleus and found in all animal cells (neuron, etc.) And primitive plants; a self-
duplicating organelle. Active in the process of cell division (mitosis); in the
formation of cilia.
Plastids – round or oval bodies containing pigments commonly found in plants.
Site of photosynthesis powerhouse unit of plant cells.
Microfilaments and microtubules – long, thin, tiny cylindrical fibrils or tubules
made up predominantly of protein tubulin. Form of spindle fibers. Form of skeletal
elements of motile organelles like cilia, flagella and components of the centriole.
Cytoskeleton. Microtubules are smaller than microfilaments.
Cell membrane – a cytoplasmic boundary or limiting membrane condensed into
a peripheral film. It is a selectively permeable or semi-permeable membrane at
may or may not allow certain ions and molecules to enter or leave the cell. Lipid-
soluble substances can easily pass through the cell membrane.
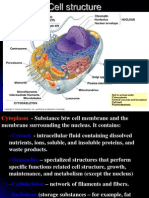
Cytoplasm – protoplasm that includes all of the protoplasm except the nucleus;
It is the executive center and has a vital reciprocal interdependence with nucleus.
Endoplasmic reticulum – a network of fine, tube-like, unit membrane mirotunnels
that traverse the cytoplasm between the nuclear envelope and the outer plasma
membrane.
Rough ER – with ribosomes attached to its membrane surface (with a diameter
of 120A to 150 A). Protein synthesis.
Smooth ER – tubular in appearance and without ribosomes attached to its
membrane surface (like the sarcoplasmic reticulum). Site of steroids synthesis,
(hormone of adrenal gland). Lipid or fats synthesis, synthesis of enzymes of
carbohydrate metabolism, intracellular transport system conveying proteins
through canals either to the exterior of the cell or to the golgi complex where they
are packaged and then released from the cell.
Ribosomes – tiny rounded bodies or spherical granule which either: attached to
the ER and synthesize hormones; or free floating in the cytoplasm and
synthesize cytoplasmic proteins like hemoglobin. Site of protein synthesis
( manufacturing units or principal factories).
Golgi complex or dictyosomes – consist of several flattened tubular
membranes stacked upon each other termed cisternae, and dilated terminal
areas at either end of the cisternae called vacuoles. Packaging (surrounded by a
membrane) of protein secretory material formed in the ER and where
carbohydrates synthesized within the golgi complex are added to the proteins as
glycoproteins (major role in the synthesis of glycoproteins).
Mitochondria – spherical, rod – shaped, cigar or sausage – shaped, somewhat
hollow structures. Double walled (unit membrane), water – filled membrane
consisting of, outer membrane which smooth, tightly stretched and completely
surrounds mitochondria. Inner membrane which is extensively invaginated into
folds, forming shelves called cristae which increase the surface for energy
production and enzyme activity. The power house of the cell, or responsible for
the production of energy in the form of ATP (adrenosine triphosphate) that
supports mechanical and chemical work performed by cells.
Lysosomes (suicidal bags or lyctic bodies) – pre-formed, membrane bund,
dense appearing structures or packages of hydrolytic enzymes collectively
known as acid hydrolases. Intracellular digestion.
Plant cell organelles
Cell Membrane - A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows
materials in and out.
Lysosome - Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and
invaders.
Cytoplasm - Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles.
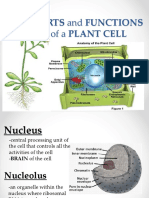
Nucleus - The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA
Nuclear Membrane - Surrounds the nucleus.
Nucleolus - A round structure in the nucleus that makes ribosomes.
Vacuole - Stores food and water.
Golgi Body - Processes and packages materials for the cell.
Mitochondria The “Powerhouse” - Breaks down food to produce energy in the
form of ATP.
Rough E.R. - Builds and transports substances through the cell. Has ribosomes
on it.
Smooth E.R. - Builds and transports substances through the cell. Does not have
ribosomes.
Ribosome - Helps make protein for the cell.
Cell Wall -Gives shape and protection to plant cells.
Chloroplast -Changes sunlight into sugar for plant cells. Contains a green
pigment called chlorophyll.
You might also like
- Breathe Strong, Perform Better by Alison McConnellDocument288 pagesBreathe Strong, Perform Better by Alison McConnellabacaterct100% (1)
- Body Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument26 pagesBody Fluids & ElectrolytesMohamad Zekry Zuhairy100% (1)
- Presentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Document13 pagesPresentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Keerthana RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument43 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFFíre B DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Organelles and FunctionsDocument15 pagesPlant Cell Organelles and FunctionsAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Fruitbodies and SclerotiaDocument4 pagesCultivation of Fruitbodies and SclerotiaEsporas De MexicoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Yoga Therapy Conf ManualDocument84 pagesAnatomy Yoga Therapy Conf ManualPablo ErpelNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Biology 1st DiscussionDocument52 pagesBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument28 pagesHealth AssessmentPiyush Dutta100% (2)
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument106 pagesCell Structure and Organisationwienna1987No ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- Animal and Plant Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell OrganellesKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Organelles GuideDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Organelles Guidenelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKarren MakamureNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall-: (Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument3 pagesCell Wall-: (Deoxyribonucleic Acidsakchham agrawalNo ratings yet
- Components of Animal and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesComponents of Animal and Plant CellsYukiNo ratings yet
- Three major parts of the cellDocument22 pagesThree major parts of the cellHab DogNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument10 pagesCellsRebecca SchmidtNo ratings yet
- PLANT CELL TERMSDocument15 pagesPLANT CELL TERMSanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes PptDocument14 pagesGrade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes PptNoel MammenNo ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: The Structures that Power Plant CellsDocument10 pagesCell Organelles: The Structures that Power Plant Cellsjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument51 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsDocument2 pagesPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsNelson De LimaNo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- lecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pageslecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure VocabDocument1 pageCell Structure VocabFatima ZaidiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell Unit of LifeNavaneeth KrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsAlix AliNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Cells Chapter 2 OverviewDocument107 pagesCells Chapter 2 Overviewida hadiNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Their FuncyionsDocument2 pagesCell Organelles and Their FuncyionsDONABEL ESPANONo ratings yet
- Robert Hooke's Discovery of Cells Using a MicroscopeDocument7 pagesRobert Hooke's Discovery of Cells Using a MicroscopelorinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Cell CytoplasmDocument55 pagesCell Cytoplasmnicolaer111100% (1)
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trixie OrganellesDocument2 pagesTrixie OrganellesMir SantillanNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- KCA HBT Test 1 Series 1 25 4 2021Document11 pagesKCA HBT Test 1 Series 1 25 4 2021KhanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Meliani Amina Plant Growthpromotion and Iaa Secretion Withpseudomonas Fluorescens and Pseudomonas PutidaDocument10 pages2017 Meliani Amina Plant Growthpromotion and Iaa Secretion Withpseudomonas Fluorescens and Pseudomonas PutidaOussama SaoulaNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 Marking Scheme June 2009Document3 pagesPaper 6 Marking Scheme June 2009MSHNo ratings yet
- AIA Lymphatics TemplateDocument4 pagesAIA Lymphatics TemplateErin MahonyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportDocument5 pagesThyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportAnonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- CSGO Matches & LivescoreDocument1 pageCSGO Matches & LivescoreВлад ГаманNo ratings yet
- Review Work 2019, CHM145020Document14 pagesReview Work 2019, CHM145020mahfooz zin noorineNo ratings yet
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- Frequencies 171.160 Hz, 174.989 Hz, and 1185.131 Hz may help combat COVID-19Document28 pagesFrequencies 171.160 Hz, 174.989 Hz, and 1185.131 Hz may help combat COVID-19Stere StereNo ratings yet
- Aice Midterm Study GuideDocument4 pagesAice Midterm Study GuidedsfsedfNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Nursing Care and AssessmentDocument31 pagesBlood Transfusion Nursing Care and AssessmentmyNo ratings yet
- Study of Behavior of Bacterial ConcreteDocument20 pagesStudy of Behavior of Bacterial ConcreteGodwin KopelliNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural NetworkDocument9 pagesArtificial Neural Networkjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology COVID-19 (SARS-Cov-2) RT-PCR: 80994699 Mr.I C SharmaDocument1 pageMolecular Biology COVID-19 (SARS-Cov-2) RT-PCR: 80994699 Mr.I C SharmaMohd YasarNo ratings yet
- Dental BooklistDocument14 pagesDental Booklistالمكتبة المليونيةNo ratings yet
- Marine Biology-LecNote-Unit-2 PDFDocument9 pagesMarine Biology-LecNote-Unit-2 PDFYashNo ratings yet
- University EssayDocument2 pagesUniversity Essaykitzun sanNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument14 pagesBacteriologyFrancene Ac-DaNo ratings yet
- The Plant Cell Wall A. IntroductionDocument6 pagesThe Plant Cell Wall A. IntroductionRizky EliandiNo ratings yet
- ANPH 111 (Anatomy and Physiology) : Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument11 pagesANPH 111 (Anatomy and Physiology) : Bachelor of Science in NursingMary Grace MapulaNo ratings yet
- Biology and Diversity of Viruses, Bacteria and Fungi (Paper Code: Bot 501)Document25 pagesBiology and Diversity of Viruses, Bacteria and Fungi (Paper Code: Bot 501)Ajzm CompanyNo ratings yet
- Price List UsDocument18 pagesPrice List UssairajNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Experiments 1-8Document23 pagesBiochemistry Lab Experiments 1-8Claudette LopezNo ratings yet
- The Science of Spiciness British English TeacherDocument8 pagesThe Science of Spiciness British English TeacherMer-maidNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction (Green Peas)Document4 pagesDNA Extraction (Green Peas)Bea Lim100% (2)