Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes
Uploaded by
Noel Mammen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesGrade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision Notes
Uploaded by
Noel MammenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Cells
Cell is the fundamental unit of life .
All the living organisms are made up of cell.
It is the structural and functional unit of life because
whole body is made up of cells.
It is known as the fundamental unit of life because
it regulates all the functions inside an organisms.
The cell is a Latin word for “a little room”.
Robert Hook (1665) discovered Cell.
Unicellular Organisms:
Composed of single cell.
Single cell constitute the structure and entire function of
the organisms.
e.g. Amoeba, Paramoecium, Euglena.
Multicellular Organisms:
Composed of many cells
Division of labour can be seen in these
organisms
e.g. plants , animals, human beings
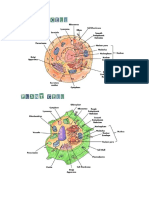
Cell Structure
Cells are made up of components called cell organelles.
A cell is capable to live and perform all their respective functions due
to the presence of cell organelles.
The structure seen in almost every cell is same: Plasma
membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm.
Cell Wall
Found in plant cells outside the
plasma membrane.
Rigid covering made up of cellulose.
Provide structural support to
the plants.
Plasma Membrane & its
functions:
It is the outermost covering of the cell.
It is called as selective
permeable membrane (because
it prevents movement of some
materials).
It helps in diffusion and
osmosis.
Composed of bilayer of lipid
and protein.
Cytoplasm
Thick solution composed of water,
salts and proteins that fills the cell.
Surrounded by cell membrane.
Nucleus of the cell is surrounded by
the cytoplasm.
Nucleus
Small, round and membrane bound structure near center of a cell.
Fluid inside the nucleus in called nucleoplasm.
Covered by double layer called nuclear membrane
Plays a central role in cellular activities/reproduction.
Nucleus contains thread like structure called chromatin material
which gets condensed into chromosomes. The chromosomes contain
information for inheritance of features from parents to next
generations in the form of DNA( Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid ) and
protein molecules.
The functional segments of DNA are called genes.
Golgi Apparatus
First discovered by a scientist Camillo Golgi.
It is a system of membrane bound vesicles
called cisternae.
It’s function include the storage,
modification
and package of cell products.
The complex sugars are made from
simple sugars in the Golgi apparatus.
It is also involved in the formation of
lysosomes.
Lysosome
s
Sac like structure in a cell surrounded
by
membrane
contain powerful digestive
enzymes(enzymes are made by RER) to
digest the worn-out cell organelles,
bacteria etc.
When the cell gets damaged, lysosomes
may burst and the enzymes digest their
own cell, hence called as “Suicidal bags
of a cell”. It is a waste disposal system
of the cell.
Mitochondria
It is covered by a double membrane.
Outer membrane is very porous and the
inner membrane is deeply folded creating
a large surface area for ATP (Adenosine
Triphosphate) molecule synthesis.
ATP is the energy currency of a cell;
hence the Mitochondria are called as
Power House of a Cell.
Mitochondria have their own DNA and
Ribosomes; therefore they can make
their own proteins.
Plastids
Double membrane bound structure
present only in plant cells
Have their own DNA and ribosomes
Enfolding of membrane is called
thylakoids and matrix is called stroma,
seat for enzymatic actions
Three types of Plastids:
1.Chromoplasts- Colored Plastids: Contains various other pigments
like yellow or orange.
2.Leucoplasts :White or colorless plastids; stores materials such as
oils, proteins, fats etc.
3.Chloroplasts – contain green pigment (chlorophyll) and useful in
photosynthesis;
You might also like
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Presentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Document13 pagesPresentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Keerthana RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Document5 pagesChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Document12 pagesBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5No ratings yet
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Document10 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Ali InamNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- cls9 cp5Document4 pagescls9 cp5Pankaj PathakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (2.1)mrtheunknownNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 6Document9 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 6Sarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument4 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsAllen MurilloNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Cell Organelles 2Document10 pagesCell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliNo ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument137 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeSudarshan S KNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- PLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellDocument9 pagesPLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellElle AdetounNo ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocument39 pagesForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFDocument5 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFmanoharrish3No ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell StructureShaik HamedNo ratings yet
- Structure and Nature of Living CellDocument11 pagesStructure and Nature of Living CellKikiez PathanasriwongNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNADocument8 pagesCell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNAQadirNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument6 pagesThe CellshaniahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Document7 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter5Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDocument16 pagesLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport MechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport Mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 5 NotesSunali BhojwaniNo ratings yet
- Ectopia Lentis PDFDocument7 pagesEctopia Lentis PDFBeerappaJanpetNo ratings yet
- Hort 106 Lecture 1 PDFDocument20 pagesHort 106 Lecture 1 PDFZarah Jane Rull NateNo ratings yet
- How It Works Book of The Human Body (Kalinel - Du)Document180 pagesHow It Works Book of The Human Body (Kalinel - Du)AMFA100% (4)
- Wear It Right (3M)Document2 pagesWear It Right (3M)wfng77No ratings yet
- Histology - Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesHistology - Male Reproductive SystemKim AcostaNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucous Membrane: by - Arindam MondalDocument92 pagesOral Mucous Membrane: by - Arindam MondalMohammed hisham khanNo ratings yet
- Basa, Gina Solon 2133027610Document3 pagesBasa, Gina Solon 2133027610ginaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 1 Wbi11 PDFDocument18 pagesEdexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 1 Wbi11 PDFtas xo100% (1)
- Dynamic Correspondance of Rowing To WeighliftingDocument6 pagesDynamic Correspondance of Rowing To WeighliftingSajeel Chaudhry100% (1)
- Invivo Omega Series Model 1445 1400 Mri Service ManualDocument98 pagesInvivo Omega Series Model 1445 1400 Mri Service ManualGerardo AlvaresNo ratings yet
- Succunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageSuccunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyFederico AndalesNo ratings yet
- Fluids Foods Did You Urinate?: Bladder DiaryDocument1 pageFluids Foods Did You Urinate?: Bladder DiaryAnika TasnimNo ratings yet
- ErythropoiesisDocument11 pagesErythropoiesisْNo ratings yet
- Lesson TemplateDocument6 pagesLesson TemplateAnonymous 9p23ZapzNo ratings yet
- Start TriageDocument29 pagesStart TriageSyifa FatiyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- Personal Control Over Aversive Stimuli and Its Relationship To StressDocument18 pagesPersonal Control Over Aversive Stimuli and Its Relationship To StressOvilia MeulitaNo ratings yet
- Hyper Kale Mia Case ReviewDocument4 pagesHyper Kale Mia Case ReviewSamina AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTDocument310 pagesAferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTNorma RamosNo ratings yet
- Eye Dominance & String PlayingDocument4 pagesEye Dominance & String Playingpaulxe100% (1)
- Railway Recruitment Board ExaminationDocument51 pagesRailway Recruitment Board ExaminationobroirohitNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument4 pagesQuestion Bankop GamingNo ratings yet
- Dave GrossmanDocument3 pagesDave Grossmantrainingalot100% (1)
- Class XI Bio MCQsDocument102 pagesClass XI Bio MCQsAdi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- The Rafiki MapDocument72 pagesThe Rafiki MapAnonymous Y2qwEuANo ratings yet
- Nausea & Vomiting FINALDocument25 pagesNausea & Vomiting FINALYosr Samia Abou SediraNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology: Chapter 3 .3 HomeostasisDocument12 pagesForm 5 Biology: Chapter 3 .3 HomeostasisZifan NafriNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 OPERANT LEARNING FinalDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 5 OPERANT LEARNING FinalWeyvin Maury Onde100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan2 CVADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan2 CVAhermesdave1No ratings yet
- A ThingDocument3 pagesA ThingIsaiah Perez0% (1)