Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell
Uploaded by
api-267979304Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell
Uploaded by
api-267979304Copyright:
Available Formats
Cell
Cell is the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living
things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire
specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become the building blocks of
large multicellular organisms, such as animals and humans. Although cells are much larger than atoms, they are still very
small. The smallest known cells are a group of tiny bacteria called mycoplasmas; some of these single-celled organisms
are spheres about 0.3 micrometre in diameter, with a total mass of 10
14
gramequal to that of 8,000,000,000 hydrogen
atoms. Cells of humans typically have a mass 400,000 times larger than the mass of a single mycoplasma bacterium, but
even human cells are only about 20 micrometres across. It would require a sheet of about 10,000 human cells to cover
the head of a pin, and each human organism is composed of more than 75,000,000,000,000 cells.
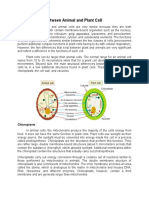
Plant Cell
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells , or cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. Unlike prokaryotic cells , the DNA in a
plant cell is housed within the nucleus. In addition to having a nucleus, plant cells also contain other membrane-bound
organelles, or tiny cellular structures, that carry out specific functions necessary for normal cellular operation. Organelles
have a wide range of responsibilities that include everything from producing hormones and enzymes to providing energy
for a plant cell.
Plant cells are similar to animal cells in that they are both eukaryotic cells and have similar organelles. Plant cells
are generally larger than animal cells. While animal cells come in various sizes and tend to have irregular shapes, plant
cells are more similar in size and are typically rectangular or cube shaped. A plant cell also contains structures not found
in an animal cell. Some of these include a cell wall , a large vacuole, and plastids. Plastids, such as chloroplasts , assist in
storing and harvesting needed substances for the plant. Animal cells also contain structures such
as centrioles , lysosomes , and cilia and flagella that are not typically found in plant cells.
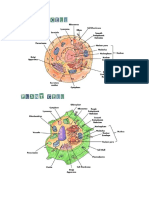
The following is a plant cell anatomy terms:
amyloplast - an organelle in some plant cells that stores starch. Amyloplasts are found in starchy plants like tubers and
fruits.
ATP - ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate; it is a high-energy molecule used for energy storage by organisms.
In plant cells, ATP is produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell, but is inside the cell wall. The cell membrane is
semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others.
Cell wall - a thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. This layer of cellulose fiber gives the cell most of its
support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant.
Centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense
center and radiating tubules. The centrosome is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the
centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. Unlike the centrosomes in animal cells,
plant cell centrosomes do not have centrioles.
Chlorophyll - chlorophyll is a molecule that can use light energy from sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide gas into
sugar and oxygen (this process is called photosynthesis). Chlorophyll is magnesium based and is usually green.
Chloroplast - an elongated or disc-shaped organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (in which energy from
sunlight is converted into chemical energy - food) takes place in the chloroplasts.
Cristae - (singular crista) the multiply-folded inner membrane of a cell's mitochondrion that are finger-like projections. The
walls of the cristae are the site of the cell's energy production (it is where ATP is generated).
Cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located.
Golgi body - (also called the Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex) a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a
stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. The Golgi body packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-
bound vesicles for "export" from the cell.
Granum - (plural grana) a stack of thylakoid disks within the chloroplast is called a granum.
Mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many
times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) for the cell.
Nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
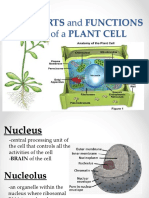
Nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA is produced.
Nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the functions
of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the
nuclear membrane
photosynthesis - a process in which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugars and
starches), oxygen and water. Chlorophyll or closely-related pigments (substances that color the plant) are essential to the
photosynthetic process.
Ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted
sacks that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Rough ER is
covered with ribosomes that give it a rough appearance. Rough ER transport materials through the cell and produces
proteins in sacks called cisternae (which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane).
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted
tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). The space within
the ER is called the ER lumen. Smooth ER transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and
digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and
lipids to the Golgi body and membranes
Stroma - part of the chloroplasts in plant cells, located within the inner membrane of chloroplasts, between the grana.
Thylakoid disk - thylakoid disks are disk-shaped membrane structures in chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll.
Chloroplasts are made up of stacks of thylakoid disks; a stack of thylakoid disks is called a granum. Photosynthesis (the
production of ATP molecules from sunlight) takes place on thylakoid disks.
Vacuole - a large, membrane-bound space within a plant cell that is filled with fluid. Most plant cells have a single vacuole
that takes up much of the cell. It helps maintain the shape of the cell.
Animal Cell
All animal cells are multicellular. They are eukaryotic cells. Animal cells are surrounded by plasma membrane and
it contains the nucleus and organelles that are membrane bound.
Animal cells are of various sizes and have irregular shapes. Most of the cells size range between 1 and 100 micrometers
and are visible only with help of microscope. Trillions of cells are found in the human body. There are many different types
of cells, approximately 210 distinct cell types in adult human body.
The following is the animal cell anatomy terms:
Cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others.
Centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense
center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the
centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centriole is the dense center of the
centrosome.
Cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located.
Golgi body - (also called the Golgi apparatus org complex) a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack
of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. It produces the membranes that surround the lysosomes. The Golgi body
packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell.
Lysosome - (also called cell vesicles) round organelles surrounded by a membrane and containing digestive enzymes.
This is where the digestion of cell nutrients takes place.
Mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many
times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) for the cell.
Nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
Nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA is produced. Some cells have more than one
nucleolus.
Nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the functions
of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the
nuclear membrane.
Ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted
sacks that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Rough ER is
covered with ribosomes that give it a rough appearance. Rough ER transports materials through the cell and produces
proteins in sacks called cisternae (which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane).
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted
tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). The space within
the ER is called the ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and
digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and
lipids to the Golgi body, lysosomes, and membranes.
Vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste
material that is on its way out of the cell.
You might also like
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocument5 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell PrintoutDocument3 pagesAnimal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printoutjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Animal CellDocument4 pagesAnatomy of An Animal CellYukiNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Cells Vocabulary PDFDocument2 pagesCells Vocabulary PDFMoody SaiiNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesCell Structure and Functionapi-217439283No ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellDaryl De LeonNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport MechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport Mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- The Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNADocument2 pagesThe Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNAEstefanía ElizondoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusDocument32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Only Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The CytoplasmDocument14 pagesOnly Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The Cytoplasmrakan ilyasNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMark MagatNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Plants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall PhagocyticDocument1 pagePlants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall PhagocyticHara Prasad MohapatraNo ratings yet
- 01 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument11 pages01 Cell and Tissue PDFAnand ClassesNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument6 pagesThe CellshaniahNo ratings yet
- All About Animal CellsDocument2 pagesAll About Animal CellsJether Marc Palmerola GardoseNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioKeneth Parohinog ABM 1No ratings yet
- cls9 cp5Document4 pagescls9 cp5Pankaj PathakNo ratings yet
- All About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysDocument8 pagesAll About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Edtech Lesson 18Document10 pagesEdtech Lesson 18api-267979304No ratings yet
- Activity 2Document13 pagesActivity 2api-267979304No ratings yet
- Group 3 Coaboration FuencyDocument16 pagesGroup 3 Coaboration Fuencyapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document10 pagesPresentation 1api-267979304No ratings yet
- Activity 1Document8 pagesActivity 1api-267979304No ratings yet
- Future ShockDocument14 pagesFuture Shockapi-267979304No ratings yet
- VennDocument2 pagesVennapi-267979304No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Scienceapi-26797930496% (74)
- MicroscopeDocument6 pagesMicroscopeapi-267979304No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in BiologyDocument4 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Biologyapi-26797930495% (20)
- Aakash Intensive Test - 01 Paper (@TEAMFLOOD)Document18 pagesAakash Intensive Test - 01 Paper (@TEAMFLOOD)Vahida Kadiwal67% (3)
- B. Tech. Biotech Syllabus MDUDocument51 pagesB. Tech. Biotech Syllabus MDUVineet50% (4)
- Class 9 - Pearson - Biology - Cell - Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesClass 9 - Pearson - Biology - Cell - Fundamental Unit of Lifeanuj KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 10 - 12 TextbookDocument209 pagesBiology Grade 10 - 12 TextbookMcentire Mwewa50% (2)
- Class 9th MCQDocument6 pagesClass 9th MCQprachi pundhirNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis HennaDocument127 pagesFinal Thesis HennaHenna TkNo ratings yet
- Review Strategies For Enteric Methane Mitigation in Cattle Fed Tropical ForagesDocument11 pagesReview Strategies For Enteric Methane Mitigation in Cattle Fed Tropical ForagesEsteban LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Essay Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument2 pagesEssay Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryoticctramel001No ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Cell MembraneDocument32 pagesElectrical Properties of Cell Membranemihaela irofte75% (4)
- Revision QuestionsDocument29 pagesRevision QuestionsBabasChong100% (1)
- Fundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery PDFDocument607 pagesFundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery PDFTurco Sekoof50% (2)
- General Biology 1 Diagnostic TestDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Diagnostic TestDearest NotesNo ratings yet
- GCE Exercise (27 Aug)Document28 pagesGCE Exercise (27 Aug)JjrlNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption: - Absorption Is The Process byDocument57 pagesDrug Absorption: - Absorption Is The Process byccccccc1No ratings yet
- RBC PreservationDocument23 pagesRBC PreservationLoiLoiChanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank 1Document159 pagesTest Bank 1eliNo ratings yet
- Conversion Eugenol To Vanillin: Evaluation of Antimicrobial ActivityDocument9 pagesConversion Eugenol To Vanillin: Evaluation of Antimicrobial ActivityFauzan FebriyantoNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument188 pagesIs Matter Around Us Puresasi.curieNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Disruption - Unit Operations and ProcessesDocument24 pagesBacterial Cell Disruption - Unit Operations and ProcessesAlexander Condo QuispeNo ratings yet
- Pathways of Nitrogen Utilization by Soil Microorganisms - A Review - Geisseler (2010)Document10 pagesPathways of Nitrogen Utilization by Soil Microorganisms - A Review - Geisseler (2010)PololoNo ratings yet
- 1 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranDocument34 pages1 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranMohammed RidzuwanNo ratings yet
- Biofilm FormationDocument12 pagesBiofilm FormationFhaliesha ZakurNo ratings yet
- Notes For Cell Biology BT-I YearDocument16 pagesNotes For Cell Biology BT-I YearKRATIKA TYAGINo ratings yet
- Haem Lecture 2.2016 PDFDocument12 pagesHaem Lecture 2.2016 PDFdorsa koraeiNo ratings yet
- Phs 201 For Nursing & Mls StudentsDocument104 pagesPhs 201 For Nursing & Mls StudentsayotomiwatemisanNo ratings yet
- RBC MembraneDocument41 pagesRBC MembranemwambungupNo ratings yet
- BodyDocument1 pageBodySaba.u AlmullaNo ratings yet
- Aqa A-Level Biology Cheatsheet PDFDocument17 pagesAqa A-Level Biology Cheatsheet PDFLiza Khan100% (6)
- AbsorptionDocument64 pagesAbsorptionZsazsaNo ratings yet
- Ef 15750Document144 pagesEf 15750dorjeesengeNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (598)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessFrom EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateFrom EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (633)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (217)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- How History Gets Things Wrong: The Neuroscience of Our Addiction to StoriesFrom EverandHow History Gets Things Wrong: The Neuroscience of Our Addiction to StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)