Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Membran Sel Sitoplasma Nukleus
Uploaded by
Asmaul Husni0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views32 pagesOriginal Title
Sel
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma Nukleus
Uploaded by
Asmaul HusniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
Sel (Biologi)
Sel merupakan unit asas semua makhluk
hidup. Secara umum setiap sel terdiri dari:
membran sel
sitoplasma
nukleus
Sel mula-mula digambarkan pada tahun 1665
oleh seorang ahli sain Inggris Robert Hooke
yang telah meneliti irisan tipis gabus melalui
mikroskop. Mahluk hidup ada yang memiliki
satu sel (uniselular) maupun banyak sel
(multiselular). Bentuk sel mahluk hidup
dibedakan menjadi:
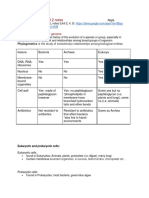
Prokaryotik dan Eukaryotik
Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic organisms:
Characteristic Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
DNA circular (endless loop); no histones linear; complexed with histones
Chromosomes single chromosome (& plasmids sometimes) multiple paired chromosomes
Nucleus nucleoid (no true nucleus) true nucleus with nuclear envelope
Nucleolus absent present
Cell division simple transverse fission mitotic division; meiosis
Cell membranes fluid mosaic w/o sterols fluid mosaic with sterols
Chloroplasts absent present in plants and some protists
Mitochondria absent present
Lysosomes absent present
Golgi apparatus absent present
Flagella simple rotating shaft 9+2 organization; non-rotating
Cytoskeleton absent present
Pili or fimbriae present absent
Ribosomes 70s type only 80s type (mostly)
Endoplasmic
absent present
reticulum
Peroxisomes absent present
Cell wall usually present; often peptidoglycan absent or present; various compositions
Reproduction asexual only sexual or asexual
Organization single celled usually multicellular (except Protists)
The cell membrane's main purpose is to regulate the movement of
materials into and out of the cell. By doing so, the internal environment
of the cell can be different than the external environment, since only
certain materials can pass through. Scientists say that the cell
membrane is selectively permeable, which means that only certain
substances can permeate (go through) the membrane. The next section
discusses how the cell membrane accomplishes this very important
function, but for now, let's discuss what the cell membrane is made of.
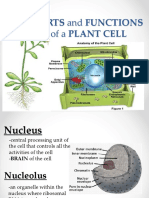
The following is a glossary of plant cell anatomy terms.
amyloplast - an organelle in some plant cells that stores starch.
Amyloplasts are found in starchy plants like tubers and fruits.
ATP - ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate; it is a high-energy
molecule used for energy storage by organisms. In plant cells, ATP is
produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell,
but is inside the cell wall. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others.
cell wall - a thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. This layer
of cellulose fiber gives the cell most of its support and structure. The cell
wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant.
centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small
body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating
tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell
division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to
opposite sides of the dividing cell.
chlorophyll - chlorophyll is a molecule that can use light energy from
sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide gas into sugar and oxygen
(this process is called photosynthesis). Chlorophyll is magnesium based
and is usually green.
chloroplast - an elongated or disc-shaped organelle containing
chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (in which energy from sunlight is converted
into chemical energy - food) takes place in the chloroplasts.
christae - (singular crista) the multiply-folded inner membrane of a cell's
mitochondrion that are finger-like projections. The walls of the cristae
are the site of the cell's energy production (it is where ATP is
generated).
cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the
organelles are located.
Golgi body - (also called the golgi apparatus or golgi complex) a
flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes
and is located near the nucleus. The golgi body packages proteins and
carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell.
granum - (plural grana) A stack of thylakoid disks within the chloroplast
is called a granum.
mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double
membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a
series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion converts the
energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell.
nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA
is produced.
nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the
nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by
controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The
nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane
photosynthesis - a process in which plants convert sunlight, water,
and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugars and starches), oxygen and
water. Chlorophyll or closely-related pigments (substances that color
the plant) are essential to the photosynthetic process.
ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic
granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of
interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are
located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer
nuclear membrane). Rough ER is covered with ribosomes that give it a
rough appearance. Rough ER transport materials through the cell and
produces proteins in sacks called cisternae (which are sent to the Golgi
body, or inserted into the cell membrane).
smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of
interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are
located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer
nuclear membrane). The space within the ER is called the ER lumen.
Smooth ER transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes
and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth
ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids
to the Golgi body and membranes
stroma - part of the chloroplasts in plant cells, located within
the inner membrane of chloroplasts, between the grana.
thylakoid disk - thylakoid disks are disk-shaped membrane
structures in chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll.
Chloroplasts are made up of stacks of thylakoid disks; a
stack of thylakoid disks is called a granum. Photosynthesis
(the production of ATP molecules from sunlight) takes place
on thylakoid disks.
vacuole - a large, membrane-bound space within a plant cell
that is filled with fluid. Most plant cells have a single vacuole
that takes up much of the cell. It helps maintain the shape of
the cell.
cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell.
The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass
into the cell and blocking others.
centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small
body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating
tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell
division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to
opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centriole is the dense center of the
centrosome.
cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the
organelles are located.
Golgi body - (also called the Golgi apparatus or golgi complex) a
flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes
and is located near the nucleus. It produces the membranes that
surround the lysosomes. The Golgi body packages proteins and
carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell.
lysosome - (also called cell vesicles) round organelles surrounded by a
membrane and containing digestive enzymes. This is where the digestion
of cell nutrients takes place.
mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a
double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many
times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The
mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell.
nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the
nucleus.
nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where
ribosomal RNA is produced. Some cells have more than one
nucleolus.
nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles,
including the nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the
functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and
contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded
by the nuclear membrane.
ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic
granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
rough endoplasmic reticulum - (rough ER) a vast system of
interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are
located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer
nuclear membrane). Rough ER is covered with ribosomes that give it a
rough appearance. Rough ER transports materials through the cell and
produces proteins in sacks called cisternae (which are sent to the Golgi
body, or inserted into the cell membrane).
smooth endoplasmic reticulum - (smooth ER) a vast system of
interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are
located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer
nuclear membrane). The space within the ER is called the ER lumen.
Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes
and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth
ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids
to the Golgi body, lysosomes, and membranes.
vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The
vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its
way out of the cell.
Mekanisme Transpor pada
Membran
• Osmosis
You might also like
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Meiosis Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages6.3 Meiosis Exam QuestionsShae50% (2)
- Animal CellDocument2 pagesAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellLeordan SanimNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- The Voice of The GenomeDocument6 pagesThe Voice of The GenomeSeaCarrotNo ratings yet
- Cell Anatomy PrintoutDocument3 pagesCell Anatomy Printoutjallie niepesNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell OrganellesKent Orriele FadriquelNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology GuideDocument37 pagesCell Biology GuideManuelNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Components of Animal and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesComponents of Animal and Plant CellsYukiNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Organelles GuideDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Organelles Guidenelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- PLANT CELL TERMSDocument15 pagesPLANT CELL TERMSanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESDocument7 pagesProkaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESChristian John Sitjar Dumo100% (1)
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Brief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisDocument52 pagesBrief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisPJ PomarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function 2012Document69 pagesCell Structure and Function 2012gpranay4100% (1)
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeDocument33 pagesCell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeKristine JoyNo ratings yet
- Biology Key TermsDocument3 pagesBiology Key TermsTia TiaNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsAlix AliNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument21 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsMarievic DavidNo ratings yet
- The Role of Cytoplasm in A CellDocument5 pagesThe Role of Cytoplasm in A CellRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cells Vocabulary PDFDocument2 pagesCells Vocabulary PDFMoody SaiiNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument28 pagesCellJanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument23 pagesPDFzjd62q6w4qNo ratings yet
- 2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelDocument56 pages2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelVe LinNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Organelles and FunctionsDocument15 pagesPlant Cell Organelles and FunctionsAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument53 pagesCell Structurepoojal singhaiNo ratings yet
- lecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pageslecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsDocument5 pagesCell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsPriyanshu Priyadarshi MeherNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Structure and Function of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesThe Cell: Structure and Function of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsshaniahNo ratings yet
- AS Biology NotesDocument20 pagesAS Biology NotesAlaska DavisNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesDocument26 pagesByjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥNo ratings yet
- Structures Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Cell Wall Peptidoglycan With Unique CelluloseDocument24 pagesStructures Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Cell Wall Peptidoglycan With Unique CelluloseJOSEPHINE SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Ethnoscience Integrated Environmental Literacy For Junior High School StudentsDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Ethnoscience Integrated Environmental Literacy For Junior High School StudentsAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Ryrtysoal 2 LimitDocument1 pageRyrtysoal 2 LimithennyykNo ratings yet
- Peraturan FutsalDocument1 pagePeraturan FutsalBANGKITNo ratings yet
- 03 10 2020 15.44.10 PDFDocument1 page03 10 2020 15.44.10 PDFAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Developmental Domain Concept Map 1Document1 pageDevelopmental Domain Concept Map 1api-451063988No ratings yet
- Sentence Completion Advanced Level Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesSentence Completion Advanced Level Test QuestionsPhuong Nghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- SGE HPLC ProtecolDocument8 pagesSGE HPLC ProtecolMarcela Robayo BarragánNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela: End Semester Examination Programme (2020-21 / Autumn) 24 JUN 2021 21:26Document11 pagesNational Institute of Technology Rourkela: End Semester Examination Programme (2020-21 / Autumn) 24 JUN 2021 21:26Veda SherlaNo ratings yet
- Students UG PPT 1Document70 pagesStudents UG PPT 1amanu kassahunNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Compounds and Their Libraries: An Insight Into Prospective Phytotherapeutics Approach For Oral Mucocutaneous CancersDocument44 pagesBioactive Compounds and Their Libraries: An Insight Into Prospective Phytotherapeutics Approach For Oral Mucocutaneous CancersKartik KaushikNo ratings yet
- The Stag Hunt and The Evolution of Social StructurDocument7 pagesThe Stag Hunt and The Evolution of Social StructurMary Katherine NavarroNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication Choice BoardDocument1 pageDna Replication Choice Boardapi-283801432No ratings yet
- Biochem CfeDocument5 pagesBiochem CfeJulius MatroNo ratings yet
- Leaf Concept MapDocument1 pageLeaf Concept MapGraceAbarcaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Pharmaceutical Botany BranchesDocument51 pagesIntroduction to Pharmaceutical Botany BranchesMarissa AldeNo ratings yet
- The Lab Session Report of Biological Techniques in Laboratory and Field (BIO403) Animals and Plants Colllection TechniquesDocument5 pagesThe Lab Session Report of Biological Techniques in Laboratory and Field (BIO403) Animals and Plants Colllection TechniquesUmmi SalamahNo ratings yet
- Kultur Akar Rambut Cinchona Ledgeriana Dan C. Succirubra Dalam Kultur in VitroDocument17 pagesKultur Akar Rambut Cinchona Ledgeriana Dan C. Succirubra Dalam Kultur in Vitronorries fachlevyNo ratings yet
- Motivation & EmotionsDocument29 pagesMotivation & Emotionsjha karunaNo ratings yet
- Organism and Population Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 13 (PDF) MDocument5 pagesOrganism and Population Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 13 (PDF) MBENJAMIN NANDANo ratings yet
- Kirsch Stein 2009Document4 pagesKirsch Stein 2009Nguyen Cong HuynhNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exams 9first Sem)Document6 pages2nd Quarter Exams 9first Sem)Rutchie Quillo TuandoNo ratings yet
- 03 XI Biology Question BankDocument240 pages03 XI Biology Question BankAnonymous fn9zdHU7No ratings yet
- MICRO&PARA-Lerio, Rose Abigail G. (DM2) - Types of Microbiology Definition of TermsDocument2 pagesMICRO&PARA-Lerio, Rose Abigail G. (DM2) - Types of Microbiology Definition of TermsRose Abigail Gamboa LerioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Part 1 Plant EcologyDocument57 pagesLecture 6 Part 1 Plant EcologyChala KelbessaNo ratings yet
- ch15 17Document18 pagesch15 1713jabbasNo ratings yet
- Robert Clarke - Hemp Diseases and Pests Management and Biological ControlDocument276 pagesRobert Clarke - Hemp Diseases and Pests Management and Biological ControlAndres VbNo ratings yet
- Assignment The Scientific MethodDocument4 pagesAssignment The Scientific Methodtvalentine99No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function For 1st Year MBBS Delivered by Miss Sumaira On 25 Jan 2010Document61 pagesCell Structure and Function For 1st Year MBBS Delivered by Miss Sumaira On 25 Jan 2010IMDCBiochem83% (6)
- Cat 2018 Slot IIDocument45 pagesCat 2018 Slot IIArvan PrimaNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 Melc 4 q2 Week4Document8 pagesLas Science 7 Melc 4 q2 Week4Heena Grace Presidente100% (1)
- EEG IntroductionDocument17 pagesEEG IntroductionKiruthikha MadhuNo ratings yet
- Bo de Thi Thu THPT Mon Tieng Anh Nam 2018 Co Dap An 1Document152 pagesBo de Thi Thu THPT Mon Tieng Anh Nam 2018 Co Dap An 1Phong PogNo ratings yet
- RVS Padmavathi College Soil Microbiology Mid Semester ExamDocument7 pagesRVS Padmavathi College Soil Microbiology Mid Semester Examshubham100% (1)