Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.3.cgm 09 0
Uploaded by
Jia-PeiWuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.3.cgm 09 0
Uploaded by
Jia-PeiWuCopyright:
Available Formats
Guidelines
InSIGHT
Your visual guide to the guidelines
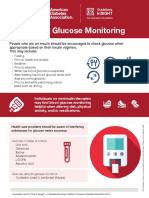
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Type of CGM Description
Real-time CGM CGM systems that measure and store glucose levels continuously
(rtCGM) and without prompting.
Intermittently CGM systems that measure glucose levels continuously but
scanned CGM
(isCGM with and without alarms) require scanning for storage of glucose values.
CGM systems that are placed on the patient in the clinician’s
office (or with remote instruction) and worn for a discrete period
of time (generally 7–14 days). Data may be blinded or visible to
Professional CGM the person wearing the device. The data are used to assess
glycemic patterns and trends. These devices are not fully owned
by the patient—they are clinic-based devices, as opposed to the
patient-owned rtCGM/isCGM devices.
rtCGM or isCGM for adults should be offered to:
Youth with type 1 diabetes on MDI or insulin pump (CSII)
Youth with type 2 diabetes on MDI or CSII
Adults with diabetes on MDI and CSII
Adults with diabetes on basal insulin
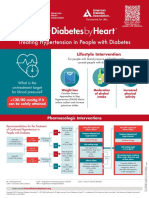
This infographic is based on recommendations from the ADA’s Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes--2023
CGM should be used as Periodic use of rtCGM, Skin reactions, either due to
close to daily as possible isCGM, or professional irritation or allergy, should
for maximal benefit. CGM can be helpful when be assessed and addressed
(isCGM at a minimum continuous use is not to aid in successful use of Learn more about
Time in Range
once every 8 hours.) appropriate, desired, or devices.
available.
professional.diabetes.org/tir
CGM, continuous glucose monitoring; isCGM, intermittently scanned CGM; rtCGM, real-time CGM;
MDI, multiple daily injections; CSII, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion/insulin pump
Learn more at diabetes.org | 1-800-DIABETES (1-800-342-2383)
Supported in part by Time in Range—a diabetes technology initiative of American Diabetes Association®.
You might also like
- Diabetes MallitusDocument33 pagesDiabetes Mallitushammu hothi100% (2)
- 201404030315rd - Skripsi Ahmad Syukri HarahapDocument80 pages201404030315rd - Skripsi Ahmad Syukri Harahapwinda istikhomahNo ratings yet
- Health Education On DMDocument12 pagesHealth Education On DMAnand Bhawna100% (4)
- Glycemic Target ADA 2018Document10 pagesGlycemic Target ADA 2018Selly DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Dexcom G - Continous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) : VJ'S COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, 7731051115Document1 pageDexcom G - Continous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) : VJ'S COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, 7731051115A SIVA RAMA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2018: 6. Glycemic TargetsDocument10 pagesStandards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2018: 6. Glycemic TargetsJimmy GrefaNo ratings yet
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2018: 6. Glycemic TargetsDocument2 pagesStandards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2018: 6. Glycemic TargetsJimmy GrefaNo ratings yet
- Minimed 670 G ManualDocument22 pagesMinimed 670 G ManualIlyas SaleemNo ratings yet
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2018: 6. Glycemic TargetsDocument10 pagesStandards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2018: 6. Glycemic TargetsjeanetteNo ratings yet
- Diabetestechnologyinthe Inpatientsettingfor ManagementofhyperglycemiaDocument15 pagesDiabetestechnologyinthe Inpatientsettingfor Managementofhyperglycemianot here 2make friends sorryNo ratings yet
- The Use of Real Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring or F - 2019 - Nutrition MetaDocument11 pagesThe Use of Real Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring or F - 2019 - Nutrition MetaVaishnavi YacheNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Da BombaDocument52 pagesProtocolo Da BombaEmerson SaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Pancreas Technology Offers Hope For Childhood DiabetesDocument11 pagesArtificial Pancreas Technology Offers Hope For Childhood DiabetesDiana PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Data, Data Everywhere - How To Analyze, Interpret and Apply Information Fro M Continuous Glucose MonitorsDocument6 pagesData, Data Everywhere - How To Analyze, Interpret and Apply Information Fro M Continuous Glucose MonitorsSeunNo ratings yet
- Extended Assignment 2020 (Technical English)Document11 pagesExtended Assignment 2020 (Technical English)Fakhriah AzmiNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Endocrinology: Ambulatory Glucose Profile: Flash Glucose MonitoringDocument3 pagesRecent Advances in Endocrinology: Ambulatory Glucose Profile: Flash Glucose MonitoringShujian ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Peters - Do We Need CGM DiabetesTechnolTher - V11 - PS128Document3 pagesPeters - Do We Need CGM DiabetesTechnolTher - V11 - PS128johnNo ratings yet
- Sampels IEEE Paper PDFDocument8 pagesSampels IEEE Paper PDFMiguel RebolloNo ratings yet
- Curr Opin Pediatr 2018 - Neonatal Hypoglycemia, Continuous Glucose MonitoringDocument5 pagesCurr Opin Pediatr 2018 - Neonatal Hypoglycemia, Continuous Glucose MonitoringCharlie CharcapeNo ratings yet
- Glucose Meter FinalDocument24 pagesGlucose Meter FinalAhmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring 508Document4 pagesContinuous Glucose Monitoring 508Hadi jameel HadiNo ratings yet
- CGM Comparison For People With Insulin Treated Research July 2023Document11 pagesCGM Comparison For People With Insulin Treated Research July 2023shahirahNo ratings yet
- LibreView Guide - Italian PaperDocument12 pagesLibreView Guide - Italian PaperJesus MuñozNo ratings yet
- MiniMed 770G System BrochureDocument6 pagesMiniMed 770G System BrochuredardolonNo ratings yet
- ITDM-Initial Certificate Consideration RequirementsDocument2 pagesITDM-Initial Certificate Consideration Requirementsandiee traderNo ratings yet
- Self Montitoring GlusoseDocument9 pagesSelf Montitoring GlusosedjsalmanNo ratings yet
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Evidence and Consensus Statement For Clinical UseDocument20 pagesContinuous Glucose Monitoring: Evidence and Consensus Statement For Clinical UseBianca CosovanuNo ratings yet
- CGM Overview HandoutDocument2 pagesCGM Overview HandoutgomcoiteNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Your Glucose LevelDocument4 pagesMonitoring Your Glucose LevelSarah OmarNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Advanced Diabetes Management Using Artificial Intelligence and Continuous Glucose Monitoring SensorsDocument18 pagesSensors: Advanced Diabetes Management Using Artificial Intelligence and Continuous Glucose Monitoring SensorsShujian ZhaoNo ratings yet
- NMRD FactSheet 20190617Document1 pageNMRD FactSheet 20190617Omar SaaedNo ratings yet
- Abridged Standards of Care 2021: 7. Diabetes TechnologyDocument1 pageAbridged Standards of Care 2021: 7. Diabetes TechnologyShefira TashaNo ratings yet
- Flash Glucose MonitoringDocument9 pagesFlash Glucose MonitoringAneed AnandNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Glocosa Subspace KNNDocument7 pagesNoninvasive Glocosa Subspace KNNhendranatjNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Glocosa Subspace KNNDocument7 pagesNoninvasive Glocosa Subspace KNNhendranatjNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of The GlunovoR ContinuousDocument13 pagesPerformance Evaluation of The GlunovoR ContinuousshahirahNo ratings yet
- In Range StudyDocument11 pagesIn Range Studyhssdj2hfdmNo ratings yet
- Glycemic Targets: American Diabetes AssociationDocument8 pagesGlycemic Targets: American Diabetes AssociationHelenaNo ratings yet
- Ethnicity of Participants Number of Times Monitor Is Scanned Per DayDocument1 pageEthnicity of Participants Number of Times Monitor Is Scanned Per DaysanajagraNo ratings yet
- 2021 - ES - CGM Pocket GuideDocument32 pages2021 - ES - CGM Pocket GuideLuiz Fernando Fonseca VieiraNo ratings yet
- 7 Diabetes Technology Standards Ofmedical Carein Diabetesd2020Document12 pages7 Diabetes Technology Standards Ofmedical Carein Diabetesd2020eberthhuarachNo ratings yet
- Standard CGM Report 0Document1 pageStandard CGM Report 0Jia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- ITDM CGM Certification AidDocument5 pagesITDM CGM Certification Aidandiee traderNo ratings yet
- Practical CGM: Improving Patient Outcomes through Continuous Glucose MonitoringFrom EverandPractical CGM: Improving Patient Outcomes through Continuous Glucose MonitoringNo ratings yet
- ITDM FAQsDocument4 pagesITDM FAQsandiee traderNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Insulin Pumps at School: Omnipod (Tubeless) T:slim Medtronic 630G Medtronic 670GDocument4 pagesA Guide To Insulin Pumps at School: Omnipod (Tubeless) T:slim Medtronic 630G Medtronic 670GghobaNo ratings yet
- Downlo 1 DDocument45 pagesDownlo 1 DSperaPerpetuumNo ratings yet
- Glucose Sensors CWDDocument83 pagesGlucose Sensors CWDJelenaNo ratings yet
- Technology Report Freestyle Libre Nursing InformaticsDocument25 pagesTechnology Report Freestyle Libre Nursing InformaticsBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Pumps and Sensors Cox PDFDocument42 pagesInsulin Pumps and Sensors Cox PDFDevang SNo ratings yet
- Diabetes (7. Tecnología de La Diabetes - Estándares de Atención Médica en Diabetes-2022)Document16 pagesDiabetes (7. Tecnología de La Diabetes - Estándares de Atención Médica en Diabetes-2022)Antony Yamid Bolaños VillarrealNo ratings yet
- GlucoLab Auto-Coding - MeterManualDocument22 pagesGlucoLab Auto-Coding - MeterManualMario BarraNo ratings yet
- ADA 2022 - Tecnologia em DiabetesDocument16 pagesADA 2022 - Tecnologia em DiabetesRafael Porto LeiteNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop System Design For Wireless ArtificialDocument6 pagesClosed Loop System Design For Wireless ArtificialAmmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Artificial Pancreas Device Systems For The Closed-Loop Control of Type 1 Diabetes: What Systems Are in Development?Document10 pagesArtificial Pancreas Device Systems For The Closed-Loop Control of Type 1 Diabetes: What Systems Are in Development?efNo ratings yet
- ADA STD of DM Care 2009 Exe SummaryDocument7 pagesADA STD of DM Care 2009 Exe SummaryAbuHumayraNo ratings yet
- FreeStyle Libre Pro Patient BrochureDocument2 pagesFreeStyle Libre Pro Patient BrochureAdvaitNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePosterSohel BaigNo ratings yet
- Vyldagliptin + Dapagliflozin + Metformin Combination in Treatment of T2DMDocument37 pagesVyldagliptin + Dapagliflozin + Metformin Combination in Treatment of T2DMAditya GautamNo ratings yet
- Bomba de InsulinaDocument15 pagesBomba de InsulinaEmerson SaNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Moh.gov - mymohresourcesPenerbitanCPGEndocrineQR T2DM 6th Edition QR Guide Digital PDFDocument8 pagesHTTPSWWW - Moh.gov - mymohresourcesPenerbitanCPGEndocrineQR T2DM 6th Edition QR Guide Digital PDFFiqa KusrinNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of PID Tuning Techniques For Blood Glucose Level of Diabetic PatientDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of PID Tuning Techniques For Blood Glucose Level of Diabetic Patient015Maulana Malik IbrahimNo ratings yet
- N Engl J Med 2022 386 1155 - AppendixDocument3 pagesN Engl J Med 2022 386 1155 - AppendixEvelynNo ratings yet
- DC 23 SrevDocument5 pagesDC 23 SrevLiz NaagNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease Updated 0Document1 pageManagement of Diabetic Kidney Disease Updated 0Jia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Standard CGM Report 0Document1 pageStandard CGM Report 0Jia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Treating Hypertension in People With DiabetesDocument1 pageTreating Hypertension in People With DiabetesJia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Ada Therapeutic Inertia Infographic Final 2Document1 pageAda Therapeutic Inertia Infographic Final 2Jia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Monitoring-CompletedDocument1 pageBlood Glucose Monitoring-CompletedJia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument6 pagesCommunity Acquired PneumoniaJia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Correction Factor 2020Document2 pagesCorrection Factor 2020Arshad SyahaliNo ratings yet
- Over Secretion and Deficiency of InsulinDocument22 pagesOver Secretion and Deficiency of InsulinYii Fei Ling100% (2)
- Insulinoma in A Patient With Type 2 Diabetes: Case Report Nama: Iqbal Putra Amirullah NIM: 030.14.098Document11 pagesInsulinoma in A Patient With Type 2 Diabetes: Case Report Nama: Iqbal Putra Amirullah NIM: 030.14.098desmawitaNo ratings yet
- E003290 FullDocument9 pagesE003290 FullANGELA CAMILA JARA LUZURIAGANo ratings yet
- Dr. Dr. Shahrul Rahman - Pendekatan Terkini Penanganan DMDocument67 pagesDr. Dr. Shahrul Rahman - Pendekatan Terkini Penanganan DMBernard Fernandes PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes AwarenessDocument37 pagesDiabetes AwarenessEkalaivanNo ratings yet
- Cookies Tepung Beras Hitam Dan Kedelai HDocument10 pagesCookies Tepung Beras Hitam Dan Kedelai HBrian Mukti NugrohoNo ratings yet
- DKA, HHS, HYPOGLYCEMIA MKDocument42 pagesDKA, HHS, HYPOGLYCEMIA MKSol Gat ChupataNo ratings yet
- Endo Test Bank (Filtered)Document3 pagesEndo Test Bank (Filtered)ganetaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Complications EnglishDocument2 pagesDiabetes Complications Englishapi-509392844No ratings yet
- Prediabetes 1Document21 pagesPrediabetes 1Nirmaa100% (2)
- Jurnal PKMDocument12 pagesJurnal PKMfidyaangraeni 61No ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Diabetes Mellitus: by Richard A. GuthrieDocument2 pagesNursing Management of Diabetes Mellitus: by Richard A. GuthrieStella GašparušNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Course During CCGDM.Document6 pagesAssignment On Course During CCGDM.Biman MondalNo ratings yet
- Final Diabetes & Its Role in PeriodonticsDocument140 pagesFinal Diabetes & Its Role in Periodonticsvinay jainNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and Insulin Injections: Your Kaiser Permanente Care InstructionsDocument12 pagesDiabetes and Insulin Injections: Your Kaiser Permanente Care InstructionsGrasiela CampbellNo ratings yet
- The Consequences of HypoglycaemiaDocument8 pagesThe Consequences of HypoglycaemiaPAM SUMNo ratings yet
- Ebook Endocrine Secrets PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Endocrine Secrets PDF Full Chapter PDFjason.green261100% (24)
- Managing Diabetes in Primary Care in The CaribbeanDocument24 pagesManaging Diabetes in Primary Care in The CaribbeanAndre SookdarNo ratings yet
- High Blood Sugar Levels Hyperglycemia. Diabetes Evaluation.Document3 pagesHigh Blood Sugar Levels Hyperglycemia. Diabetes Evaluation.Ibn SadiqNo ratings yet
- Essay About DiabetesDocument3 pagesEssay About DiabetesKin Demotica100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyAnnie Laiza BacayNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument10 pagesCase ReportFika Wilda AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- HbA1c Diagnostic PathwayDocument23 pagesHbA1c Diagnostic Pathwayrisal didinNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesDiabetes MellitusElyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Demografi Rawat Inap PDFDocument90 pagesDemografi Rawat Inap PDFNhaddz ERnNo ratings yet
- Babor. Belen. Bulaklak. Estayan. Guevarra, M. Guevarra, S. Juaneza. MalvarDocument34 pagesBabor. Belen. Bulaklak. Estayan. Guevarra, M. Guevarra, S. Juaneza. MalvarElla DevezaNo ratings yet