Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxonomical Classification of Plants and Animals
Taxonomical Classification of Plants and Animals
Uploaded by
Christyn DecembranoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxonomical Classification of Plants and Animals
Taxonomical Classification of Plants and Animals
Uploaded by
Christyn DecembranoCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxonomical
Classification of
Plants and Animals
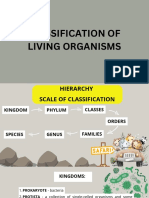
Classifying organisms into different groups makes it easier to understand the similarities and
Taxonomy differences between different species. It also helps in understanding the evolutionary relationships
among different species. Here is a look at 10 of the different taxonomic classifications of plants and
animals.
Kingdom: Plantae – Plants are divided into three major divisions: the
gymnosperms (conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, and other cone-bearing plants), the
angiosperms (flowering plants), and the bryophytes (mosses and liverworts).
Phylum: Tracheophyta – This is a group of plants that have specialized tissues
for transporting water and minerals throughout their bodies. Examples include
ferns, conifers, and flowering plants.
Plants Class: Magnoliopsida – This class contains all flowering plants.
Order: Rosales – This order includes many flowering plants such as roses, apple
trees, and currants.
Family: Rosaceae – Plants of this family have simple, alternate leaves and showy
flowers. Examples include roses, strawberries, and cherries.
Kingdom: Animalia – Animals are divided into two main types: vertebrates
(animals with a backbone) and invertebrates (animals without a backbone).
Phylum: Chordata – This group includes animals with a hollow dorsal nerve cord
and a notochord. Examples include fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and
mammals.
Class: Mammalia – This class consists of animals that possess features such as
Animals mammary glands which they use to feed their young. Examples include humans,
cats, dogs, and horses.
Order: Carnivora – Animals in this order are carnivorous, meaning that they
feed primarily on the flesh of other animals. Examples include cats, dogs, bears,
and weasels.
Family: Canidae – Canids are a family of mammals that includes dogs, wolves,
foxes, and other species.
You might also like
- Taxonomy DefinitionDocument7 pagesTaxonomy DefinitionchristinesalasNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes Biology PDFDocument144 pages1st Year Notes Biology PDFmrtweets67% (6)
- Medicinal Plant FamiliesDocument14 pagesMedicinal Plant FamiliesAlejandra GuerreroNo ratings yet
- DM Guide To HuntingDocument12 pagesDM Guide To Hunting678ojyhiop100% (2)
- Phylum Chordata-Reptiles PDFDocument42 pagesPhylum Chordata-Reptiles PDFartyharshaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ZoologyDocument17 pagesBasic Concepts of Zoologyseravanakumar100% (1)
- Notes BiologyDocument144 pagesNotes BiologySrikanth VsrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMDocument34 pagesChapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMAthirah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan VertebratesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan VertebratesPrakasha B GNo ratings yet
- AsdfghjklDocument3 pagesAsdfghjklDELA VEGA, WAXENE DAYL ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesDiversity in Living OrganismsDeepak DevNo ratings yet
- EerrrrDocument3 pagesEerrrrDELA VEGA, WAXENE DAYL ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Identification & Classification: Canete - Correa - Dagondon - Del Prado - DizonDocument16 pagesNomenclature Identification & Classification: Canete - Correa - Dagondon - Del Prado - DizonChing DizonNo ratings yet
- Essence Living WorldDocument5 pagesEssence Living WorldtarunNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living Things (I)Document4 pagesClassification of Living Things (I)Ifechukwu ObasiNo ratings yet
- La Flora y La Fauna.Document19 pagesLa Flora y La Fauna.esthefaniacontreras16No ratings yet
- Diversity IN Living WorldDocument36 pagesDiversity IN Living WorldAnuradha PorwalNo ratings yet
- HierarchyDocument4 pagesHierarchyBinazir RavanbakhshNo ratings yet
- Assignment Scientific Taxonomy and Earths Biodiversity PaperDocument4 pagesAssignment Scientific Taxonomy and Earths Biodiversity Papertvalentine99No ratings yet
- Phenetic Analysis of Several Species From Famili Aracceae in Biology Faculty Jenderal Soedirman UniversityDocument14 pagesPhenetic Analysis of Several Species From Famili Aracceae in Biology Faculty Jenderal Soedirman UniversityRizki AuliaNo ratings yet
- Diversity KvpyDocument205 pagesDiversity KvpysailuhariNo ratings yet
- Animal DiversityDocument87 pagesAnimal DiversityharshitaNo ratings yet
- Essence: A) B) C) D) E) F)Document4 pagesEssence: A) B) C) D) E) F)tarunNo ratings yet
- RutaceaeDocument4 pagesRutaceaeBMikeNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: The Origin of SpeciesDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: The Origin of Speciesnasrin banuNo ratings yet
- Sci 8 4TH Quarter Module 6Document35 pagesSci 8 4TH Quarter Module 6Diosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: BiologyDocument9 pagesAnimal Kingdom: BiologyHarsh SarafNo ratings yet
- Plantclassification 120808061114 Phpapp02Document31 pagesPlantclassification 120808061114 Phpapp02Sendaydiego Rainne GzavinNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy: The Science of Classifying OrganismsDocument39 pagesTaxonomy: The Science of Classifying OrganismsBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document16 pagesCH 1exercisestartNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1.classification PrinciplesDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 1.classification Principlessmar8389% (9)
- Taxonomy PDFDocument5 pagesTaxonomy PDFMd AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy Definition: Binomial Nomenclature OrganismDocument5 pagesTaxonomy Definition: Binomial Nomenclature Organismjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- 2nd Jump ReportDocument17 pages2nd Jump Reportzyan reyesNo ratings yet
- Classification Introduction 1 Async TaskDocument4 pagesClassification Introduction 1 Async Taskzoha shahzadNo ratings yet
- RubiaceaeDocument8 pagesRubiaceaex456456456xNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Living World 1Document5 pagesChapter 1 The Living World 1YashiNo ratings yet
- Review: Classification ClassificationDocument28 pagesReview: Classification ClassificationGerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Linnaeuss System of ClassificationDocument33 pagesLinnaeuss System of Classificationheartyjune.ortizo0610No ratings yet
- The Classification of TaxonomyDocument14 pagesThe Classification of TaxonomyDanica Rose Daza MacahiloNo ratings yet
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- Document 1Document15 pagesDocument 1angel anglNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 7Document13 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 7CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Identification of Invertebrate Taxonomic CharacterDocument6 pagesIdentification of Invertebrate Taxonomic CharacterDaisy KavinskyNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument3 pagesBiodiversityAlessa LamesNo ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument13 pagesThe Living WorldSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- Script OrganismsDocument4 pagesScript OrganismsCarlina FerreraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledIan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living Organism G8Document5 pagesClassification of Living Organism G8Akeisha PascuaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes BiologyDocument144 pages1st Year Notes BiologyAkbar Dad BabarNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Diversityplants 1216160447352701 9Document23 pagesEvolution and Diversityplants 1216160447352701 9joyfrangonzagaNo ratings yet
- Zoo VocabularyDocument2 pagesZoo VocabularyAna Isabel Lobo CésarNo ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument2 pagesThe Living WorldEdu TechNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument24 pagesAnimal Kingdom ClassificationGel Novida-ChavezNo ratings yet
- Living World Class XiDocument32 pagesLiving World Class XivijithamuraliNo ratings yet
- Fern AllyDocument3 pagesFern Allyx456456456xNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Medical EntranceDocument40 pagesBiology Notes For Medical EntranceNickOoPandeyNo ratings yet
- Diagram of PlantsDocument3 pagesDiagram of PlantsAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- Sci KingdomsDocument6 pagesSci KingdomsClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 Finals Reviewer 1Document13 pagesBio 103 Finals Reviewer 1Lorie Jane De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Bryophytes (Liverworts) PDFDocument7 pagesBryophytes (Liverworts) PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Species RichnessDocument4 pagesSpecies RichnessFarhad HossainNo ratings yet
- PopoDocument1 pagePopoChristyn DecembranoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 6 GROUP h0000Document44 pagesCHAPTER 1 6 GROUP h0000Christyn Decembrano100% (1)
- Format For Science Class ProjectDocument1 pageFormat For Science Class ProjectChristyn DecembranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Group 2Document10 pagesChapter 1 Group 2Christyn DecembranoNo ratings yet
- Soal Pts B.ing Kelas 12Document9 pagesSoal Pts B.ing Kelas 12Shannaz AmeliaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI THỬ LẦN 1 - (in 220621)Document4 pagesĐỀ THI THỬ LẦN 1 - (in 220621)Ngọc DiệpNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: AGRICULTURE 0600/11Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: AGRICULTURE 0600/11Sraboni ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Basics of Biology: Professor Vishal Trivedi Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, IIT Guwahati, Assam, IndiaDocument32 pagesBasics of Biology: Professor Vishal Trivedi Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, IIT Guwahati, Assam, IndiaAKKARSHANA P BIOTECH-2018 BATCHNo ratings yet
- Characters of BirdsDocument11 pagesCharacters of Birdsraseelabegum6No ratings yet
- Elementary Reading Comprehension Test 01Document3 pagesElementary Reading Comprehension Test 01Jiu jiuNo ratings yet
- Captivity of Marine AnimalsDocument22 pagesCaptivity of Marine AnimalsJulia OrdonaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematic VI g4 and 6Document12 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematic VI g4 and 6Ivy Novero SibuloNo ratings yet
- Raças Diversas EspéciesDocument606 pagesRaças Diversas EspéciesSophia ReisNo ratings yet
- Lesson-4 EvsDocument3 pagesLesson-4 EvsPrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Modern Science in Bible Lands - John DawsonDocument627 pagesModern Science in Bible Lands - John DawsonDennis M. GilmanNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document4 pagesQuestion 1ChaterineNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning: Decision Trees in Aima and WekaDocument20 pagesMachine Learning: Decision Trees in Aima and WekaMarcosNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Evolution by Natural Selection: Dodo BirdDocument27 pagesEvidence of Evolution by Natural Selection: Dodo BirdjennieNo ratings yet
- Anna Rufa Ruth Blasco AvesDocument13 pagesAnna Rufa Ruth Blasco AvesNegan DeanNo ratings yet
- What - Are - The - Difference and Similarities - Between - Mammals and ReptilesDocument20 pagesWhat - Are - The - Difference and Similarities - Between - Mammals and ReptilesHibiscusXVNo ratings yet
- Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species:, ,, ,, ,, and - EachDocument8 pagesDomain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species:, ,, ,, ,, and - EachsethurajeswariNo ratings yet
- Endemic & Endangered SpeciesDocument3 pagesEndemic & Endangered SpeciesVinoth KannaNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living Things and Their ClassificationDocument11 pagesVariety of Living Things and Their ClassificationAyuni100% (1)
- Uas Teknologi Pendidikan Tifani, Nadea, SyifaDocument45 pagesUas Teknologi Pendidikan Tifani, Nadea, Syifanlulu5344No ratings yet
- Habitats Final DraftDocument15 pagesHabitats Final Draftapi-497358383No ratings yet
- Report Text TestDocument2 pagesReport Text TestAbiezer AnggaNo ratings yet
- Manuscript OriginalDocument59 pagesManuscript OriginalGadisa WaktoleNo ratings yet
- Uriah Kriegel - The Sources of Intentionality - (Philosophy of Mind Series) Oxford University Press (2014)Document286 pagesUriah Kriegel - The Sources of Intentionality - (Philosophy of Mind Series) Oxford University Press (2014)Sebastian Castañeda PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Reading - Matching HeadingsDocument2 pagesWeek 2 Reading - Matching HeadingsTruc PhanNo ratings yet
- CH24 Study GuideDocument9 pagesCH24 Study GuideweldeenytNo ratings yet