Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENGG 410 Quiz No 2
Uploaded by
Joana Rosette TordecillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGG 410 Quiz No 2
Uploaded by
Joana Rosette TordecillaCopyright:
Available Formats
QUIZ NO.
Directions: Answer the following problems and present a logical solution. Write legibly using
engineering lettering on a letter sized bond paper with 1 inch invisible margin on all sides. No
need to copy the problem. Just draw the FBD if required and then the solution. Do not forget
to box ONLY the final answer. Round off ONLY at the final answer – 2 decimal places for
answers greater than 1.0 and 4 decimal places to answers less than 1.0. After finishing the
quiz, scan the sheets or take photos and turn in a copy through the google classroom. This
questionnaire is issued Saturday, October 17, 7:00 AM and the deadline is at Sunday,
October 18, 5:00 PM. You may submit ahead of time. Any file names will do. BE HONEST, YOU
KNOW THE RULES.
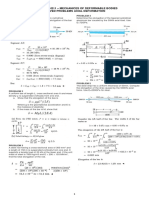
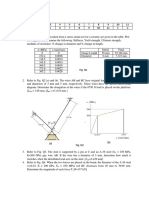
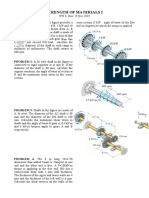
1.0 The composite shaft, consisting of aluminum, copper, and steel sections, is subjected to
the loading shown. Determine the displacement of end A with respect to end and the
normal stress in each section. The cross sectional area and modulus of elasticity for each
section are shown in the figure. Neglect the size of the collars at B and C. Also, determine
the displacement of B with respect to C of the composite shaft.
3.75 2.50
2.00
3.00
3.75 2.00
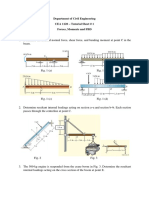
2.0 If P = 450 kN determine the minimum diameter of bolt that can be used in the clevis
shown. Use shearing strength value of the bolt is 280 MPa.
300 280
25
60
ENGG 410 | Fundamentals of Deformable Bodies
QUIZ NO. 2
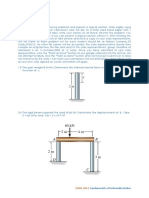
3.0 The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in. and is lightly attached to the
rigid supports at A and B when T1 = 70°F. Determine the force P that must be applied
to the collar so that, when T1 = 0°F, the reaction at B is zero.
4.0 Two A992 steel pipes, each having a cross- sectional area of 0.4 in2, are screwed
together using a union at B as shown. Originally the assembly is adjusted so that no
load is on the pipe. If the union is then tightened so that its screw, having a lead of
0.15 in., undergoes two full turns, determine the average normal stress developed in
the pipe. Assume that the union at B and couplings at A and C are rigid. Neglect
the size of the union. Note: The lead would cause the pipe, when unloaded, to
shorten 0.15 in. when the union is rotated one revolution.
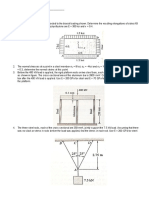
5.0 The beam is made from three polystyrene strips that are glued together as shown. If
the glue has shear strength of 95 kPa, determine the maximum load P that can be
applied without causing the glue to lose its bond.
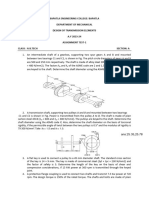
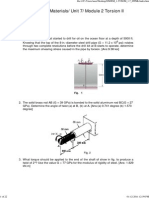
6.0 The 60-mm-diameter shaft rotates at 300 rev min. This motion is caused by the
unequal belt tensions on the pulley of 800 N and 450 N. Determine the power
transmitted and the maximum shear stress developed in the shaft.
ENGG 410 | Fundamentals of Deformable Bodies
QUIZ NO. 2
7.0 The shaft is made of A992 steel and has an allowable shear stress of 75 MPa. When
the shaft is rotating at 300 rpm, the motor supplies 8 kW of power, while gears A and
B withdraw 5 kW and 3 kW, respectively. Determine the required minimum diameter
of the shaft to the nearest millimeter. Also, find the rotation of gear A relative to C.
ENGG 410 | Fundamentals of Deformable Bodies
You might also like
- Solved Problems Axial DeformationDocument6 pagesSolved Problems Axial DeformationChristopher Largado100% (1)
- Concrete 7 Short Column With Axial LoadDocument3 pagesConcrete 7 Short Column With Axial LoadGrace Ann CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- RC Lecture 11 - ColumnsDocument19 pagesRC Lecture 11 - ColumnsShean Berwin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6Document1 pageQuiz 6Nikki Marie G OclaritNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Design For Tension MemberDocument14 pagesChapter-2 Design For Tension Memberzakai zakiNo ratings yet
- Strema 102Document4 pagesStrema 102Hazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document52 pagesCH 04Ng Heng Lim83% (12)
- Rammed Earth Construction Part 21210466806514Document17 pagesRammed Earth Construction Part 21210466806514Jorge Alonso100% (3)
- Simple TensionDocument40 pagesSimple Tensionponcatoera83% (6)
- Doha Cables Profile 2015Document15 pagesDoha Cables Profile 2015Ahmed Farouk100% (1)
- FEM 18ME73 AssignmentsDocument10 pagesFEM 18ME73 AssignmentsFOODIE USNo ratings yet
- BC7068 E-TdsDocument3 pagesBC7068 E-TdsHoài NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MOM2Tutorial 10-1Document3 pagesMOM2Tutorial 10-1Ishola mujeebNo ratings yet
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Document10 pagesMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsNo ratings yet
- Mec32 HW3Document4 pagesMec32 HW3Isabelle LunaNo ratings yet
- DME Question Bank Unit (3-4-5)Document7 pagesDME Question Bank Unit (3-4-5)PrathamNo ratings yet
- QB Unit-3,4,5Document7 pagesQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Dte Assignment-1 A.Y 23-24Document2 pagesDte Assignment-1 A.Y 23-24asfvkjsv asgbaegbNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02Document2 pagesAssignment 02adhnan_rasheed0% (1)
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloNo ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Document4 pagesDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - DMEDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshNo ratings yet
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 2-2 - Axial LoadDocument4 pagesENGG 410 Problem Set 2-2 - Axial LoadJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- ME-2127 Solid Mechanics-MSEDocument14 pagesME-2127 Solid Mechanics-MSEFazle RabbyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-2Document4 pagesTutorial 2-2nageshNo ratings yet
- Project ProblemsDocument9 pagesProject Problemsvivek geddamNo ratings yet
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocument5 pagesScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- ME-6503 Design of Machine Elements - 16 MarksDocument12 pagesME-6503 Design of Machine Elements - 16 MarksMadhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem SetDocument22 pagesStrength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem Setneeru143No ratings yet
- MECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumDocument2 pagesMECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumRahulNo ratings yet
- 107503MEDocument7 pages107503MEPrathamNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2FDocument9 pagesAssignment # 2FCrisnico PeligrinoNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document5 pagesSheet 2Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and CouplingDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and Couplingrip111176100% (1)
- Dme I Mock Test Question BankDocument5 pagesDme I Mock Test Question BankRushikesh SwamiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126Document7 pagesAssignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126MOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356No ratings yet
- SM - TSET 4 of 12Document2 pagesSM - TSET 4 of 12battuarunNo ratings yet
- BCEE 344, Winter 2018, Assignment #5, Due: Apr 16, 2018, in Class R. Tadayon Submitting Your Assignment by Email Is Not AcceptableDocument1 pageBCEE 344, Winter 2018, Assignment #5, Due: Apr 16, 2018, in Class R. Tadayon Submitting Your Assignment by Email Is Not Acceptablejess856gmailcomNo ratings yet
- 2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNDocument2 pages2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1001) RCS-1Document2 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1001) RCS-1Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Dme Question BankDocument4 pagesDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- Assignment - 2Document4 pagesAssignment - 2vaijanath patilNo ratings yet
- Assignment04 (2:11:14)Document2 pagesAssignment04 (2:11:14)Gabriel SmithNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 On-Line Edition PDFDocument11 pagesAssignment 2 On-Line Edition PDFEm CervasNo ratings yet
- Strain ProblemsDocument4 pagesStrain ProblemsBianca GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Question Chapter 8Document5 pagesQuestion Chapter 8Mohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials I: PROBLEM 1. Gear C in The Figure Provides ADocument2 pagesStrength of Materials I: PROBLEM 1. Gear C in The Figure Provides AzıptıNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Anand DevNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Fundamental of Deformable Bodies - Columns AssignmentDocument2 pagesInstructions:: Fundamental of Deformable Bodies - Columns AssignmentJeff Hentzen F. SimeneNo ratings yet
- 0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsDocument3 pages0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Ce003 PsDocument4 pagesCe003 PsJaimeNo ratings yet
- HW#02Document8 pagesHW#02tozandehjaniNo ratings yet
- Cve224 Homework 1Document5 pagesCve224 Homework 1Deniz GüneşNo ratings yet
- Tsu m18 Practice Problems Smat1Document2 pagesTsu m18 Practice Problems Smat1Mark Lester ValdozNo ratings yet
- Torsion 01Document20 pagesTorsion 01Danielle Ruthie GalitNo ratings yet
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityFrom EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNo ratings yet
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus: Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityFrom EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus: Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNo ratings yet
- 10-ENGG 410 CHAPTER 8 - Part 1Document16 pages10-ENGG 410 CHAPTER 8 - Part 1Joana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressDocument4 pagesENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Research Activity No.1Document8 pagesResearch Activity No.1Joana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Well TestDocument7 pagesWell TestJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Production EngineeringDocument21 pagesProduction EngineeringJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Well TestDocument7 pagesWell TestJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- ACDCModuleUsersGuide PDFDocument366 pagesACDCModuleUsersGuide PDFRahman EjazNo ratings yet
- EP19702124NWB1Document15 pagesEP19702124NWB1amanraza.canNo ratings yet
- Gabungan Pengujian Black Dot TGA & DSC r02Document19 pagesGabungan Pengujian Black Dot TGA & DSC r02haryonoari68No ratings yet
- Red Dot CatalogDocument52 pagesRed Dot CatalogHamouda YaseenNo ratings yet
- PrestressingDocument46 pagesPrestressingGaurav naddaNo ratings yet
- All-Natural, Eco-Friendly Composite Foam For Highly Efficient Atmospheric Water HarvestingDocument10 pagesAll-Natural, Eco-Friendly Composite Foam For Highly Efficient Atmospheric Water HarvestingsalemNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Kerja Proses Produksi Kayu Lapis BagusDocument25 pagesPedoman Kerja Proses Produksi Kayu Lapis BagusliaNo ratings yet
- Sikaswell s-2Document4 pagesSikaswell s-2Kenji TanNo ratings yet
- Jauhemetallurgian Perusteet: Sintering - ISO DefinitionDocument16 pagesJauhemetallurgian Perusteet: Sintering - ISO DefinitionStevie Alfian RizkiNo ratings yet
- Paper 5Document13 pagesPaper 5180320119134.me.rayush.hariNo ratings yet
- (3.4) Fundamental Concept of Stress and DeformationDocument70 pages(3.4) Fundamental Concept of Stress and DeformationIan Arnold Fami100% (1)
- HBL 295 - Fact 776Document1 pageHBL 295 - Fact 776ORLANDO GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12. Electricity and Circuits: Very Short Q&ADocument8 pagesChapter 12. Electricity and Circuits: Very Short Q&ASubhojit MitraNo ratings yet
- DEKS Flashings For Metal Roofs CatalogDocument3 pagesDEKS Flashings For Metal Roofs CatalogSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- Location: Pit Slab Section Properties: Calculation For Crackwidth Check (Y Direction Bottom)Document2 pagesLocation: Pit Slab Section Properties: Calculation For Crackwidth Check (Y Direction Bottom)Pitolwala ZuzarNo ratings yet
- Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesAhsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringMD RafiNo ratings yet
- Flange Insulation Sets: Trusted. WorldwideDocument10 pagesFlange Insulation Sets: Trusted. WorldwidesathgurumamNo ratings yet
- 2nd Progress Billing Warehouse FaustinoDocument2 pages2nd Progress Billing Warehouse FaustinoHenry TuganoNo ratings yet
- Intr To Civil EngineeringDocument70 pagesIntr To Civil EngineeringRanjithaNo ratings yet
- Info RecyclingDocument6 pagesInfo RecyclingAmelie CoetzeeNo ratings yet
- LdpeDocument1 pageLdpeArdy WiyogoNo ratings yet
- Short and Long Term Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Asphalt Mixtures PDFDocument14 pagesShort and Long Term Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Asphalt Mixtures PDFAli YousefNo ratings yet
- DCS1 (4th) Dec2018Document2 pagesDCS1 (4th) Dec2018Anupam RawalNo ratings yet
- Section 031000 - Concrete FormworkDocument31 pagesSection 031000 - Concrete FormworkBotirNo ratings yet
- Endress-Hauser Promag 55S ENDocument4 pagesEndress-Hauser Promag 55S ENLwazi HanisiNo ratings yet
- Indian Schedule Rates-02Document100 pagesIndian Schedule Rates-02abbasNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing 1 & 2Document29 pagesManufacturing 1 & 2SontappagariViswanathNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc Welding of High Strength 0.3 % C-Crmov (Esr) SteelDocument6 pagesPlasma Arc Welding of High Strength 0.3 % C-Crmov (Esr) Steelagilan89No ratings yet