Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DISCRETE
Uploaded by
Carina SiarotOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DISCRETE
Uploaded by
Carina SiarotCopyright:
Available Formats
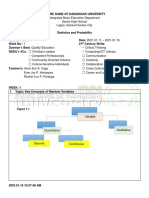
Random Variables and Probability Distribution
Description of Random Variables
Example of continuous Random Variable
1. Average age of people born in July
2. Amount of sugar in a cup of coffee
6
1
3. Weight of newborn in the hospital
7
Sample problem of probability distribution
A Random Variable is a result of chance event,
that you can measure or count.
A Random Variable is a numerical quantity that
assigned to the outcome of an experiment. Ex. Supposed three coins are tossed. Let x be the
A Random Variable can be classified as being Random Variable representing the number of heads.
either discrete or continuous depending on the Construct the probability distribution and draw the
numerical values it assumes. histogram.
1. S = HHH, HHT, HTT, HTH,THH,TTH,THT,TTT
2 8
OUTCOME V(H)
HHH 3
2.COUNT #
HHT 2
OF HEADS
HTT 1
HTH 2
Classification of Random THH 2
TTH 1
Variable
9
THT 1
TTT 0
3 DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
NO. OF HEADS X 0, 1, 2, 3,
PROBABILITY, P(X)
A discrete Random Variable has a countable
1o
number of possible values
Example of discrete Random Variable
1. Number of people in July
2.Number of COVID 19 positive cases in
Hermosa, Bataan.
4 v
HISTOGRAM
4/8
3. Numbers of pens in a box
3/8
5 CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLE
A continuous Random Variable can assume an
11 2/8
1/8
infinite number of values in one or more intervals. 0 1 2 3
KAZCEL SIAROT
11 HUMSS LOVINGKINDNESS
You might also like
- Practical Research 1 SlideshowDocument96 pagesPractical Research 1 SlideshowGresel GabawanNo ratings yet
- Bollard Pull CalculationsDocument16 pagesBollard Pull CalculationsLuis Sierra100% (1)
- Credit Card NCC BANKDocument1 pageCredit Card NCC BANKKazi Foyez AhmedNo ratings yet
- Melc Competency Code: Random VariableDocument10 pagesMelc Competency Code: Random VariableOnecup RiceNo ratings yet
- Ept - Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pagesEpt - Reading ComprehensionCarina Siarot100% (1)
- Hetron Fabrication Process PDFDocument57 pagesHetron Fabrication Process PDFDyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument30 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributionsJoy DizonNo ratings yet
- M1112SP-IIIa-1, 2, 3Document4 pagesM1112SP-IIIa-1, 2, 3chingferdie_11178% (9)
- Basement Grade & WaterproofingDocument18 pagesBasement Grade & WaterproofingjparsbNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Ms. Geremy A. Casindac Mathematics Teacher Andres Bonifacio High School - Arellano UniversityDocument25 pagesStatistics and Probability: Ms. Geremy A. Casindac Mathematics Teacher Andres Bonifacio High School - Arellano UniversityRyu HajimeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Random Variables and Probability Distributions: Janet C. Fernando Subject TeacherDocument23 pagesLesson 2. Random Variables and Probability Distributions: Janet C. Fernando Subject TeacherYuan Daryle Fate HermosoNo ratings yet
- Ge MathDocument56 pagesGe MathKristel Unay0% (1)
- Guidelines For Subsea Pipeline Cathodic Protection SurveyDocument38 pagesGuidelines For Subsea Pipeline Cathodic Protection SurveyjavadNo ratings yet
- Sip-Calbugos EsDocument164 pagesSip-Calbugos EsJeffrey G. PaladNo ratings yet
- Stats NotesDocument2 pagesStats Notess8704386No ratings yet
- Random VariableDocument23 pagesRandom VariableAzeleah Nosil VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Constructing Probability DistributionsDocument6 pagesRandom Variables and Constructing Probability DistributionsÇhärlöttë Çhrístíñë Dë ÇöldëNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument33 pagesStatisticsdlabdon0310No ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Lesson1Document9 pagesStatistics and Probability Lesson1Astherielle RiegoNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Modules 1-8Document30 pagesStat and Prob Modules 1-8Alaiza LucasNo ratings yet
- Stat 3rd Week 1Document13 pagesStat 3rd Week 1Reyboy TagsipNo ratings yet
- Local Media6460876862289465897Document61 pagesLocal Media6460876862289465897Ian Angel Benaning OsnanNo ratings yet
- Exploring Random VariablesDocument13 pagesExploring Random VariablesRex FajardoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Constructing Probability Distribution AutosavedDocument42 pagesLesson 2 Constructing Probability Distribution AutosavedLHYRA KATHLEEN LOPEZNo ratings yet
- 03 Constructing Probability DistributionsDocument19 pages03 Constructing Probability DistributionsKikay AchuchuNo ratings yet
- LR1 - Statistics and Probability - LESSON 1 2Document5 pagesLR1 - Statistics and Probability - LESSON 1 2Leanne HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StatDocument107 pagesChapter 1 StatSherry-Ann TulauanNo ratings yet
- Week2 Random VariablesDocument32 pagesWeek2 Random VariablesMorissette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Las 2 Constructing Probability DistributionsDocument11 pagesLas 2 Constructing Probability DistributionsJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document2 pagesLesson 2bonifacio gianga jrNo ratings yet
- Random VariablesDocument35 pagesRandom VariablesMary Grace Manzano AdevaNo ratings yet
- Stats and Probability ReviewerDocument12 pagesStats and Probability ReviewerEUNICE RAQUEL BUCAGNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument2 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityMarc Tristan TubonNo ratings yet
- Janrie M. Raguine, Mat Probability Distribution of Discrete Random Variable (Q3 - Wk. 1, LAS 3)Document1 pageJanrie M. Raguine, Mat Probability Distribution of Discrete Random Variable (Q3 - Wk. 1, LAS 3)Gladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- L2 Constructing Probability DistributionDocument20 pagesL2 Constructing Probability DistributionRex FajardoNo ratings yet
- Stat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK1Document12 pagesStat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK1rico.odalNo ratings yet
- Properties of A Probability DistributionDocument8 pagesProperties of A Probability DistributionB - Clores, Mark RyanNo ratings yet
- IE401 Lecture 5 Random Variabbles and Its Probability DistributionDocument10 pagesIE401 Lecture 5 Random Variabbles and Its Probability DistributionKarl PinedaNo ratings yet
- Grade11 Statistics and Probabilty - Module 1Document4 pagesGrade11 Statistics and Probabilty - Module 1Erickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- Week2 Random VariablesDocument32 pagesWeek2 Random VariablesMorissette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Random VariablesDocument36 pagesRandom VariableskiedzserdinaNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument5 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributionBryan OrquizaNo ratings yet
- Constructing Probability Distribution: A Module For All Track-StrandDocument7 pagesConstructing Probability Distribution: A Module For All Track-StrandKarylle Alberto SanchezNo ratings yet
- LAS-1-STAT ABM G11-St. Catherine - Macaday, Venze Adrianne D.Document2 pagesLAS-1-STAT ABM G11-St. Catherine - Macaday, Venze Adrianne D.Venze Adrianne Damasco MNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Sap LessonDocument21 pagesWeek 1 Sap LessonSanny RelizanNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Statistics and Probability Subject!: Let H Head and T Tails: HH, HT, TH, TTDocument6 pagesWelcome To Statistics and Probability Subject!: Let H Head and T Tails: HH, HT, TH, TTKyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- 1 Random VariableDocument138 pages1 Random VariableJhon Lienard EsmenaNo ratings yet
- 2 Random Variables Discrete and ContinousDocument33 pages2 Random Variables Discrete and Continousdavido davidoNo ratings yet
- L1 Exploring Random VariablesDocument13 pagesL1 Exploring Random VariablesRex FajardoNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument13 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityDeborah BandahalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document8 pagesLesson 2123 123No ratings yet
- 3rd MQA HandoutDocument6 pages3rd MQA HandoutMarvin CanamanNo ratings yet
- Probability Distribution For A Discrete Random Variable andDocument9 pagesProbability Distribution For A Discrete Random Variable andHanz WendellNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument15 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityKathleen madronioNo ratings yet
- 1 - 2exploring Random Variables CG 1 AND 2 Lesson1Document16 pages1 - 2exploring Random Variables CG 1 AND 2 Lesson1CHARLYN JOY SUMALINOG100% (1)
- Stat (Random Variable) ModularDocument39 pagesStat (Random Variable) ModularJoy ManaogNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument112 pages3 PDFChe B. RoganNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document8 pagesWeek 1ryk cesarNo ratings yet
- Ejhay StaDocument14 pagesEjhay StaEjhay CarambasNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument21 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributionDia CoraldeNo ratings yet
- Random Variables ObservationDocument234 pagesRandom Variables ObservationMa. Cristina MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Constructing Probability Mass Function & HistogramDocument6 pagesLesson 4 - Constructing Probability Mass Function & HistogramAndrea Marie LaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Week 1 1Document21 pagesStatistics Week 1 1chelsipoblete02No ratings yet
- SP WS1Document3 pagesSP WS1PADERES MARGARETTE GALARIONo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument15 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityJazmine GarciaNo ratings yet
- Statistic and Probability Assign. #2Document16 pagesStatistic and Probability Assign. #2Kyla Mae OrquijoNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document5 pagesWeek 1Carina SiarotNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Fourth QuarterCarina SiarotNo ratings yet
- ART June-12Document2 pagesART June-12Carina SiarotNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument1 pageTable of ContentsCarina SiarotNo ratings yet
- ManokDocument162 pagesManokCarina SiarotNo ratings yet
- Ept - Reading Comprehension2Document4 pagesEpt - Reading Comprehension2Carina SiarotNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 - 1ST QuarterDocument88 pagesGrade 1 - 1ST QuarterCarina SiarotNo ratings yet
- PartsDocument4 pagesPartsburakkkkkkkkNo ratings yet
- Cornell-Engineers-Sample-Drawings PAGE1Document1 pageCornell-Engineers-Sample-Drawings PAGE1mohanumaNo ratings yet
- SOPDocument2 pagesSOPwingwiryawanNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Building Design and Analysis: Project: Proposed Two-Storey Residential HouseDocument106 pagesReinforced Concrete Building Design and Analysis: Project: Proposed Two-Storey Residential HouseRonaldo BatlaganNo ratings yet
- Brand CoolnessDocument21 pagesBrand CoolnessDaiene VilarNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument50 pagesManualmohan2380% (1)
- Soal LATIHAN PSAT Bahasa Inggris XIDocument19 pagesSoal LATIHAN PSAT Bahasa Inggris XIFebyliany NursabillaNo ratings yet
- Chrysler Customer Specifics For PPAP, AMEF 5th Edition August 2015Document8 pagesChrysler Customer Specifics For PPAP, AMEF 5th Edition August 2015Absalón Rocael Anzueto100% (1)
- A Guide To Face Detection in Python - Towards Data ScienceDocument26 pagesA Guide To Face Detection in Python - Towards Data ScienceerivandoramosNo ratings yet
- Speech Act Approach (Revised)Document15 pagesSpeech Act Approach (Revised)Udiana Puspa DewiNo ratings yet
- 70-270: MCSE Guide To Microsoft Windows XP Professional Second Edition, EnhancedDocument46 pages70-270: MCSE Guide To Microsoft Windows XP Professional Second Edition, EnhancedManish BansalNo ratings yet
- Eng 10 Cur-MapDocument7 pagesEng 10 Cur-MapFe JanduganNo ratings yet
- GRM 1Document55 pagesGRM 1Mady RadaNo ratings yet
- Taf - Fepa Safety Leaflet Flap Discs EnglishDocument2 pagesTaf - Fepa Safety Leaflet Flap Discs EnglishkerolcarrollNo ratings yet
- WbnotDocument2 pagesWbnotJeshiNo ratings yet
- Rajala Varaprasad Reddy: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesRajala Varaprasad Reddy: ObjectiveRAKESH REDDY THEEGHALANo ratings yet
- PrintDocument7 pagesPrintAkshay SagareNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalDocument12 pagesEvaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalGustavo IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Proyectos de Aplicación en El Mundo Midas GTS NXDocument46 pagesProyectos de Aplicación en El Mundo Midas GTS NXEnrique BarragánNo ratings yet
- Q1-L1 - English 10 Activity No. 1.4Document2 pagesQ1-L1 - English 10 Activity No. 1.4Thal S. GayakNo ratings yet
- Happy Birthday, Madame Chapeau Hat ActivityDocument2 pagesHappy Birthday, Madame Chapeau Hat ActivityAbrams BooksNo ratings yet
- Hydrotech Company ProfileDocument46 pagesHydrotech Company ProfileBOBANSO KIOKONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 in Innovation ManagementDocument11 pagesLesson 1 in Innovation ManagementRoss EvanNo ratings yet